University of Málaga
Attention operator has been widely used as a basic brick in visual understanding since it provides some flexibility through its adjustable kernels. However, this operator suffers from inherent limitations: (1) the attention kernel is not discriminative enough, resulting in high redundancy, and (2) the complexity in computation and memory is quadratic in the sequence length. In this paper, we propose a novel attention operator, called Lightweight Structure-aware Attention (LiSA), which has a better representation power with log-linear complexity. Our operator transforms the attention kernels to be more discriminative by learning structural patterns. These structural patterns are encoded by exploiting a set of relative position embeddings (RPEs) as multiplicative weights, thereby improving the representation power of the attention kernels. Additionally, the RPEs are approximated to obtain log-linear complexity. Our experiments and analyses demonstrate that the proposed operator outperforms self-attention and other existing operators, achieving state-of-the-art results on ImageNet-1K and other downstream tasks such as video action recognition on Kinetics-400, object detection \& instance segmentation on COCO, and semantic segmentation on ADE-20K.
MoTime introduces a comprehensive suite of eight multimodal time series datasets for forecasting, enabling systematic evaluation of how external modalities enhance predictions in varying-history and cold-start scenarios. Experiments demonstrate that external modalities consistently improve forecasting performance, with a notable finding that LLM-based retrieval-augmented generation effectively enables prediction in cold-start situations by leveraging contextual information alone.
We introduce the concept of 1Q, the first wireless generation of integrated classical and quantum communication. 1Q features quantum base stations (QBSs) that support entanglement distribution via free-space optical links alongside traditional radio communications. Key new components include quantum cells, quantum user equipment (QUEs), and hybrid resource allocation spanning classical time-frequency and quantum entanglement domains. Several application scenarios are discussed and illustrated through system design requirements for quantum key distribution, blind quantum computing, and distributed quantum sensing. A range of unique quantum constraints are identified, including decoherence timing, fidelity requirements, and the interplay between quantum and classical error probabilities. Protocol adaptations extend cellular connection management to incorporate entanglement generation, distribution, and handover procedures, expanding the Quantum Internet to the cellular wireless.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains the leading cause of death globally and invasive coronary angiography (ICA) is considered the gold standard of anatomical imaging evaluation when CAD is suspected. However, risk evaluation based on ICA has several limitations, such as visual assessment of stenosis severity, which has significant interobserver variability. This motivates to development of a lesion classification system that can support specialists in their clinical procedures. Although deep learning classification methods are well-developed in other areas of medical imaging, ICA image classification is still at an early stage. One of the most important reasons is the lack of available and high-quality open-access datasets. In this paper, we reported a new annotated ICA images dataset, CADICA, to provide the research community with a comprehensive and rigorous dataset of coronary angiography consisting of a set of acquired patient videos and associated disease-related metadata. This dataset can be used by clinicians to train their skills in angiographic assessment of CAD severity and by computer scientists to create computer-aided diagnostic systems to help in such assessment. In addition, baseline classification methods are proposed and analyzed, validating the functionality of CADICA and giving the scientific community a starting point to improve CAD detection.
We study decision problems under uncertainty, where the decision-maker has
access to K data sources that carry {\em biased} information about the
underlying risk factors. The biases are measured by the mismatch between the
risk factor distribution and the K data-generating distributions with respect
to an optimal transport (OT) distance. In this situation the decision-maker can
exploit the information contained in the biased samples by solving a
distributionally robust optimization (DRO) problem, where the ambiguity set is
defined as the intersection of K OT neighborhoods, each of which is centered
at the empirical distribution on the samples generated by a biased data source.
We show that if the decision-maker has a prior belief about the biases, then
the out-of-sample performance of the DRO solution can improve with K --
irrespective of the magnitude of the biases. We also show that, under standard
convexity assumptions, the proposed DRO problem is computationally tractable if
either K or the dimension of the risk factors is kept constant.
Brain tumor resection is a complex procedure with significant implications for patient survival and quality of life. Predictions of patient outcomes provide clinicians and patients the opportunity to select the most suitable onco-functional balance. In this study, global features derived from structural magnetic resonance imaging in a clinical dataset of 49 pre- and post-surgery patients identified potential biomarkers associated with survival outcomes. We propose a framework that integrates Explainable AI (XAI) with neuroimaging-based feature engineering for survival assessment, offering guidance for surgical decision-making. In this study, we introduce a global explanation optimizer that refines survival-related feature attribution in deep learning models, enhancing interpretability and reliability. Our findings suggest that survival is influenced by alterations in regions associated with cognitive and sensory functions, indicating the importance of preserving areas involved in decision-making and emotional regulation during surgery to improve outcomes. The global explanation optimizer improves both fidelity and comprehensibility of explanations compared to state-of-the-art XAI methods. It effectively identifies survival-related variability, underscoring its relevance in precision medicine for brain tumor treatment.
