4Paradigm Inc.
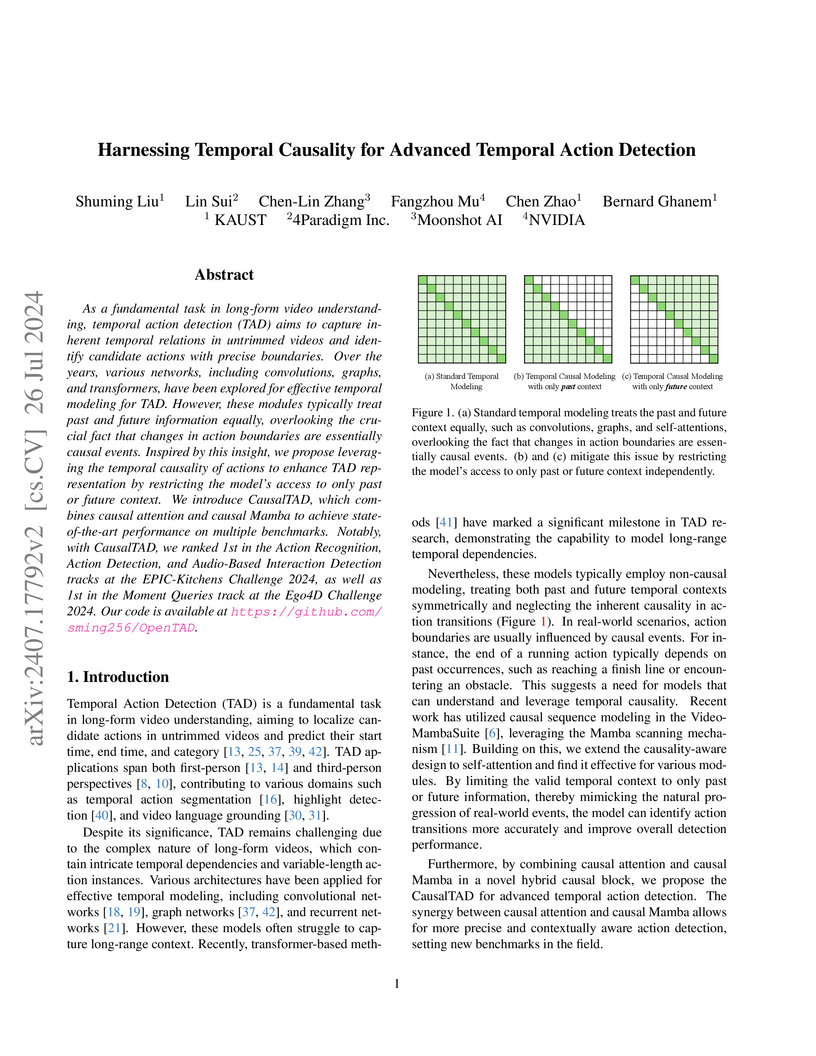
CausalTAD presents a temporal action detection model that explicitly leverages temporal causality through a Hybrid Causal Block, which integrates causal Mamba and causal attention mechanisms. This approach achieved state-of-the-art performance, including first-place rankings in the Ego4D Moment Query and EPIC-Kitchens Challenges 2024.
A research collaboration led by Tsinghua University presents a comprehensive survey of self-play methods in non-cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning. It introduces a unified framework that integrates diverse algorithms, notably including regret-minimization approaches, and categorizes existing solutions while analyzing their applications and future challenges.
Conflict-Driven Clause Learning (CDCL) is the mainstream framework for
solving the Satisfiability problem (SAT), and CDCL solvers typically rely on
various heuristics, which have a significant impact on their performance.
