Data61Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation
 The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of MelbourneUniversity of Technology SydneyThe University of Sydney
The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of MelbourneUniversity of Technology SydneyThe University of Sydney Australian National UniversityKing Fahd University of Petroleum and MineralsUniversity of Engineering and TechnologyThe University of Western AustraliaCommonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research OrganisationSDAIA-KFUPM Joint Research Center for Artificial Intelligence
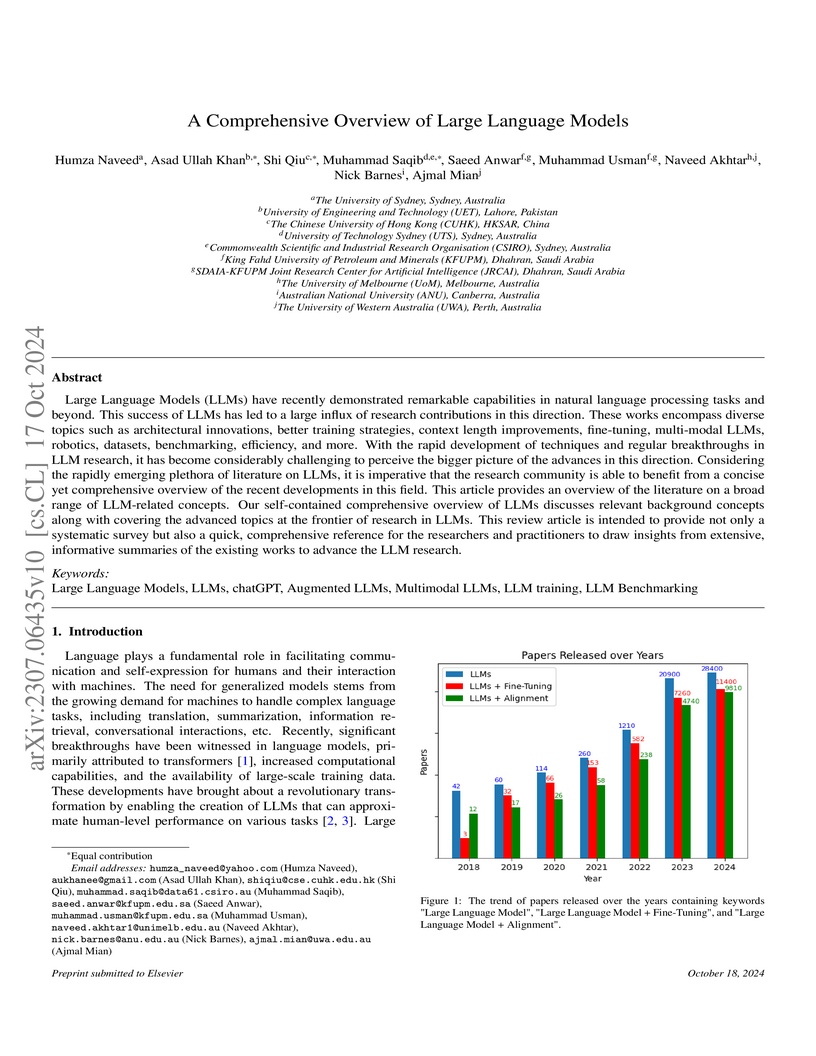
Australian National UniversityKing Fahd University of Petroleum and MineralsUniversity of Engineering and TechnologyThe University of Western AustraliaCommonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research OrganisationSDAIA-KFUPM Joint Research Center for Artificial IntelligenceThis paper synthesizes the extensive and rapidly evolving literature on Large Language Models (LLMs), offering a structured resource on their architectures, training strategies, and applications. It provides a comprehensive overview of existing works, highlighting key design aspects, model capabilities, augmentation strategies, and efficiency techniques, while also discussing challenges and future research directions.