25 Jan 2024
The latest trends in cancer research and nanomedicine focus on using
nanocarriers to target cancer stem cells (CSCs). Specifically, lipid liquid
nanocapsules are usually developed as nanocarriers for lipophilic drug
delivery. Here, we developed olive oil liquid NCs (O2LNCs) functionalized by
covalent coupling of an anti-CD44-fluorescein isothiocyanate antibody
({\alpha}CD44). First, O2LNCs are formed by a core of olive oil surrounded by a
shell containing phospholipids, a nonionic surfactant, and deoxycholic acid
molecules. Then, O2LNCs were coated with an {\alpha}CD44 antibody
({\alpha}CD44-O2LNC). The optimization of an {\alpha}CD44 coating procedure, a
complete physicochemical characterization, as well as clear evidence of their
efficacy in vitro and in vivo were demonstrated. Our results indicate the high
targeted uptake of these {\alpha}CD44-O2LNCs, and the increased antitumor
efficacy (up to four times) of paclitaxel-loaded-{\alpha}CD44-O2LNC compared to
free paclitaxel in pancreatic CSCs (PCSCs). Also, {\alpha}CD44-O2LNCs were able
to selectively target PCSCs in an orthotopic xenotransplant in vivo model.
In this article we present a novel and general methodology for building
second order finite volume implicit-explicit (IMEX) numerical schemes for
solving two dimensional financial parabolic PDEs with mixed derivatives. In
particular, applications to basket and Heston models are presented. The
obtained numerical schemes have excellent properties and are able to overcome
the well-documented difficulties related with numerical approximations in the
financial literature. The methods achieve true second order convergence with
non-regular initial conditions. Besides, the IMEX time integrator allows to
overcome the tiny time-step induced by the diffusive term in the explicit
schemes, also providing very accurate and non-oscillatory approximations of the
Greeks. Finally, in order to assess all the aforementioned good properties of
the developed numerical schemes, we compute extremely accurate semi-analytic
solutions using multi-dimensional Fourier cosine expansions. A novel technique
to truncate the Fourier series for basket options is presented and it is
efficiently implemented using multi-GPUs.
07 Jan 2021
The purpose of this Conference is to present the main lines of base projects that are founded on research already begun in previous years. In this sense, this manuscript will present the main lines of research in Diabetes Mellitus type 1 and Machine Learning techniques in an Internet of Things environment, so that we can summarize the future lines to be developed as follows: data collection through biosensors, massive data processing in the cloud, interconnection of biodevices, local computing vs. cloud computing, and possibilities of machine learning techniques to predict blood glucose values, including both variable selection algorithms and predictive techniques.
16 Jul 2023
In real-time and high-resolution Earth observation imagery, Low Earth Orbit
(LEO) satellites capture images that are subsequently transmitted to ground to
create an updated map of an area of interest. Such maps provide valuable
information for meteorology or environmental monitoring, but can also be
employed in near-real time operation for disaster detection, identification,
and management. However, the amount of data generated by these applications can
easily exceed the communication capabilities of LEO satellites, leading to
congestion and packet dropping. To avoid these problems, the Inter-Satellite
Links (ISLs) can be used to distribute the data among the satellites for
processing. In this paper, we address an energy minimization problem based on a
general satellite mobile edge computing (SMEC) framework for real-time and
very-high resolution Earth observation. Our results illustrate that the optimal
allocation of data and selection of the compression parameters increase the
amount of images that the system can support by a factor of 12 when compared to
directly downloading the data. Further, energy savings greater than 11% were
observed in a real-life scenario of imaging a volcanic island, while a
sensitivity analysis of the image acquisition process demonstrates that
potential energy savings can be as high as 92%.
Gait is a popular biometric pattern used for identifying people based on their way of walking. Traditionally, gait recognition approaches based on deep learning are trained using the whole training dataset. In fact, if new data (classes, view-points, walking conditions, etc.) need to be included, it is necessary to re-train again the model with old and new data samples.
In this paper, we propose iLGaCo, the first incremental learning approach of covariate factors for gait recognition, where the deep model can be updated with new information without re-training it from scratch by using the whole dataset. Instead, our approach performs a shorter training process with the new data and a small subset of previous samples. This way, our model learns new information while retaining previous knowledge.
