Alibaba-NTU Singapore Joint Research Institute
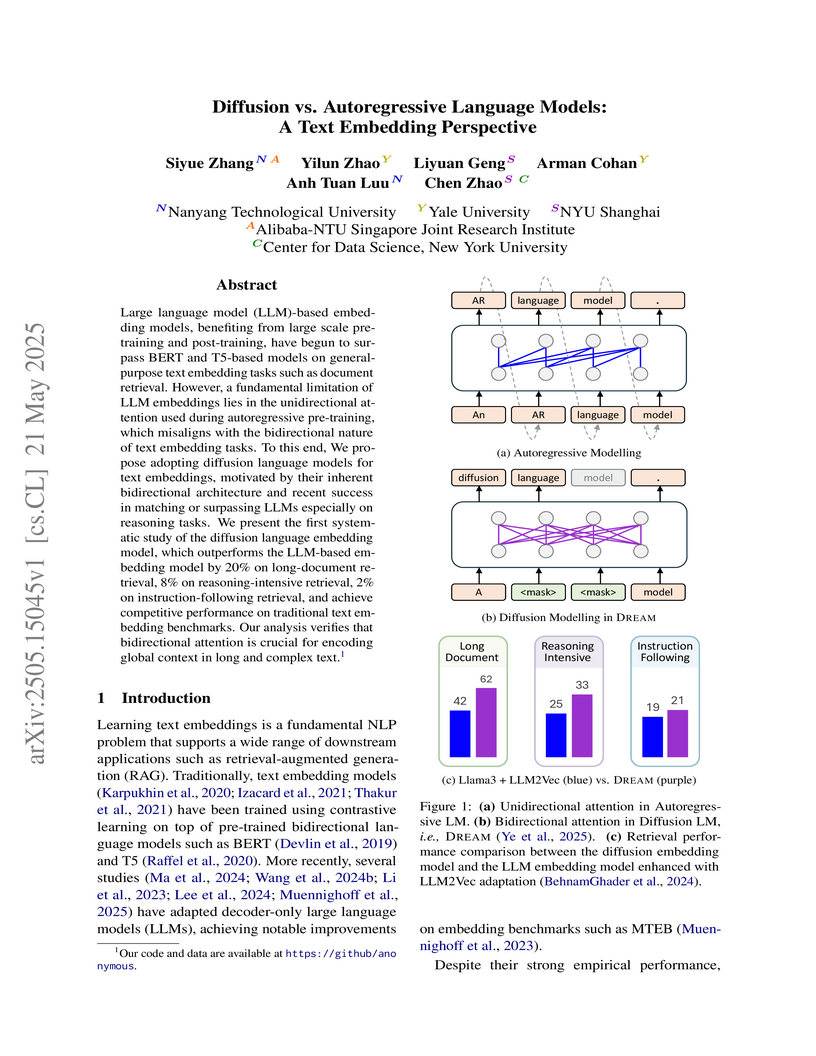
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University, Yale University, and NYU Shanghai demonstrate that diffusion language models outperform autoregressive LLMs for text embedding tasks, with their DIFFEMBED approach achieving 20% improvement on long-document retrieval and 8% improvement on reasoning-intensive retrieval by leveraging the inherent bidirectional attention architecture of diffusion models, while also introducing REASONAUG, a new training dataset for logical reasoning tasks.
The GEM framework introduces a generative, entropy-guided preference modeling approach for few-shot alignment of large language models, enabling them to internally evaluate and refine their reasoning. It achieved an average preference-prediction accuracy of 75.7% across general benchmarks and 78.2% agreement with medical expert preferences, leading to improved performance on reasoning and truthfulness tasks with limited supervision.
Multimodal recommender systems amalgamate multimodal information (e.g., textual descriptions, images) into a collaborative filtering framework to provide more accurate recommendations. While the incorporation of multimodal information could enhance the interpretability of these systems, current multimodal models represent users and items utilizing entangled numerical vectors, rendering them arduous to interpret. To address this, we propose a Disentangled Graph Variational Auto-Encoder (DGVAE) that aims to enhance both model and recommendation interpretability. DGVAE initially projects multimodal information into textual contents, such as converting images to text, by harnessing state-of-the-art multimodal pre-training technologies. It then constructs a frozen item-item graph and encodes the contents and interactions into two sets of disentangled representations utilizing a simplified residual graph convolutional network. DGVAE further regularizes these disentangled representations through mutual information maximization, aligning the representations derived from the interactions between users and items with those learned from textual content. This alignment facilitates the interpretation of user binary interactions via text. Our empirical analysis conducted on three real-world datasets demonstrates that DGVAE significantly surpasses the performance of state-of-the-art baselines by a margin of 10.02%. We also furnish a case study from a real-world dataset to illustrate the interpretability of DGVAE. Code is available at: \url{this https URL}.
