EnsL
07 May 2025
Six-dimensional chiral gauged Einstein-Maxwell supergravity admits a two-parameter rotating dyonic string solution whose near horizon limit is the direct product of AdS3 and a squashed three-sphere S3. For a particular relation between the two parameters, the solution preserves 1/2 supersymmetry. We determine the complete Kaluza-Klein spectrum of the theory around these AdS3 backgrounds. For the supersymmetric backgrounds, the states organize into infinite towers of long and short multiplets of OSp(2|2). In a certain limit of parameters, both the supersymmetric and the non-supersymmetric spectra exhibit scale separation. In the latter case there are five topologically massive vectors and five scalars retaining finite masses with integer conformal dimensions, and in the supersymmetric case there are supersymmetric partners with half integer conformal dimensions, while all other masses diverge.
Diffusion models (DMs) have rapidly emerged as a powerful framework for image generation and restoration. However, existing DMs are primarily trained in a supervised manner by using a large corpus of clean images. This reliance on clean data poses fundamental challenges in many real-world scenarios, where acquiring noise-free data is hard or infeasible, and only noisy and potentially incomplete measurements are available. While some methods can train DMs using noisy data, they are generally effective only when the amount of noise is very mild or when some additional noise-free data is available. In addition, existing methods for training DMs from incomplete measurements require access to multiple complementary acquisition processes, an assumption that poses a significant practical limitation. Here we introduce the first approach for learning DMs for image restoration using only noisy measurement data from a single operator. As a first key contribution, we show that DMs, and more broadly minimum mean squared error denoisers, exhibit a weak form of scale equivariance linking rescaling in signal amplitude to changes in noise intensity. We then leverage this theoretical insight to develop a denoising score-matching strategy that generalizes robustly to noise levels lower than those present in the training data, thereby enabling the learning of DMs from noisy measurements. To further address the challenges of incomplete and noisy data, we integrate our method with equivariant imaging, a complementary self-supervised learning framework that exploits the inherent invariants of imaging problems, to train DMs for image restoration from single-operator measurements that are both incomplete and noisy. We validate the effectiveness of our approach through extensive experiments on image denoising, demosaicing, and inpainting, along with comparisons with the state of the art.
Plug-and-play algorithms constitute a popular framework for solving inverse imaging problems that rely on the implicit definition of an image prior via a denoiser. These algorithms can leverage powerful pre-trained denoisers to solve a wide range of imaging tasks, circumventing the necessity to train models on a per-task basis. Unfortunately, plug-and-play methods often show unstable behaviors, hampering their promise of versatility and leading to suboptimal quality of reconstructed images. In this work, we show that enforcing equivariance to certain groups of transformations (rotations, reflections, and/or translations) on the denoiser strongly improves the stability of the algorithm as well as its reconstruction quality. We provide a theoretical analysis that illustrates the role of equivariance on better performance and stability. We present a simple algorithm that enforces equivariance on any existing denoiser by simply applying a random transformation to the input of the denoiser and the inverse transformation to the output at each iteration of the algorithm. Experiments on multiple imaging modalities and denoising networks show that the equivariant plug-and-play algorithm improves both the reconstruction performance and the stability compared to their non-equivariant counterparts.
18 Sep 2023
Consistent reductions of higher-dimensional (matter-coupled) gravity theories
on spheres have been constructed and classified in an important paper by
Cveti\v{c}, L\"u and Pope. We close a gap in the classification and study the
case when the resulting lower-dimensional theory is two-dimensional. We
construct the consistent reduction of Einstein-Maxwell-dilaton gravity on a
d-sphere Sd to two-dimensional dilaton-gravity coupled to a gauged sigma
model with target space SL(d+1)/SO(d+1). The truncation contains
solutions of type AdS2×Σd where the internal space Σd is
a deformed sphere. In particular, the construction includes the consistent
truncation around the near-horizon geometry of the boosted Kerr string. In
turn, we find that an AdS2×Sd background with the round Sd within
a consistent truncation requires d>3 and an additional cosmological term in
the higher-dimensional theory.