We evaluate iLGaCo on CASIA-B dataset in two incremental ways: adding new view-points and adding new walking conditions. In both cases, our results are close to the classical `training-from-scratch' approach, obtaining a marginal drop in accuracy ranging from 0.2% to 1.2%, what shows the efficacy of our approach. In addition, the comparison of iLGaCo with other incremental learning methods, such as LwF and iCarl, shows a significant improvement in accuracy, between 6% and 15% depending on the experiment.
This survey compiles ideas and recommendations from more than a dozen
researchers with different backgrounds and from different institutes around the
world. Promoting best practice in benchmarking is its main goal. The article
discusses eight essential topics in benchmarking: clearly stated goals,
well-specified problems, suitable algorithms, adequate performance measures,
thoughtful analysis, effective and efficient designs, comprehensible
presentations, and guaranteed reproducibility. The final goal is to provide
well-accepted guidelines (rules) that might be useful for authors and
reviewers. As benchmarking in optimization is an active and evolving field of
research this manuscript is meant to co-evolve over time by means of periodic
updates.
Solving complex real problems often demands advanced algorithms, and then continuous improvements in the internal operations of a search technique are needed. Hybrid algorithms, parallel techniques, theoretical advances, and much more are needed to transform a general search algorithm into an efficient, useful one in practice. In this paper, we study how surrogates are helping metaheuristics from an important and understudied point of view: their energy profile. Even if surrogates are a great idea for substituting a time-demanding complex fitness function, the energy profile, general efficiency, and accuracy of the resulting surrogate-assisted metaheuristic still need considerable research. In this work, we make a first step in analyzing particle swarm optimization in different versions (including pre-trained and retrained neural networks as surrogates) for its energy profile (for both processor and memory), plus a further study on the surrogate accuracy to properly drive the search towards an acceptable solution. Our conclusions shed new light on this topic and could be understood as the first step towards a methodology for assessing surrogate-assisted algorithms not only accounting for time or numerical efficiency but also for energy and surrogate accuracy for a better, more holistic characterization of optimization and learning techniques.
15 Jan 2021
In recent years, feature selection has become a challenging problem in
several machine learning fields, such as classification problems. Support
Vector Machine (SVM) is a well-known technique applied in classification tasks.
Various methodologies have been proposed in the literature to select the most
relevant features in SVM. Unfortunately, all of them either deal with the
feature selection problem in the linear classification setting or propose
ad-hoc approaches that are difficult to implement in practice. In contrast, we
propose an embedded feature selection method based on a min-max optimization
problem, where a trade-off between model complexity and classification accuracy
is sought. By leveraging duality theory, we equivalently reformulate the
min-max problem and solve it without further ado using off-the-shelf software
for nonlinear optimization. The efficiency and usefulness of our approach are
tested on several benchmark data sets in terms of accuracy, number of selected
features and interpretability.
08 May 2025
Ruiz-Medina and Torres-Signes developed new local linear Fréchet functional regression methods for time-correlated bivariate curve data where both predictors and responses are functions on Riemannian manifolds. The paper presents both extrinsic and intrinsic approaches, demonstrating their performance through simulations and a real-world application to geophysical data.
In this article, we propose novel boundary treatment algorithms to avoid
order reduction when implicit-explicit Runge-Kutta time discretization is used
for solving convection-diffusion-reaction problems with time-dependent
Di\-richlet boundary conditions. We consider Cartesian meshes and PDEs with
stiff terms coming from the diffusive parts of the PDE. The algorithms treat
boundary values at the implicit-explicit internal stages in the same way as the
interior points. The boundary treatment strategy is designed to work with
multidimensional problems with possible nonlinear advection and source terms.
The proposed methods recover the designed order of convergence by numerical
verification. For the spatial discretization, in this work, we consider Local
Discontinuous Galerkin methods, although the developed boundary treatment
algorithms can operate with other discretization schemes in space, such as
Finite Differences, Finite Elements or Finite Volumes.