Nanyang Technological University researchers introduced MP4SR, a multimodal pre-training framework that integrates item images and text into sequential recommendation systems using contrastive learning. This approach significantly mitigates data sparsity and enhances cold-start recommendations by learning robust, generalized multimodal sequence representations.
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University and Alibaba-NTU Singapore Joint Research Institute developed MASAC, a multi-agent reinforcement learning approach, for sustainably scheduling AIGC fine-tuning workloads across geo-distributed data centers. This framework achieved a 28.6% improvement in overall system utility by optimizing GPU utilization, energy costs, and carbon emissions, while also balancing transmission overheads.
This paper presents an open-source toolbox, MMRec for multimodal recommendation. MMRec simplifies and canonicalizes the process of implementing and comparing multimodal recommendation models. The objective of MMRec is to provide a unified and configurable arena that can minimize the effort in implementing and testing multimodal recommendation models. It enables multimodal models, ranging from traditional matrix factorization to modern graph-based algorithms, capable of fusing information from multiple modalities simultaneously. Our documentation, examples, and source code are available at \url{this https URL}.
This survey paper provides the first comprehensive review of neural Open Information Extraction (OpenIE), categorizing models into tagging-based and generative approaches. It critically analyzes current evaluation methodologies and benchmarks, identifies key challenges hindering the field's advancement, and proposes a strategic roadmap for future research directions.
Messages in human conversations inherently convey emotions. The task of
detecting emotions in textual conversations leads to a wide range of
applications such as opinion mining in social networks. However, enabling
machines to analyze emotions in conversations is challenging, partly because
humans often rely on the context and commonsense knowledge to express emotions.
In this paper, we address these challenges by proposing a Knowledge-Enriched
Transformer (KET), where contextual utterances are interpreted using
hierarchical self-attention and external commonsense knowledge is dynamically
leveraged using a context-aware affective graph attention mechanism.
Experiments on multiple textual conversation datasets demonstrate that both
context and commonsense knowledge are consistently beneficial to the emotion
detection performance. In addition, the experimental results show that our KET
model outperforms the state-of-the-art models on most of the tested datasets in
F1 score.
Empathetic conversational models have been shown to improve user satisfaction and task outcomes in numerous domains. In Psychology, persona has been shown to be highly correlated to personality, which in turn influences empathy. In addition, our empirical analysis also suggests that persona plays an important role in empathetic conversations. To this end, we propose a new task towards persona-based empathetic conversations and present the first empirical study on the impact of persona on empathetic responding. Specifically, we first present a novel large-scale multi-domain dataset for persona-based empathetic conversations. We then propose CoBERT, an efficient BERT-based response selection model that obtains the state-of-the-art performance on our dataset. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments to investigate the impact of persona on empathetic responding. Notably, our results show that persona improves empathetic responding more when CoBERT is trained on empathetic conversations than non-empathetic ones, establishing an empirical link between persona and empathy in human conversations.
16 May 2019
With the rapid development of recommender systems, accuracy is no longer the only golden criterion for evaluating whether the recommendation results are satisfying or not. In recent years, diversity has gained tremendous attention in recommender systems research, which has been recognized to be an important factor for improving user satisfaction. On the one hand, diversified recommendation helps increase the chance of answering ephemeral user needs. On the other hand, diversifying recommendation results can help the business improve product visibility and explore potential user interests. In this paper, we are going to review the recent advances in diversified recommendation. Specifically, we first review the various definitions of diversity and generate a taxonomy to shed light on how diversity have been modeled or measured in recommender systems. After that, we summarize the major optimization approaches to diversified recommendation from a taxonomic view. Last but not the least, we project into the future and point out trending research directions on this topic.
Text-to-SQL parsing and end-to-end question answering (E2E TQA) are two main approaches for Table-based Question Answering task. Despite success on multiple benchmarks, they have yet to be compared and their synergy remains unexplored. In this paper, we identify different strengths and weaknesses through evaluating state-of-the-art models on benchmark datasets: Text-to-SQL demonstrates superiority in handling questions involving arithmetic operations and long tables; E2E TQA excels in addressing ambiguous questions, non-standard table schema, and complex table contents. To combine both strengths, we propose a Synergistic Table-based Question Answering approach that integrate different models via answer selection, which is agnostic to any model types. Further experiments validate that ensembling models by either feature-based or LLM-based answer selector significantly improves the performance over individual models.