We study the effect of density-assisted hopping on different dimerized lattice geometries, such as bilayers and ladder structures. We show analytically that the density-assisted hopping induces an attractive interaction in the lower (bonding) band of the dimer structure and a repulsion in the upper (anti-bonding) band. Overcoming the onsite repulsion, this can lead to the appearance of superconductivity. The superconductivity depends strongly on the filling, and present a pairing structure more complex than s-wave pairing. Combining numerical and analytical methods such as the matrix product states ansatz, bosonization and perturbative calculations we map out the phase diagram of the two-leg ladder system and identify its superconducting phase. We characterize the transition from the non-density-assisted repulsive regime to the spin-gapped superconducting regime as a Berezinskii-Kosterlitz-Thouless transition.
In this paper, we propose an approach combining diffusion models and inverse problems for the reconstruction of circumstellar disk images. Our method builds upon the Rhapsodie framework for polarimetric imaging, substituting its classical prior with a diffusion model trained on synthetic data. Our formulation explicitly incorporates stellar leakage while efficiently handling missing data and high level noise inherent to high-contrast polarimetric imaging. Experiments show significant improvement over conventional methods within our framework of assumptions, opening new perspectives for studying circumstellar environments.
Proper initialisation strategy is of primary importance to mitigate gradient explosion or vanishing when training neural networks. Yet, the impact of initialisation parameters still lacks a precise theoretical understanding for several well-established architectures. Here, we propose a new initialisation for networks with sinusoidal activation functions such as \texttt{SIREN}, focusing on gradients control, their scaling with network depth, their impact on training and on generalization. To achieve this, we identify a closed-form expression for the initialisation of the parameters, differing from the original \texttt{SIREN} scheme. This expression is derived from fixed points obtained through the convergence of pre-activation distribution and the variance of Jacobian sequences. Controlling both gradients and targeting vanishing pre-activation helps preventing the emergence of inappropriate frequencies during estimation, thereby improving generalization. We further show that this initialisation strongly influences training dynamics through the Neural Tangent Kernel framework (NTK). Finally, we benchmark \texttt{SIREN} with the proposed initialisation against the original scheme and other baselines on function fitting and image reconstruction. The new initialisation consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods across a wide range of reconstruction tasks, including those involving physics-informed neural networks.
02 Jan 2025
We consider the dimensional reduction of N=(2,0) conformal supergravity in six dimensions on a two-torus to N=4 conformal supergravity in four dimensions. At the level of kinematics, the six-dimensional Weyl multiplet is shown to reduce to a mixture of the N=4 Weyl and vector multiplets, which can be reinterpreted as a new off-shell multiplet of N=4 conformal supergravity. Similar multiplets have been constructed in other settings and are referred to as dilaton Weyl multiplets. We derive it here for the first time in a maximally supersymmetric context in four dimensions. Furthermore, we present the non-linear relations between all the six- and four-dimensional bosonic and fermionic fields, that are obtained by comparing the off-shell supersymmetry transformation rules.
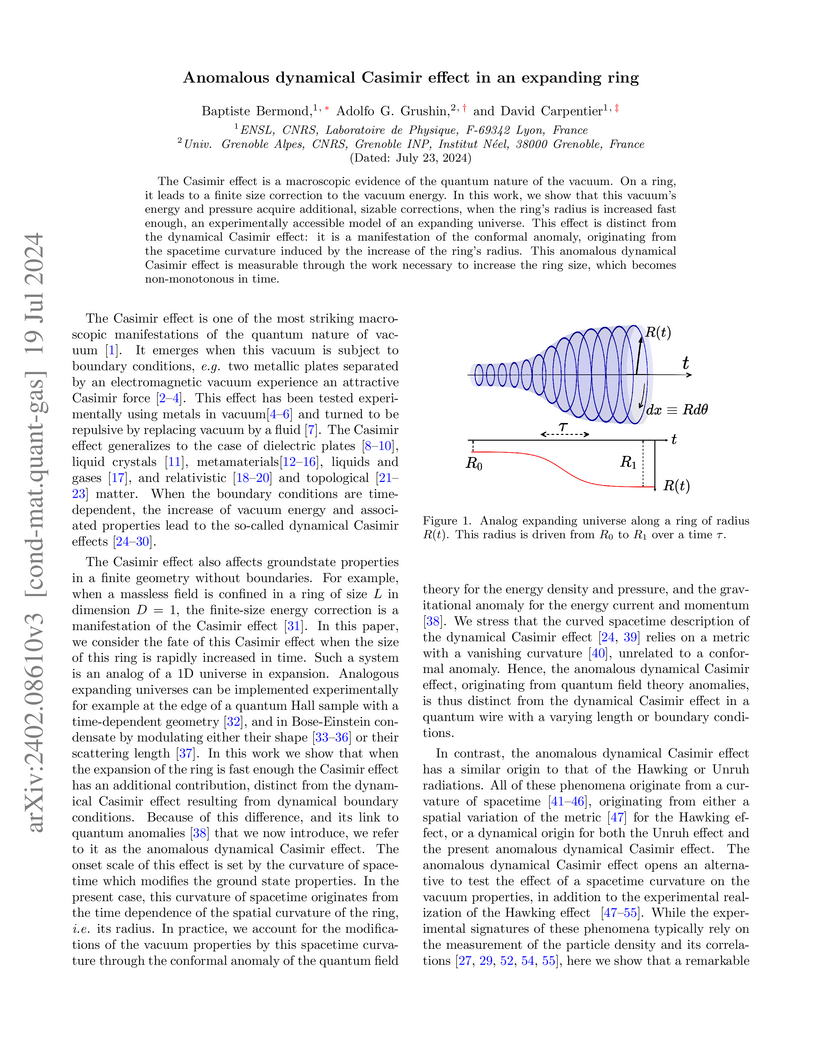
The Casimir effect is a macroscopic evidence of the quantum nature of the
vacuum. On a ring, it leads to a finite size correction to the vacuum energy.