24 Mar 2020
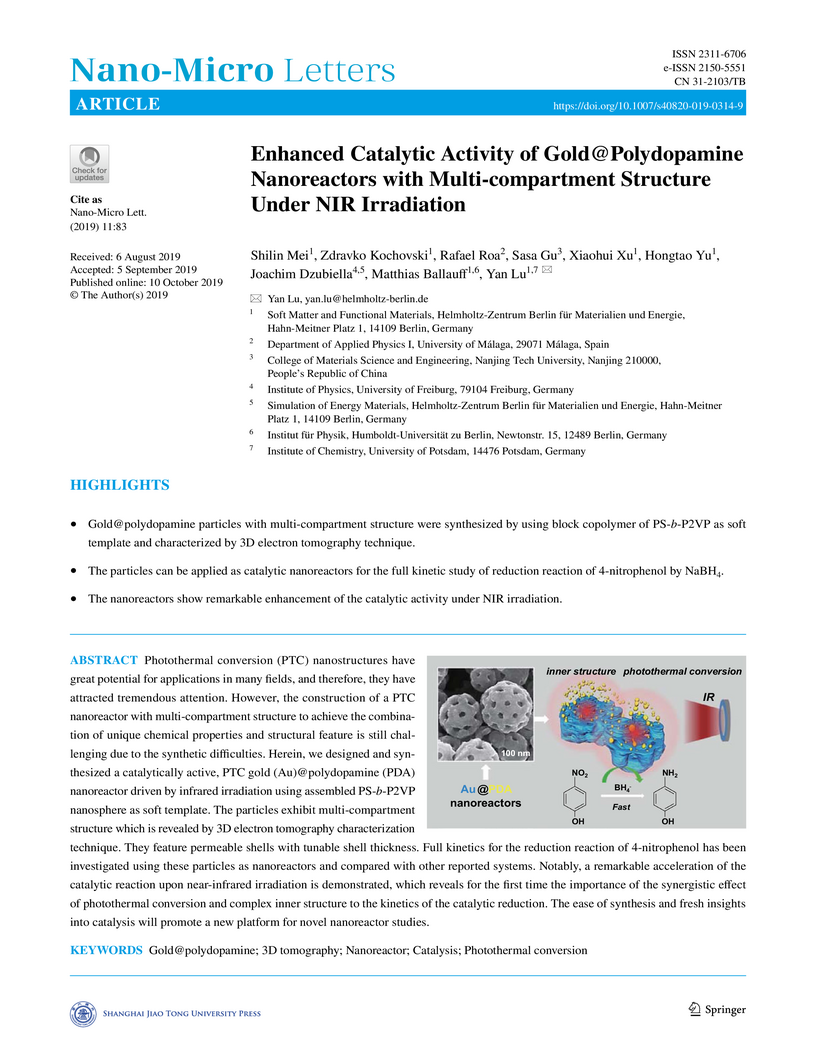
Photothermal conversion (PTC) nanostructures have great potential for
applications in many fields, and therefore, they have attracted tremendous
attention. However, the construction of a PTC nanoreactor with
multi-compartment structure to achieve the combination of unique chemical
properties and structural feature is still challenging due to the synthetic
difficulties. Herein, we designed and synthesized a catalytically active, PTC
gold (Au)@polydopamine (PDA) nanoreactor driven by infrared irradiation using
assembled PS-b-P2VP nanosphere as soft template. The particles exhibit
multi-compartment structure which is revealed by 3D electron tomography
characterization technique. They feature permeable shells with tunable shell
thickness. Full kinetics for the reduction reaction of 4-nitrophenol has been
investigated using these particles as nanoreactors and compared with other
reported systems. Notably, a remarkable acceleration of the catalytic reaction
upon near-infrared irradiation is demonstrated, which reveals for the first
time the importance of the synergistic effect of photothermal conversion and
complex inner structure to the kinetics of the catalytic reduction. The ease of
synthesis and fresh insights into catalysis will promote a new platform for
novel nanoreactor studies.
In pseudo-Boolean optimization, a variable interaction graph represents
variables as vertices, and interactions between pairs of variables as edges. In
black-box optimization, the variable interaction graph may be at least
partially discovered by using empirical linkage learning techniques. These
methods never report false variable interactions, but they are computationally
expensive. The recently proposed local search with linkage learning discovers
the partial variable interaction graph as a side-effect of iterated local
search. However, information about the strength of the interactions is not
learned by the algorithm. We propose local search with linkage learning 2,
which builds a weighted variable interaction graph that stores information
about the strength of the interaction between variables. The weighted variable
interaction graph can provide new insights about the optimization problem and
behavior of optimizers. Experiments with NK landscapes, knapsack problem, and
feature selection show that local search with linkage learning 2 is able to
efficiently build weighted variable interaction graphs. In particular,
experiments with feature selection show that the weighted variable interaction
graphs can be used for visualizing the feature interactions in machine
learning. Additionally, new transformation operators that exploit the
interactions between variables can be designed. We illustrate this ability by
proposing a new perturbation operator for iterated local search.