Affect conveys important implicit information in human communication. Having
the capability to correctly express affect during human-machine conversations
is one of the major milestones in artificial intelligence. In recent years,
extensive research on open-domain neural conversational models has been
conducted. However, embedding affect into such models is still under explored.
In this paper, we propose an end-to-end affect-rich open-domain neural
conversational model that produces responses not only appropriate in syntax and
semantics, but also with rich affect. Our model extends the Seq2Seq model and
adopts VAD (Valence, Arousal and Dominance) affective notations to embed each
word with affects. In addition, our model considers the effect of negators and
intensifiers via a novel affective attention mechanism, which biases attention
towards affect-rich words in input sentences. Lastly, we train our model with
an affect-incorporated objective function to encourage the generation of
affect-rich words in the output responses. Evaluations based on both perplexity
and human evaluations show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art
baseline model of comparable size in producing natural and affect-rich
responses.
As a critical clue of video super-resolution (VSR), inter-frame alignment significantly impacts overall performance. However, accurate pixel-level alignment is a challenging task due to the intricate motion interweaving in the video. In response to this issue, we introduce a novel paradigm for VSR named Semantic Lens, predicated on semantic priors drawn from degraded videos. Specifically, video is modeled as instances, events, and scenes via a Semantic Extractor. Those semantics assist the Pixel Enhancer in understanding the recovered contents and generating more realistic visual results. The distilled global semantics embody the scene information of each frame, while the instance-specific semantics assemble the spatial-temporal contexts related to each instance. Furthermore, we devise a Semantics-Powered Attention Cross-Embedding (SPACE) block to bridge the pixel-level features with semantic knowledge, composed of a Global Perspective Shifter (GPS) and an Instance-Specific Semantic Embedding Encoder (ISEE). Concretely, the GPS module generates pairs of affine transformation parameters for pixel-level feature modulation conditioned on global semantics. After that, the ISEE module harnesses the attention mechanism to align the adjacent frames in the instance-centric semantic space. In addition, we incorporate a simple yet effective pre-alignment module to alleviate the difficulty of model training. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our model over existing state-of-the-art VSR methods.
The success of Federated Learning (FL) depends on the quantity and quality of the data owners (DOs) as well as their motivation to join FL model training. Reputation-based FL participant selection methods have been proposed. However, they still face the challenges of the cold start problem and potential selection bias towards highly reputable DOs. Such a bias can result in lower reputation DOs being prematurely excluded from future FL training rounds, thereby reducing the diversity of training data and the generalizability of the resulting models. To address these challenges, we propose the Gradual Participant Selection scheme for Auction-based Federated Learning (GPS-AFL). Unlike existing AFL incentive mechanisms which generally assume that all DOs required for an FL task must be selected in one go, GPS-AFL gradually selects the required DOs over multiple rounds of training as more information is revealed through repeated interactions. It is designed to strike a balance between cost saving and performance enhancement, while mitigating the drawbacks of selection bias in reputation-based FL. Extensive experiments based on real-world datasets demonstrate the significant advantages of GPS-AFL, which reduces costs by 33.65% and improved total utility by 2.91%, on average compared to the best-performing state-of-the-art approach.
Synthetic lethality (SL) is a promising concept for novel discovery of anti-cancer drug targets. However, wet-lab experiments for detecting SLs are faced with various challenges, such as high cost, low consistency across platforms or cell lines. Therefore, computational prediction methods are needed to address these issues. This paper proposes a novel SL prediction method, named SL2MF, which employs logistic matrix factorization to learn latent representations of genes from the observed SL data. The probability that two genes are likely to form SL is modeled by the linear combination of gene latent vectors. As known SL pairs are more trustworthy than unknown pairs, we design importance weighting schemes to assign higher importance weights for known SL pairs and lower importance weights for unknown pairs in SL2MF. Moreover, we also incorporate biological knowledge about genes from protein-protein interaction (PPI) data and Gene Ontology (GO). In particular, we calculate the similarity between genes based on their GO annotations and topological properties in the PPI network. Extensive experiments on the SL interaction data from SynLethDB database have been conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of SL2MF.
The semantic communication system enables wireless devices to communicate effectively with the semantic meaning of the data. Wireless powered Internet of Things (IoT) that adopts the semantic communication system relies on harvested energy to transmit semantic information. However, the issue of energy constraint in the semantic communication system is not well studied. In this paper, we propose a semantic-based energy valuation and take an economic approach to solve the energy allocation problem as an incentive mechanism design. In our model, IoT devices (bidders) place their bids for the energy and power transmitter (auctioneer) decides the winner and payment by using deep learning based optimal auction. Results show that the revenue of wireless power transmitter is maximized while satisfying Individual Rationality (IR) and Incentive Compatibility (IC).