Modern CDCL solvers, such as MiniSat and Kissat, commonly incorporate several
heuristics and select one to use according to simple rules, requiring
significant time and expert effort to fine-tune in practice. The pervasion of
Large Language Models (LLMs) provides a potential solution to address this
issue. However, generating a CDCL solver from scratch is not effective due to
the complexity and context volume of SAT solvers. Instead, we propose AutoSAT,
a framework that automatically optimizes heuristics in a pre-defined modular
search space based on existing CDCL solvers. Unlike existing automated
algorithm design approaches focusing on hyperparameter tuning and operator
selection, AutoSAT can generate new efficient heuristics. In this first attempt
at optimizing SAT solvers using LLMs, several strategies including the greedy
hill climber and (1+1) Evolutionary Algorithm are employed to guide LLMs to
search for better heuristics. Experimental results demonstrate that LLMs can
generally enhance the performance of CDCL solvers. A realization of AutoSAT
outperforms MiniSat on 9 out of 12 datasets and even surpasses the
state-of-the-art hybrid solver Kissat on 4 datasets.
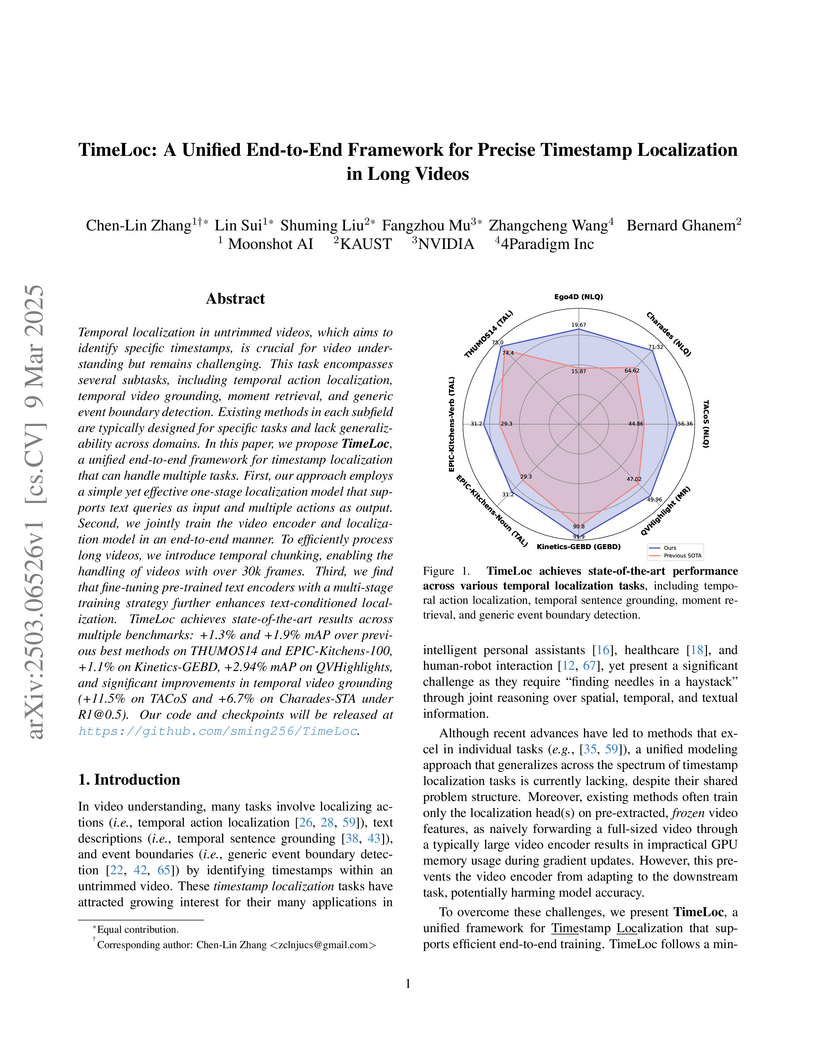
Temporal localization in untrimmed videos, which aims to identify specific
timestamps, is crucial for video understanding but remains challenging. This
task encompasses several subtasks, including temporal action localization,
temporal video grounding, moment retrieval, and generic event boundary
detection. Existing methods in each subfield are typically designed for
specific tasks and lack generalizability across domains. In this paper, we
propose TimeLoc, a unified end-to-end framework for timestamp localization that
can handle multiple tasks. First, our approach employs a simple yet effective
one-stage localization model that supports text queries as input and multiple
actions as output. Second, we jointly train the video encoder and localization
model in an end-to-end manner. To efficiently process long videos, we introduce
temporal chunking, enabling the handling of videos with over 30k frames. Third,
we find that fine-tuning pre-trained text encoders with a multi-stage training
strategy further enhances text-conditioned localization. TimeLoc achieves
state-of-the-art results across multiple benchmarks: +1.3% and +1.9% mAP over
previous best methods on THUMOS14 and EPIC-Kitchens-100, +1.1% on