11 Jul 2024
This research from CSIRO Data61 introduces PINN-Ray, a Physics-Informed Neural Network designed to model the complex, nonlinear deformation of soft robotic Fin Ray fingers. By assimilating just nine experimental data points, PINN-Ray achieves a Mean Absolute Error of 0.03 mm in displacement prediction, significantly outperforming traditional Finite Element Models and standard PINN approaches while also accurately estimating internal stress and strain distributions.
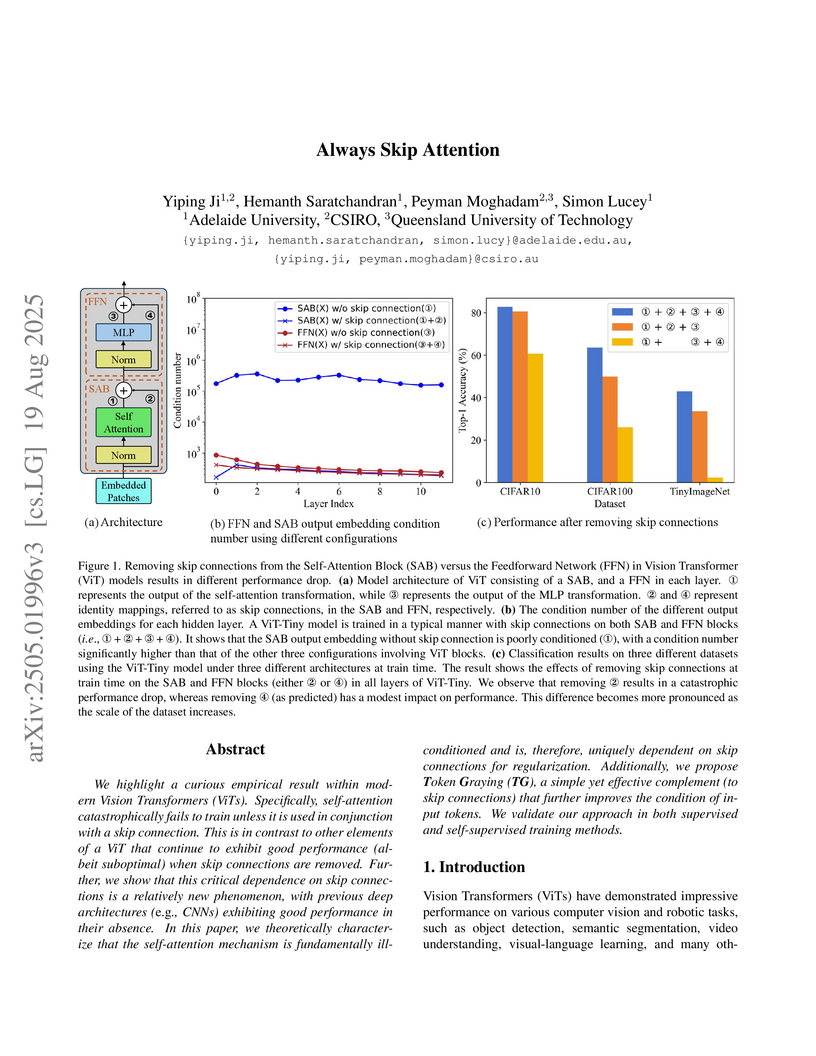
Researchers at Adelaide University and CSIRO found that the self-attention mechanism in Vision Transformers requires skip connections to prevent catastrophic training failure, attributing this to its intrinsic ill-conditioning. They introduced Token Graying, a pre-conditioning method that improved ViT accuracy on ImageNet-1K by up to 0.3% with minimal computational cost.