In this work, we show that this vacuum's energy and pressure acquire
additional, sizable corrections, when the ring's radius is increased fast
enough, an experimentally accessible model of an expanding universe. This
effect is distinct from the dynamical Casimir effect: it is a manifestation of
the conformal anomaly, originating from the spacetime curvature induced by the
increase of the ring's radius. This anomalous dynamical Casimir effect is
measurable through the work necessary to increase the ring size, which becomes
non-monotonous in time.
23 Aug 2025
 CNRS
CNRS NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center Space Telescope Science Institute
Space Telescope Science Institute Université Paris-Saclay
Université Paris-Saclay University of Central FloridaNorthern Arizona UniversitySouthwest Research InstituteUniversity of OviedoLowell ObservatoryEnsLInstitut d’Astrophysique SpatialeAssociation of Universities for Research in AstronomyUniversit
Lyon 1
University of Central FloridaNorthern Arizona UniversitySouthwest Research InstituteUniversity of OviedoLowell ObservatoryEnsLInstitut d’Astrophysique SpatialeAssociation of Universities for Research in AstronomyUniversit
Lyon 1We present observations of the mid-sized Kuiper belt objects (KBOs) Salacia-Actaea and Máni, obtained with the Near-Infrared Spectrograph on JWST. The satellite Actaea was fully blended with Salacia at the spatial resolution of the integral field unit, and we extracted the combined spectrum. The 0.7-5.1 μm reflectance spectra of Salacia-Actaea and Máni display prominent water-ice absorption bands at 1.5, 2, 3, and 4-5 μm. The ν3 fundamental vibrational band of carbon dioxide ice at 4.25 μm is present in both spectra. From a quantitative band-depth analysis of the entire current JWST spectroscopic sample of water-ice-rich KBOs, we find strong evidence for a positive covariance between relative water-ice abundance and size, which may indicate the emergent impacts of internal differentiation and cryovolcanic production of surface water ice on mid-sized KBOs. A detailed look at the distribution of 2- and 3-μm band depths suggests additional sources of variability, such as different water-ice grain sizes. In addition, we report an apparent transition in the carbon dioxide band depth at diameters of roughly 300-500 km, with larger objects showing systematically weaker absorptions, although selection effects within the sample do not allow us to confidently distinguish between a size-dependent phenomenon and a correlation with dynamical class. The band shape of the carbon dioxide feature also varies with size: while small KBOs have narrow bands centered at ~4.27 μm, the largest objects have broader, blue-shifted features that may include contributions from carbon dioxide in an irradiated, mixed, and/or layered state.