Kinetics-GEBD, +2.94% mAP on QVHighlights, and significant improvements in
temporal video grounding (+11.5% on TACoS and +6.7% on Charades-STA under
R1@0.5). Our code and checkpoints will be released at
this https URL
In this study, we present EventRL, a reinforcement learning approach developed to enhance event extraction for large language models (LLMs). EventRL utilizes outcome supervision with specific reward functions to tackle prevalent challenges in LLMs, such as instruction following and hallucination, manifested as the mismatch of event structure and the generation of undefined event types. We evaluate EventRL against existing methods like Few-Shot Prompting (FSP) (based on GPT4) and Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) across various LLMs, including GPT-4, LLaMa, and CodeLLaMa models. Our findings show that EventRL significantly outperforms these conventional approaches by improving the performance in identifying and structuring events, particularly in handling novel event types. The study emphasizes the critical role of reward function selection and demonstrates the benefits of incorporating code data for better event extraction. While increasing model size leads to higher accuracy, maintaining the ability to generalize is essential to avoid overfitting.
LLMARENA presents a novel framework for evaluating large language models as agents in dynamic, multi-agent environments, aiming to mitigate data leakage and assess complex interactive skills. Experiments across 14 LLMs demonstrate GPT-4's superior performance, yet highlight persistent limitations in spatial comprehension, opponent modeling, and team collaboration for current models.
GC-CAD, developed by 4Paradigm Inc., introduces a self-supervised Graph Neural Network framework for efficient and accurate mechanical CAD part similarity retrieval. It directly processes Boundary Representation (BRep) data, leveraging contrastive learning to learn robust geometric and topological representations without manual labeling, demonstrating significant improvements in retrieval accuracy and computational efficiency on industrial-scale datasets.
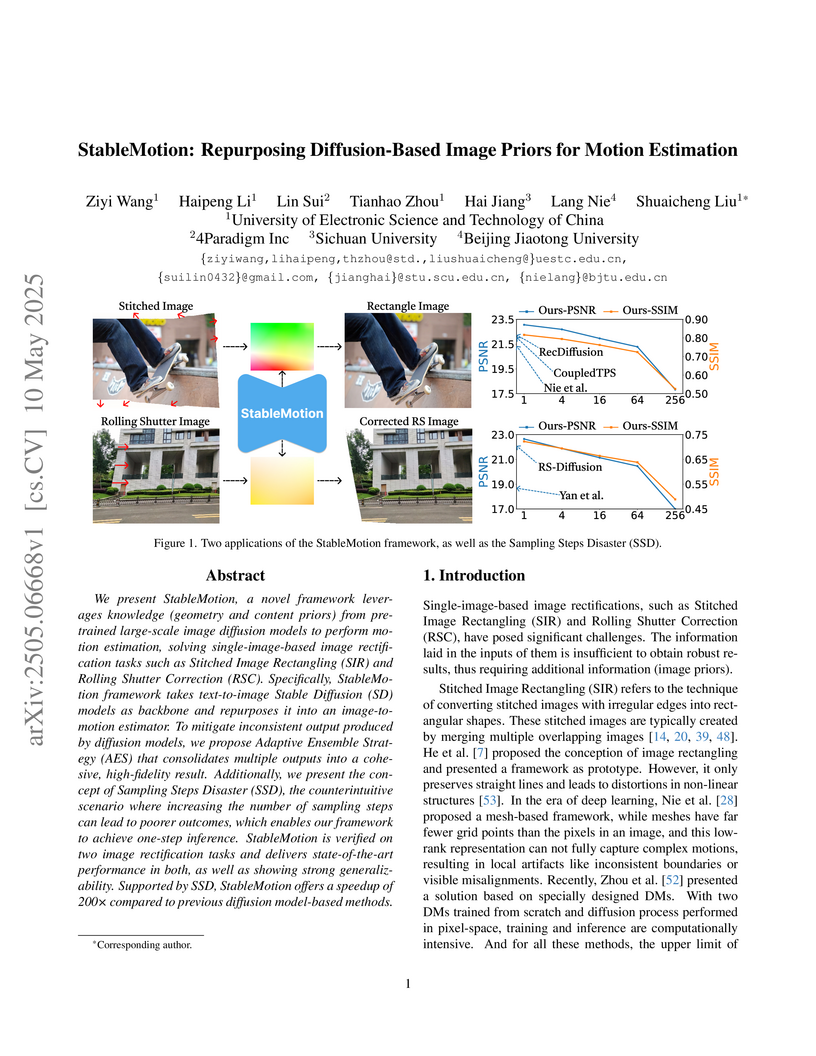
We present StableMotion, a novel framework leverages knowledge (geometry and
content priors) from pretrained large-scale image diffusion models to perform
motion estimation, solving single-image-based image rectification tasks such as
Stitched Image Rectangling (SIR) and Rolling Shutter Correction (RSC).