18 Oct 2025
Quantum machine learning (QML) has emerged as a promising area of research for enhancing the performance of classical machine learning systems by leveraging quantum computational principles. However, practical deployment of QML remains limited due to current hardware constraints such as limited number of qubits and quantum noise. This chapter introduces a hybrid quantum-classical architecture that combines the advantages of quantum computing with transfer learning techniques to address high-resolution image classification. Specifically, we propose a Quantum Transfer Learning (QTL) model that integrates classical convolutional feature extraction with quantum variational circuits. Through extensive simulations on diverse datasets including Ants \& Bees, CIFAR-10, and Road Sign Detection, we demonstrate that QTL achieves superior classification performance compared to both conventional and quantum models trained without transfer learning. Additionally, we also investigate the model's vulnerability to adversarial attacks and demonstrate that incorporating adversarial training significantly boosts the robustness of QTL, enhancing its potential for deployment in security sensitive applications.
20 Feb 2019
Multi-agent path finding (MAPF) is an essential component of many large-scale, real-world robot deployments, from aerial swarms to warehouse automation. However, despite the community's continued efforts, most state-of-the-art MAPF planners still rely on centralized planning and scale poorly past a few hundred agents. Such planning approaches are maladapted to real-world deployments, where noise and uncertainty often require paths be recomputed online, which is impossible when planning times are in seconds to minutes. We present PRIMAL, a novel framework for MAPF that combines reinforcement and imitation learning to teach fully-decentralized policies, where agents reactively plan paths online in a partially-observable world while exhibiting implicit coordination. This framework extends our previous work on distributed learning of collaborative policies by introducing demonstrations of an expert MAPF planner during training, as well as careful reward shaping and environment sampling. Once learned, the resulting policy can be copied onto any number of agents and naturally scales to different team sizes and world dimensions. We present results on randomized worlds with up to 1024 agents and compare success rates against state-of-the-art MAPF planners. Finally, we experimentally validate the learned policies in a hybrid simulation of a factory mockup, involving both real-world and simulated robots.
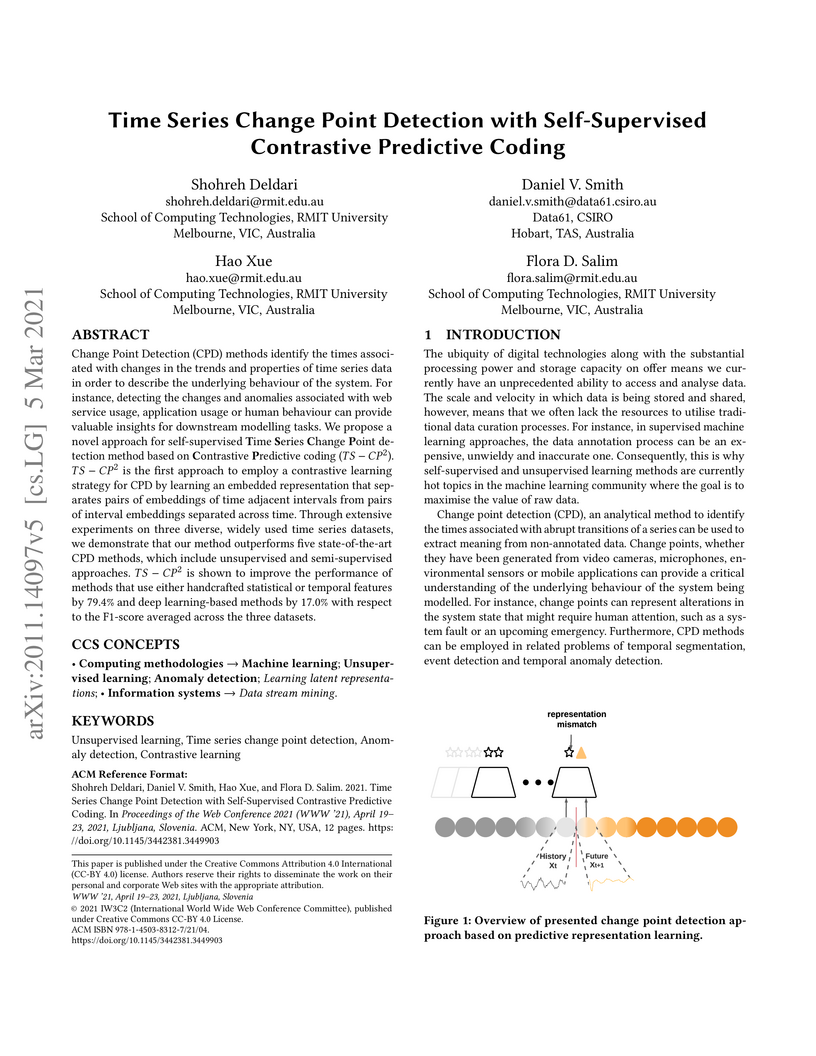
Change Point Detection (CPD) methods identify the times associated with changes in the trends and properties of time series data in order to describe the underlying behaviour of the system. For instance, detecting the changes and anomalies associated with web service usage, application usage or human behaviour can provide valuable insights for downstream modelling tasks. We propose a novel approach for self-supervised Time Series Change Point detection method based onContrastivePredictive coding (TS-CP^2). TS-CP^2 is the first approach to employ a contrastive learning strategy for CPD by learning an embedded representation that separates pairs of embeddings of time adjacent intervals from pairs of interval embeddings separated across time. Through extensive experiments on three diverse, widely used time series datasets, we demonstrate that our method outperforms five state-of-the-art CPD methods, which include unsupervised and semi-supervisedapproaches. TS-CP^2 is shown to improve the performance of methods that use either handcrafted statistical or temporal features by 79.4% and deep learning-based methods by 17.0% with respect to the F1-score averaged across the three datasets.