It is well-known that exploiting label correlations is crucially important to
multi-label learning. Most of the existing approaches take label correlations
as prior knowledge, which may not correctly characterize the real relationships
among labels. Besides, label correlations are normally used to regularize the
hypothesis space, while the final predictions are not explicitly correlated. In
this paper, we suggest that for each individual label, the final prediction
involves the collaboration between its own prediction and the predictions of
other labels. Based on this assumption, we first propose a novel method to
learn the label correlations via sparse reconstruction in the label space.
Then, by seamlessly integrating the learned label correlations into model
training, we propose a novel multi-label learning approach that aims to
explicitly account for the correlated predictions of labels while training the
desired model simultaneously. Extensive experimental results show that our
approach outperforms the state-of-the-art counterparts.
Rationality and emotion are two fundamental elements of humans. Endowing
agents with rationality and emotion has been one of the major milestones in AI.
However, in the field of conversational AI, most existing models only
specialize in one aspect and neglect the other, which often leads to dull or
unrelated responses. In this paper, we hypothesize that combining rationality
and emotion into conversational agents can improve response quality. To test
the hypothesis, we focus on one fundamental aspect of rationality, i.e.,
commonsense, and propose CARE, a novel model for commonsense-aware emotional
response generation. Specifically, we first propose a framework to learn and
construct commonsense-aware emotional latent concepts of the response given an
input message and a desired emotion. We then propose three methods to
collaboratively incorporate the latent concepts into response generation.
Experimental results on two large-scale datasets support our hypothesis and
show that our model can produce more accurate and commonsense-aware emotional
responses and achieve better human ratings than state-of-the-art models that
only specialize in one aspect.
28 Feb 2021
We study the problem of imposing conversational goals/keywords on open-domain
conversational agents, where the agent is required to lead the conversation to
a target keyword smoothly and fast. Solving this problem enables the
application of conversational agents in many real-world scenarios, e.g.,
recommendation and psychotherapy. The dominant paradigm for tackling this
problem is to 1) train a next-turn keyword classifier, and 2) train a
keyword-augmented response retrieval model. However, existing approaches in
this paradigm have two limitations: 1) the training and evaluation datasets for
next-turn keyword classification are directly extracted from conversations
without human annotations, thus, they are noisy and have low correlation with
human judgements, and 2) during keyword transition, the agents solely rely on
the similarities between word embeddings to move closer to the target keyword,
which may not reflect how humans converse. In this paper, we assume that human
conversations are grounded on commonsense and propose a keyword-guided neural
conversational model that can leverage external commonsense knowledge graphs
(CKG) for both keyword transition and response retrieval. Automatic evaluations
suggest that commonsense improves the performance of both next-turn keyword
prediction and keyword-augmented response retrieval. In addition, both
self-play and human evaluations show that our model produces responses with
smoother keyword transition and reaches the target keyword faster than
competitive baselines.
With the AI of Things (AIoT) development, a huge amount of visual data, e.g., images and videos, are produced in our daily work and life. These visual data are not only used for human viewing or understanding but also for machine analysis or decision-making, e.g., intelligent surveillance, automated vehicles, and many other smart city applications. To this end, a new image codec paradigm for both human and machine uses is proposed in this work. Firstly, the high-level instance segmentation map and the low-level signal features are extracted with neural networks. Then, the instance segmentation map is further represented as a profile with the proposed 16-bit gray-scale representation. After that, both 16-bit gray-scale profile and signal features are encoded with a lossless codec. Meanwhile, an image predictor is designed and trained to achieve the general-quality image reconstruction with the 16-bit gray-scale profile and signal features. Finally, the residual map between the original image and the predicted one is compressed with a lossy codec, used for high-quality image reconstruction. With such designs, on the one hand, we can achieve scalable image compression to meet the requirements of different human consumption; on the other hand, we can directly achieve several machine vision tasks at the decoder side with the decoded 16-bit gray-scale profile, e.g., object classification, detection, and segmentation. Experimental results show that the proposed codec achieves comparable results as most learning-based codecs and outperforms the traditional codecs (e.g., BPG and JPEG2000) in terms of PSNR and MS-SSIM for image reconstruction. At the same time, it outperforms the existing codecs in terms of the mAP for object detection and segmentation.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.