Specifically, StableMotion framework takes text-to-image Stable Diffusion (SD)
models as backbone and repurposes it into an image-to-motion estimator. To
mitigate inconsistent output produced by diffusion models, we propose Adaptive
Ensemble Strategy (AES) that consolidates multiple outputs into a cohesive,
high-fidelity result. Additionally, we present the concept of Sampling Steps
Disaster (SSD), the counterintuitive scenario where increasing the number of
sampling steps can lead to poorer outcomes, which enables our framework to
achieve one-step inference. StableMotion is verified on two image rectification
tasks and delivers state-of-the-art performance in both, as well as showing
strong generalizability. Supported by SSD, StableMotion offers a speedup of 200
times compared to previous diffusion model-based methods.
Event extraction is a fundamental task in natural language processing that involves identifying and extracting information about events mentioned in text. However, it is a challenging task due to the lack of annotated data, which is expensive and time-consuming to obtain. The emergence of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT provides an opportunity to solve language tasks with simple prompts without the need for task-specific datasets and fine-tuning. While ChatGPT has demonstrated impressive results in tasks like machine translation, text summarization, and question answering, it presents challenges when used for complex tasks like event extraction. Unlike other tasks, event extraction requires the model to be provided with a complex set of instructions defining all event types and their schemas. To explore the feasibility of ChatGPT for event extraction and the challenges it poses, we conducted a series of experiments. Our results show that ChatGPT has, on average, only 51.04% of the performance of a task-specific model such as EEQA in long-tail and complex scenarios. Our usability testing experiments indicate that ChatGPT is not robust enough, and continuous refinement of the prompt does not lead to stable performance improvements, which can result in a poor user experience. Besides, ChatGPT is highly sensitive to different prompt styles.
This comprehensive survey from Tsinghua University, 4Paradigm Inc., and ICT, CAS, provides a structured overview of Automated Machine Learning (AutoML), formally defining it as a bi-level optimization problem and presenting a detailed taxonomy of its principles and practices. It demonstrates AutoML's utility in automating ML pipeline configuration and significantly optimizing neural architecture search and foundation models, including specific examples where AutoPEFT achieved improved results over full fine-tuning.
We introduce SwiftSage, a novel agent framework inspired by the dual-process
theory of human cognition, designed to excel in action planning for complex
interactive reasoning tasks. SwiftSage integrates the strengths of behavior
cloning and prompting large language models (LLMs) to enhance task completion
performance. The framework comprises two primary modules: the Swift module,
representing fast and intuitive thinking, and the Sage module, emulating
deliberate thought processes. The Swift module is a small encoder-decoder LM
fine-tuned on the oracle agent's action trajectories, while the Sage module
employs LLMs such as GPT-4 for subgoal planning and grounding. We develop a
heuristic method to harmoniously integrate the two modules, resulting in a more
efficient and robust problem-solving process. In 30 tasks from the ScienceWorld
benchmark, SwiftSage significantly outperforms other methods such as SayCan,
ReAct, and Reflexion, demonstrating its effectiveness in solving complex
interactive tasks.