This paper presents a comprehensive survey of Physics-Informed Medical Image Analysis (PIMIA), providing a unified taxonomy for how physics knowledge is incorporated and quantitatively assessing the performance enhancements from integrating physics into various medical imaging tasks. It delineates current research trends, challenges, and future directions in this rapidly growing field.
11 Jun 2025
Why do deep neural networks (DNNs) benefit from very high dimensional
parameter spaces? Their huge parameter complexities vs stunning performance in
practice is all the more intriguing and not explainable using the standard
theory of model selection for regular models. In this work, we propose a
geometrically flavored information-theoretic approach to study this phenomenon.
With the belief that simplicity is linked to better generalization, as grounded
in the theory of minimum description length, the objective of our analysis is
to examine and bound the complexity of DNNs. We introduce the locally varying
dimensionality of the parameter space of neural network models by considering
the number of significant dimensions of the Fisher information matrix, and
model the parameter space as a manifold using the framework of singular
semi-Riemannian geometry. We derive model complexity measures which yield short
description lengths for deep neural network models based on their singularity
analysis thus explaining the good performance of DNNs despite their large
number of parameters.
The SVE-Math framework enhances Multimodal Large Language Models' visual perception of mathematical diagrams by integrating a specialized Geometric-Grounded Vision Encoder (GeoGLIP) and a Feature Router. This approach improves accuracy in visual mathematical reasoning, leading to a 15% performance gain over other 7B models on the MathVerse benchmark and comparable performance to GPT-4V on MathVista.
PACE enhances parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) by introducing a consistency regularization strategy that implicitly reduces weight gradient norms and aligns the fine-tuned model with its pre-trained counterpart. This method demonstrates improved generalization across various visual and language tasks, outperforming existing PEFT approaches.
Symbolic Regression is the study of algorithms that automate the search for
analytic expressions that fit data. While recent advances in deep learning have
generated renewed interest in such approaches, the development of symbolic
regression methods has not been focused on physics, where we have important
additional constraints due to the units associated with our data. Here we
present Φ-SO, a Physical Symbolic Optimization framework for recovering
analytical symbolic expressions from physics data using deep reinforcement
learning techniques by learning units constraints. Our system is built, from
the ground up, to propose solutions where the physical units are consistent by
construction. This is useful not only in eliminating physically impossible
solutions, but because the "grammatical" rules of dimensional analysis restrict
enormously the freedom of the equation generator, thus vastly improving
performance. The algorithm can be used to fit noiseless data, which can be
useful for instance when attempting to derive an analytical property of a
physical model, and it can also be used to obtain analytical approximations to
noisy data. We test our machinery on a standard benchmark of equations from the
Feynman Lectures on Physics and other physics textbooks, achieving
state-of-the-art performance in the presence of noise (exceeding 0.1%) and show
that it is robust even in the presence of substantial (10%) noise. We showcase
its abilities on a panel of examples from astrophysics.