Multi-level methods are widely used for the solution of large-scale problems, because of their computational advantages and exploitation of the complementarity between the involved sub-problems. After a re-interpretation of multi-level methods from a block-coordinate point of view, we propose a multi-level algorithm for the solution of nonlinear optimization problems and analyze its evaluation complexity. We apply it to the solution of partial differential equations using physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) and show on a few test problems that the approach results in better solutions and significant computational savings
The free energy per lattice site of a quantum spin chain in the thermodynamic limit is determined by a single `dominant' Eigenvalue of an associated quantum transfer matrix in the infinite Trotter number limit. For integrable quantum spin chains, related with solutions of the Yang-Baxter equation, an appropriate choice of the quantum transfer matrix enables to study its spectrum, e.g.\ by means of the algebraic Bethe Ansatz. In its turn, the knowledge of the full spectrum allows one to study its universality properties such as the appearance of a conformal spectrum in the low-temperature regime. More generally, accessing the full spectrum is a necessary step for deriving thermal form factor series representations of the correlation functions of local operators for the spin chain under consideration. These are statements that have been established by physicists on a heuristic level and that are calling for a rigorous mathematical justification. In this work we implement certain aspects of this programme with the example of the XXZ quantum spin chain in the antiferromagnetic massless regime and in the low-temperature limit. We rigorously establish the existence, uniqueness and characterise the form of the solutions to the non-linear integral equations that are equivalent to the Bethe Ansatz equations for the quantum transfer matrix of this model. This allows us to describe that part of the quantum transfer matrix spectrum that is related to the Bethe Ansatz and that does not collapse to zero in the infinite Trotter number limit. Within the considered part of the spectrum we rigorously identify the dominant Eigenvalue and show that those correlations lengths that diverge in the low-temperature limit are given, to the leading order, by the spectrum of the free Boson c=1 conformal field theory. This rigorously establishes a long-standing conjecture present in the physics literature.
Interacting one-dimensional bosons with long range hopping decaying as a power law r−α with distance r are considered with the renormalization group and the self-consistent harmonic approximation. For α≥3, the ground state is always a Tomonaga-Luttinger liquid, whereas for \alpha <3, a ground state with long range order breaking the continuous global gauge symmetry becomes possible for sufficiently weak repulsion. At positive temperature, continuous symmetry breaking becomes restricted to \alpha<2, and for 2<\alpha<3, a Tomonaga-Luttinger liquid with the Tomonaga-Luttinger exponent diverging at low temperature is found.
Understanding extreme events and their probability is key for the study of climate change impacts, risk assessment, adaptation, and the protection of living beings. Forecasting the occurrence probability of extreme heatwaves is a primary challenge for risk assessment and attribution, but also for fundamental studies about processes, dataset and model validation, and climate change studies. In this work we develop a methodology to build forecasting models which are based on convolutional neural networks, trained on extremely long climate model outputs. We demonstrate that neural networks have positive predictive skills, with respect to random climatological forecasts, for the occurrence of long-lasting 14-day heatwaves over France, up to 15 days ahead of time for fast dynamical drivers (500 hPa geopotential height fields), and also at much longer lead times for slow physical drivers (soil moisture). This forecast is made seamlessly in time and space, for fast hemispheric and slow local drivers. We find that the neural network selects extreme heatwaves associated with a North-Hemisphere wavenumber-3 pattern. The main scientific message is that most of the time, training neural networks for predicting extreme heatwaves occurs in a regime of lack of data. We suggest that this is likely to be the case for most other applications to large scale atmosphere and climate phenomena. For instance, using one hundred years-long training sets, a regime of drastic lack of data, leads to severely lower predictive skills and general inability to extract useful information available in the 500 hPa geopotential height field at a hemispheric scale in contrast to the dataset of several thousand years long. We discuss perspectives for dealing with the lack of data regime, for instance rare event simulations and how transfer learning may play a role in this latter task.
Temporal networks are commonly used to model real-life phenomena. When these
phenomena represent interactions and are captured at a fine-grained temporal
resolution, they are modeled as link streams. Community detection is an
essential network analysis task. Although many methods exist for static
networks, and some methods have been developed for temporal networks
represented as sequences of snapshots, few works can handle link streams. This
article introduces the first adaptation of the well-known Modularity quality
function to link streams. Unlike existing methods, it is independent of the
time scale of analysis. After introducing the quality function, and its
relation to existing static and dynamic definitions of Modularity, we show
experimentally its relevance for dynamic community evaluation.
Building on the idea of Tolman and Ehrenfest that heat has weight, Luttinger
established a deep connection between gravitational fields and thermal
transport. However, this relation does not include anomalous quantum
fluctuations that become paramount in strongly curved spacetime. In this work,
we revisit the celebrated Tolman-Ehrenfest and Luttinger relations and show how
to incorporate the quantum energy scales associated with these fluctuations,
captured by gravitational anomalies of quantum field theories. We point out
that such anomalous fluctuations naturally occur in the quantum atmosphere of a
black hole. Our results reveal that analogous fluctuations are also observable
in thermal conductors in flat-space time provided local temperature varies
strongly. As a consequence, we establish that the gravitational anomalies
manifest themselves naturally in non-linear thermal response of a quantum wire.