TiZero presents a multi-agent reinforcement learning system that successfully trains agents for the full 11 vs. 11 Google Research Football game mode entirely from scratch, achieving a TrueSkill rating of 45.2 and an 85.0% win rate against strong baselines through curriculum learning and novel self-play strategies.
Stochastically Extended Adversarial (SEA) model is introduced by Sachs et al. [2022] as an interpolation between stochastic and adversarial online convex optimization. Under the smoothness condition, they demonstrate that the expected regret of optimistic follow-the-regularized-leader (FTRL) depends on the cumulative stochastic variance σ1:T2 and the cumulative adversarial variation Σ1:T2 for convex functions. They also provide a slightly weaker bound based on the maximal stochastic variance σmax2 and the maximal adversarial variation Σmax2 for strongly convex functions. Inspired by their work, we investigate the theoretical guarantees of optimistic online mirror descent (OMD) for the SEA model. For convex and smooth functions, we obtain the same O(σ1:T2+Σ1:T2) regret bound, without the convexity requirement of individual functions. For strongly convex and smooth functions, we establish an O((σmax2+Σmax2)log(σ1:T2+Σ1:T2)) bound, better than their O((σmax2+Σmax2)logT) result. For exp-concave and smooth functions, we achieve a new O(dlog(σ1:T2+Σ1:T2)) bound. Owing to the OMD framework, we broaden our work to study dynamic regret minimization and scenarios where the online functions are non-smooth. We establish the first dynamic regret guarantee for the SEA model with convex and smooth functions, which is more favorable than static regret bounds in non-stationary scenarios. Furthermore, to deal with non-smooth and convex functions in the SEA model, we propose novel algorithms building on optimistic OMD with an implicit update, which provably attain static regret and dynamic regret guarantees without smoothness conditions.
DGPO presents a reinforcement learning algorithm that efficiently discovers multiple distinct, high-performing strategies for a given task by introducing a latent variable to a probabilistic graphical model and optimizing a novel pairwise diversity metric. The approach achieves superior diversity-reward trade-offs and significantly improved sample efficiency compared to existing methods across various complex environments.
Designing versatile graph learning approaches is important, considering the diverse graphs and tasks existing in real-world applications. Existing methods have attempted to achieve this target through automated machine learning techniques, pre-training and fine-tuning strategies, and large language models. However, these methods are not versatile enough for graph learning, as they work on either limited types of graphs or a single task. In this paper, we propose to explore versatile graph learning approaches with LLM-based agents, and the key insight is customizing the graph learning procedures for diverse graphs and tasks. To achieve this, we develop several LLM-based agents, equipped with diverse profiles, tools, functions and human experience. They collaborate to configure each procedure with task and data-specific settings step by step towards versatile solutions, and the proposed method is dubbed GL-Agent. By evaluating on diverse tasks and graphs, the correct results of the agent and its comparable performance showcase the versatility of the proposed method, especially in complex this http URL low resource cost and the potential to use open-source LLMs highlight the efficiency of GL-Agent.
While hyper-parameters (HPs) are important for knowledge graph (KG) learning,
existing methods fail to search them efficiently. To solve this problem, we
first analyze the properties of different HPs and measure the transfer ability
from small subgraph to the full graph. Based on the analysis, we propose an
efficient two-stage search algorithm KGTuner, which efficiently explores HP
configurations on small subgraph at the first stage and transfers the
top-performed configurations for fine-tuning on the large full graph at the
second stage. Experiments show that our method can consistently find better HPs
than the baseline algorithms within the same time budget, which achieves
{9.1\%} average relative improvement for four embedding models on the
large-scale KGs in open graph benchmark.