We propose a one-class neural network (OC-NN) model to detect anomalies in
complex data sets. OC-NN combines the ability of deep networks to extract a
progressively rich representation of data with the one-class objective of
creating a tight envelope around normal data. The OC-NN approach breaks new
ground for the following crucial reason: data representation in the hidden
layer is driven by the OC-NN objective and is thus customized for anomaly
detection. This is a departure from other approaches which use a hybrid
approach of learning deep features using an autoencoder and then feeding the
features into a separate anomaly detection method like one-class SVM (OC-SVM).
The hybrid OC-SVM approach is sub-optimal because it is unable to influence
representational learning in the hidden layers. A comprehensive set of
experiments demonstrate that on complex data sets (like CIFAR and GTSRB), OC-NN
performs on par with state-of-the-art methods and outperformed conventional
shallow methods in some scenarios.
Deconfounded Causality-aware Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Problem-Solving Improvement of LLMs
Deconfounded Causality-aware Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning for Problem-Solving Improvement of LLMs
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable efficiency in
tackling various tasks based on human instructions, but studies reveal that
they often struggle with tasks requiring reasoning, such as math or physics.
This limitation raises questions about whether LLMs truly comprehend embedded
knowledge or merely learn to replicate the token distribution without a true
understanding of the content. In this paper, we delve into this problem and aim
to enhance the reasoning capabilities of LLMs. First, we investigate if the
model has genuine reasoning capabilities by visualizing the text generation
process at the attention and representation level. Then, we formulate the
reasoning process of LLMs into a causal framework, which provides a formal
explanation of the problems observed in the visualization. Finally, building
upon this causal framework, we propose Deconfounded Causal Adaptation (DCA), a
novel parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) method to enhance the model's
reasoning capabilities by encouraging the model to extract the general
problem-solving skills and apply these skills to different questions.
Experiments show that our method outperforms the baseline consistently across
multiple benchmarks, and with only 1.2M tunable parameters, we achieve better
or comparable results to other fine-tuning methods. This demonstrates the
effectiveness and efficiency of our method in improving the overall accuracy
and reliability of LLMs.
Diabetes, resulting from inadequate insulin production or utilization, causes extensive harm to the body. Existing diagnostic methods are often invasive and come with drawbacks, such as cost constraints. Although there are machine learning models like Classwise k Nearest Neighbor (CkNN) and General Regression Neural Network (GRNN), they struggle with imbalanced data and result in under-performance. Leveraging advancements in sensor technology and machine learning, we propose a non-invasive diabetes diagnosis using a Back Propagation Neural Network (BPNN) with batch normalization, incorporating data re-sampling and normalization for class balancing. Our method addresses existing challenges such as limited performance associated with traditional machine learning. Experimental results on three datasets show significant improvements in overall accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity compared to traditional methods. Notably, we achieve accuracies of 89.81% in Pima diabetes dataset, 75.49% in CDC BRFSS2015 dataset, and 95.28% in Mesra Diabetes dataset. This underscores the potential of deep learning models for robust diabetes diagnosis. See project website this https URL
Diffusion models (DMs) have been investigated in various domains due to their ability to generate high-quality data, thereby attracting significant attention. However, similar to traditional deep learning systems, there also exist potential threats to DMs. To provide advanced and comprehensive insights into safety, ethics, and trust in DMs, this survey comprehensively elucidates its framework, threats, and countermeasures. Each threat and its countermeasures are systematically examined and categorized to facilitate thorough analysis. Furthermore, we introduce specific examples of how DMs are used, what dangers they might bring, and ways to protect against these dangers. Finally, we discuss key lessons learned, highlight open challenges related to DM security, and outline prospective research directions in this critical field. This work aims to accelerate progress not only in the technical capabilities of generative artificial intelligence but also in the maturity and wisdom of its application.