In addition, we propose a systematic way to identify thermal analogues of black
hole's anomalous quantum fluctuations associated to gravitational anomalies. We
identify their signatures in propagating energy waves following a thermal
quench, as well as in the energy density of heating Floquet states induced by
repeated quenches.
The ubiquitous phenomena of crystallization and melting occur in various
geophysical contexts across many spatial and temporal scales. In particular,
they take place in the iron core of terrestrial planets and moons, profoundly
influencing their dynamics and magnetic field generation. Crystallization and
melting entail intricate multiphase flows, buoyancy effects, and
out-of-equilibrium thermodynamics, posing challenges for theoretical modeling
and numerical simulations. Besides, due to the inaccessible nature of the
planetary deep interior, our understanding relies on indirect data from
seismology, mineral physics, geochemistry, and magnetism. Consequently,
phase-change-driven flows in planetary cores constitute a compelling yet
challenging area of research. This paper provides an overview of the role of
laboratory fluid dynamics experiments in elucidating the solid-liquid phase
change phenomena occurring thousands of kilometers beneath our feet and within
other planetary depths, along with their dynamic repercussions. Drawing
parallel with metallurgy, it navigates through all scales of phase change
dynamics, from microscopic processes (nucleation and crystal growth) to
macroscopic consequences (solid-liquid segregation and large-scale flows). The
review delves into the two primary planetary solidification regimes, top-down
and bottom-up, and elucidates the formation of mushy and/or slurry layers in
the various relevant configurations. Additionally, it outlines remaining
challenges, including insights from ongoing space missions poised to unveil the
diverse planetary regimes.
We show how to use Exceptional Field Theory to compute the full Kaluza-Klein spectra of 10- and 11-dimensional supergravity around deformations of backgrounds of maximal gauged supergravity by scalar modes that do not form part of the consistent truncation. This includes deformations of AdS4×S7 and AdS5×S5 by modes that are not part of the N=8 supermultiplet. As an application, we compute the full Kaluza-Klein spectrum of the N=1 and N=0 squashed S7. In this example, all conformal dimensions are captured by a universal formula in terms of the Casimir operators and additional quantum numbers which organise the spectrum.
14 Nov 2023
Integrable structures arise in general relativity when the spacetime
possesses a pair of commuting Killing vectors admitting 2-spaces orthogonal to
the group orbits. The physical interpretation of such spacetimes depends on the
norm of the Killing vectors. They include stationary axisymmetric spacetimes,
Einstein-Rosen waves with two polarizations, Gowdy models, and colliding plane
gravitational waves.
We review the general formalism of linear systems with variable spectral
parameter, solution generating techniques, and various classes of exact
solutions. In the case of the Einstein-Rosen waves, we also discuss the Poisson
algebra of charges and its quantization.
This is an invited contribution to the 2nd edition of the Encyclopedia of
Mathematical Physics.
The meltwater mixing line (MML) model provides a theoretical prediction of
near-ice water mass properties that is useful to compare with observations. If
oceanographic measurements reported in a temperature-salinity diagram overlap
with the MML prediction, then it is usually concluded that the local dynamics
are dominated by the turbulent mixing of an ambient water mass with nearby
melting ice. While the MML model is consistent with numerous observations, it
is built on an assumption that is difficult to test with field measurements,
especially near the ice boundary, namely that the effective (turbulent and
molecular) salt and temperature diffusivities are equal. In this paper, this
assumption is tested via direct numerical simulations of a canonical model for
externally-forced ice-ocean boundary layers in a uniform ambient. We focus on
the well-mixed regime by considering an ambient temperature close to freezing
and run the simulations until a statistical steady state is reached. The
results validate the assumption of equal effective diffusivities across most of
the boundary layer. Importantly, the validity of the MML model implies a linear
correlation between the mean salinity and temperature profiles normal to the
interface that can be leveraged to construct a reduced ice-ocean boundary layer
model based on a single scalar variable called thermal driving. We demonstrate
that the bulk dynamics predicted by the reduced thermal driving model are in
good agreement with the bulk dynamics predicted by the full
temperature-salinity model. Then, we show how the results from the thermal
driving model can be used to estimate the interfacial heat and salt fluxes, and
the melt rate.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.