24 Mar 2024
The advent of deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has significantly advanced the field of robotics, particularly in the control and coordination of quadruped robots. However, the complexity of real-world tasks often necessitates the deployment of multi-robot systems capable of sophisticated interaction and collaboration. To address this need, we introduce the Multi-agent Quadruped Environment (MQE), a novel platform designed to facilitate the development and evaluation of multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) algorithms in realistic and dynamic scenarios. MQE emphasizes complex interactions between robots and objects, hierarchical policy structures, and challenging evaluation scenarios that reflect real-world applications. We present a series of collaborative and competitive tasks within MQE, ranging from simple coordination to complex adversarial interactions, and benchmark state-of-the-art MARL algorithms. Our findings indicate that hierarchical reinforcement learning can simplify task learning, but also highlight the need for advanced algorithms capable of handling the intricate dynamics of multi-agent interactions. MQE serves as a stepping stone towards bridging the gap between simulation and practical deployment, offering a rich environment for future research in multi-agent systems and robot learning. For open-sourced code and more details of MQE, please refer to this https URL .
01 Apr 2025
Feature management is essential for many online machine learning applications
and can often become the performance bottleneck (e.g., taking up to 70% of the
overall latency in sales prediction service). Improper feature configurations
(e.g., introducing too many irrelevant features) can severely undermine the
model's generalization capabilities. However, managing online ML features is
challenging due to (1) large-scale, complex raw data (e.g., the 2018 PHM
dataset contains 17 tables and dozens to hundreds of columns), (2) the need for
high-performance, consistent computation of interdependent features with
complex patterns, and (3) the requirement for rapid updates and deployments to
accommodate real-time data changes. In this demo, we present FeatInsight, a
system that supports the entire feature lifecycle, including feature design,
storage, visualization, computation, verification, and lineage management.
FeatInsight (with OpenMLDB as the execution engine) has been deployed in over
100 real-world scenarios on 4Paradigm's Sage Studio platform, handling up to a
trillion-dimensional feature space and enabling millisecond-level feature
updates. We demonstrate how FeatInsight enhances feature design efficiency
(e.g., for online product recommendation) and improve feature computation
performance (e.g., for online fraud detection). The code is available at
this https URL
Reasoning on the knowledge graph (KG) aims to infer new facts from existing ones. Methods based on the relational path have shown strong, interpretable, and transferable reasoning ability. However, paths are naturally limited in capturing local evidence in graphs. In this paper, we introduce a novel relational structure, i.e., relational directed graph (r-digraph), which is composed of overlapped relational paths, to capture the KG's local evidence. Since the r- digraphs are more complex than paths, how to efficiently construct and effectively learn from them are challenging. Directly encoding the r-digraphs cannot scale well and capturing query-dependent information is hard in r-digraphs. We propose a variant of graph neural network, i.e., RED-GNN, to address the above challenges. Specifically, RED-GNN makes use of dynamic programming to recursively encodes multiple r-digraphs with shared edges, and utilizes a query-dependent attention mechanism to select the strongly correlated edges. We demonstrate that RED-GNN is not only efficient but also can achieve significant performance gains in both inductive and transductive reasoning tasks over existing methods. Besides, the learned attention weights in RED-GNN can exhibit interpretable evidence for KG reasoning.
Various data mining tasks have been proposed to study Community Question
Answering (CQA) platforms like Stack Overflow. The relatedness between some of
these tasks provides useful learning signals to each other via Multi-Task
Learning (MTL). However, due to the high heterogeneity of these tasks, few
existing works manage to jointly solve them in a unified framework. To tackle
this challenge, we develop a multi-relational graph based MTL model called
Heterogeneous Multi-Task Graph Isomorphism Network (HMTGIN) which efficiently
solves heterogeneous CQA tasks. In each training forward pass, HMTGIN embeds
the input CQA forum graph by an extension of Graph Isomorphism Network and skip
connections. The embeddings are then shared across all task-specific output
layers to compute respective losses. Moreover, two cross-task constraints based
on the domain knowledge about tasks' relationships are used to regularize the
joint learning. In the evaluation, the embeddings are shared among different
task-specific output layers to make corresponding predictions. To the best of
our knowledge, HMTGIN is the first MTL model capable of tackling CQA tasks from
the aspect of multi-relational graphs. To evaluate HMTGIN's effectiveness, we
build a novel large-scale multi-relational graph CQA dataset with over two
million nodes from Stack Overflow. Extensive experiments show that: (1)
HMTGIN is superior to all baselines on five tasks; (2) The proposed MTL
strategy and cross-task constraints have substantial advantages.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.