06 Dec 2024
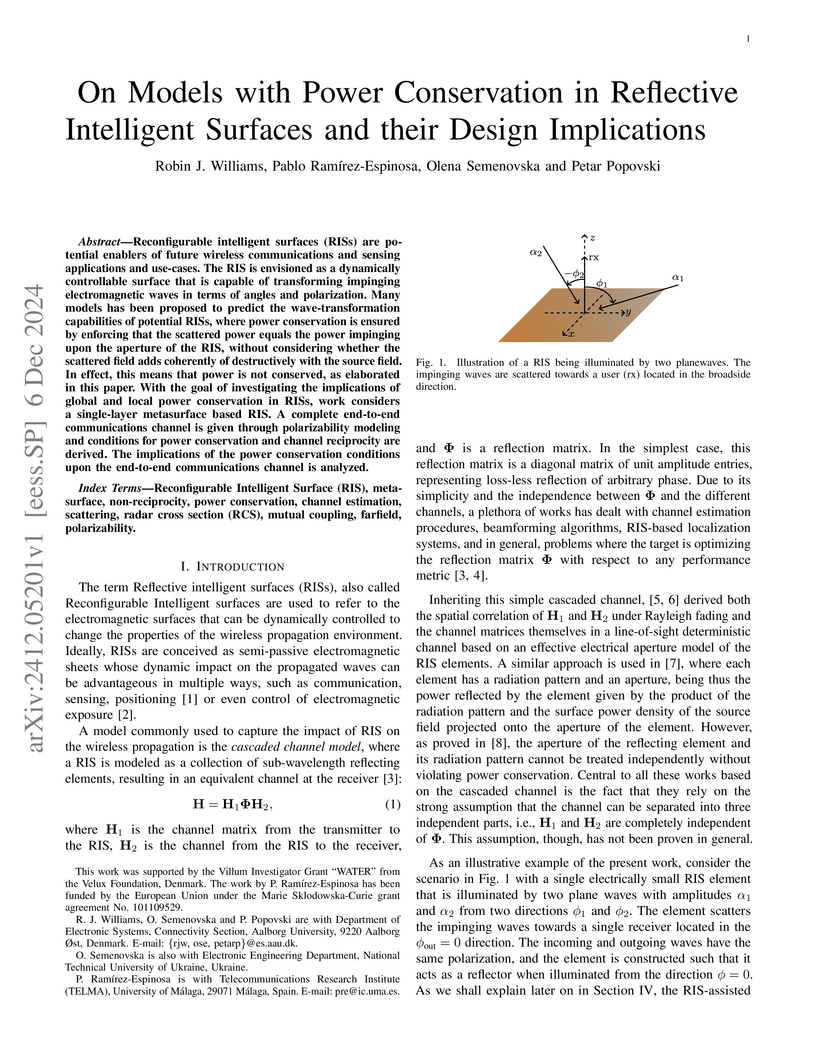
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) are potential enablers of future wireless communications and sensing applications and use-cases. The RIS is envisioned as a dynamically controllable surface that is capable of transforming impinging electromagnetic waves in terms of angles and polarization. Many models has been proposed to predict the wave-transformation capabilities of potential RISs, where power conservation is ensured by enforcing that the scattered power equals the power impinging upon the aperture of the RIS, without considering whether the scattered field adds coherently of destructively with the source field. In effect, this means that power is not conserved, as elaborated in this paper. With the goal of investigating the implications of global and local power conservation in RISs, work considers a single-layer metasurface based RIS. A complete end-to-end communications channel is given through polarizability modeling and conditions for power conservation and channel reciprocity are derived. The implications of the power conservation conditions upon the end-to-end communications channel is analyzed.
Huygens' metawaveguides represent a transformative concept in photonic device engineering, enabling unprecedented control over light propagation. This study presents, for the first time, integrated Huygens'-based microring resonators and directional and contra-directional couplers, specifically designed for operation at the 1550 nm telecommunication wavelength. By leveraging the unique properties of resonant Huygens' waveguides, we demonstrate efficient evanescent directional coupling with high-Q resonators, characterized by negative group index and near-zero dispersion, which are critical for enhancing performance in compact, high-performance add-drop filters. The research further explores the implications of these novel structures on group index and group velocity dispersion, providing insights into their potential applications in nonlinear optics and quantum information technologies. Notably, the introduction of a hybrid subwavelength grating-Huygens' contra-directional coupler facilitates backward coupling between resonant and non-resonant metawaveguides, achieving a broad spectral rejection bandwidth. Our findings advance the integration of resonant metamaterials into scalable photonic platforms, laying the groundwork for innovative applications in optical communications, quantum photonics and sensing systems.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.