30 Oct 2019
Sequential Monte Carlo methods, also known as particle methods, are a popular set of techniques for approximating high-dimensional probability distributions and their normalizing constants. These methods have found numerous applications in statistics and related fields; e.g. for inference in non-linear non-Gaussian state space models, and in complex static models. Like many Monte Carlo sampling schemes, they rely on proposal distributions which crucially impact their performance. We introduce here a class of controlled sequential Monte Carlo algorithms, where the proposal distributions are determined by approximating the solution to an associated optimal control problem using an iterative scheme. This method builds upon a number of existing algorithms in econometrics, physics, and statistics for inference in state space models, and generalizes these methods so as to accommodate complex static models. We provide a theoretical analysis concerning the fluctuation and stability of this methodology that also provides insight into the properties of related algorithms. We demonstrate significant gains over state-of-the-art methods at a fixed computational complexity on a variety of applications.
Graph contrastive learning attracts/disperses node representations for similar/dissimilar node pairs under some notion of similarity. It may be combined with a low-dimensional embedding of nodes to preserve intrinsic and structural properties of a graph. In this paper, we extend the celebrated Laplacian Eigenmaps with contrastive learning, and call them COntrastive Laplacian EigenmapS (COLES). Starting from a GAN-inspired contrastive formulation, we show that the Jensen-Shannon divergence underlying many contrastive graph embedding models fails under disjoint positive and negative distributions, which may naturally emerge during sampling in the contrastive setting. In contrast, we demonstrate analytically that COLES essentially minimizes a surrogate of Wasserstein distance, which is known to cope well under disjoint distributions. Moreover, we show that the loss of COLES belongs to the family of so-called block-contrastive losses, previously shown to be superior compared to pair-wise losses typically used by contrastive methods. We show on popular benchmarks/backbones that COLES offers favourable accuracy/scalability compared to DeepWalk, GCN, Graph2Gauss, DGI and GRACE baselines.
25 Jun 2025
Representation Learning with Parameterised Quantum Circuits for Advancing Speech Emotion Recognition
Representation Learning with Parameterised Quantum Circuits for Advancing Speech Emotion Recognition
Quantum machine learning (QML) offers a promising avenue for advancing representation learning in complex signal domains. In this study, we investigate the use of parameterised quantum circuits (PQCs) for speech emotion recognition (SER) a challenging task due to the subtle temporal variations and overlapping affective states in vocal signals. We propose a hybrid quantum classical architecture that integrates PQCs into a conventional convolutional neural network (CNN), leveraging quantum properties such as superposition and entanglement to enrich emotional feature representations. Experimental evaluations on three benchmark datasets IEMOCAP, RECOLA, and MSP-IMPROV demonstrate that our hybrid model achieves improved classification performance relative to a purely classical CNN baseline, with over 50% reduction in trainable parameters. This work provides early evidence of the potential for QML to enhance emotion recognition and lays the foundation for future quantum-enabled affective computing systems.
14 Jun 2025
Professor Muhammad Usman's review details the state and prospects of Quantum Machine Learning (QML), particularly Quantum Adversarial Machine Learning (QAML), highlighting its potential to enhance cybersecurity. The review notes that classical adversarial attacks do not effectively transfer to QML models, while QML-generated attacks can successfully fool classical machine learning systems.
24 Jun 2025
FuncVul, developed by Data61, CSIRO, introduces a model for function-level vulnerability detection that leverages code chunks and a fine-tuned GraphCodeBERT. It achieves improved accuracy in pinpointing specific vulnerable segments and detecting multiple vulnerabilities within a single function by utilizing a novel LLM-assisted data generation pipeline.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.