Ask or search anything...
A comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
View blogToken-wise Feature Caching (ToCa) accelerates Diffusion Transformers without requiring model retraining by adaptively caching intermediate features at a granular token and layer level. This method achieves up to 2.75x speedup while preserving or improving generation quality across various text-to-image and text-to-video models.
View blogVideo Compression Commander (VidCom²) introduces a plug-and-play inference acceleration framework for Video Large Language Models (VideoLLMs) that intelligently prunes redundant visual tokens. The approach reduces LLM generation latency by 70.8% and peak GPU memory usage by approximately 9.6%, while retaining 99.6% of original performance at 25% token retention.
View blogFNSPID is a comprehensive financial dataset integrating 24 years of time-aligned stock prices and financial news for 4,775 S&P500 companies, featuring LLM-derived sentiment scores and multiple summarization methods. Experiments using FNSPID showed that Transformer models achieved a 0.988 R-squared for stock prediction, with LLM-based sentiment consistently improving accuracy across various deep learning architectures.
View blogLSceneLLM, developed by researchers from South China University of Technology, Tencent Robotics X, and others, presents an adaptive framework for large 3D scene understanding that mimics human visual processing by focusing on task-relevant regions. The approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across large indoor (XR-Scene), single-room indoor (ScanQA), and large outdoor (NuscenesQA) benchmarks, significantly improving fine-grained detail recognition and setting a new standard for embodied AI applications.
View blogA novel system, Instant4D, reconstructs high-quality dynamic 3D scenes from uncalibrated monocular videos within minutes. It achieves a 30x speed-up over existing methods, reducing training time to as little as 2 minutes and increasing PSNR by 7.15 dB on challenging datasets compared to concurrent baselines.
View blogA comprehensive survey examines the integration of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) techniques in computer vision tasks, analyzing applications across visual understanding, generation, and embodied AI while mapping key challenges and opportunities for extending RAG beyond text-based retrieval into multimodal frameworks.
View blogFinBen introduces the first comprehensive open-source evaluation benchmark for large language models in finance, integrating 36 datasets across 24 tasks and seven critical financial aspects. Its extensive evaluation of 15 LLMs reveals strong performance in basic NLP but significant deficiencies in complex reasoning, quantitative forecasting, and robust decision-making, while showcasing advanced models' capabilities in areas like stock trading.
View blogThe "Global Compression Commander" (GlobalCom²) framework accelerates inference for High-Resolution Large Vision-Language Models (HR-LVLMs) and VideoLLMs by intelligently compressing visual tokens using a global-to-local guidance strategy. It achieves a 90.9% reduction in FLOPs, a 40.0% decrease in peak GPU memory, and a 1.8x inference throughput boost at 10% token retention, while maintaining over 90% of original model performance.
View blogConditional Representation Learning (CRL) introduces an efficient framework that leverages LLMs and VLMs to generate image representations specifically tailored to arbitrary user-specified criteria, moving beyond universal embeddings. The framework demonstrates substantial performance gains across customized classification and retrieval tasks, including notable improvements of up to 40% in few-shot accuracy and 75% in clustering for non-dominant criteria compared to baseline VLMs.
View blogResearchers from multiple Asian institutions introduce GEMeX, the largest chest X-ray VQA dataset with 1.6 million question-answer pairs, featuring both textual explanations and visual grounding for answers. Benchmarking shows existing large vision-language models perform poorly, while a fine-tuned model achieves substantial performance gains and improved visual grounding, highlighting the dataset's utility for developing explainable medical AI.
View blogMCTrack introduces a unified 3D multi-object tracking framework designed to achieve state-of-the-art performance across KITTI, nuScenes, and Waymo datasets. It also proposes a standardized data format and novel motion-centric evaluation metrics, enhancing generalizability and comprehensive assessment for autonomous driving.
View blogResearchers from Sichuan University and collaborators developed V2Drop, a method that accelerates Large Vision-Language Models by progressively dropping redundant visual tokens based on their representational variation across LLM layers. This approach significantly enhances inference speed and reduces memory usage while preserving performance, addressing limitations of prior attention-guided compression techniques.
View blogMIXLORA integrates Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) with a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture to improve Large Language Model fine-tuning for multi-task learning. The method delivers an average accuracy increase of 9.8% over LoRA in multi-task scenarios and reduces GPU memory consumption by 40% with its high-throughput optimization framework.
View blog Monash University
Monash University
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
 Fudan University
Fudan University


 University of Pittsburgh
University of Pittsburgh Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University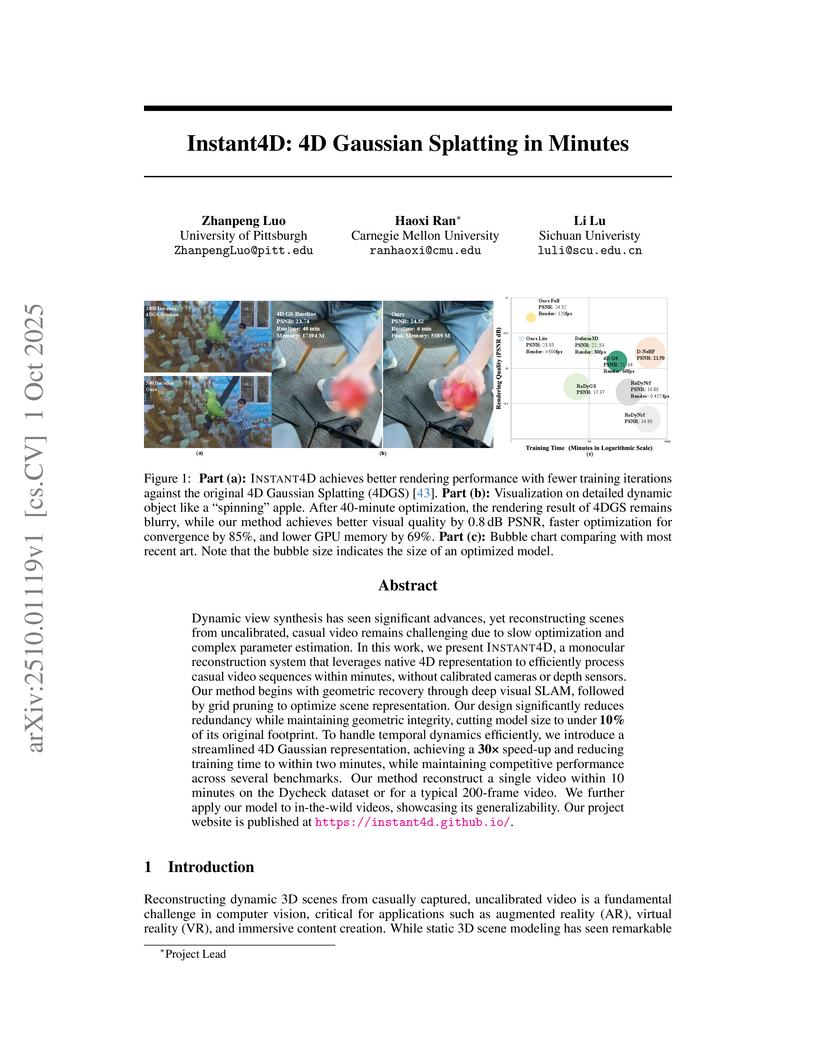
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich



 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University


 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences
 The Chinese University of Hong Kong
The Chinese University of Hong Kong

 National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore
 University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China
 Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University
 Emory University
Emory University