Huawei Technologies France
28 Aug 2025
CyberSleuth introduces an autonomous LLM agent for web attack forensics that processes raw packet-level traces and application logs to identify targeted services and exploited CVEs. The agent delivers structured forensic reports and demonstrated up to 90% service identification and 80% CVE detection accuracy on independent incidents involving recent vulnerabilities.
Hierarchical organization is fundamental to biological systems and human
societies, yet artificial intelligence systems often rely on monolithic
architectures that limit adaptability and scalability. Current hierarchical
reinforcement learning (HRL) approaches typically restrict hierarchies to two
levels or require centralized training, which limits their practical
applicability. We introduce TAME Agent Framework (TAG), a framework for
constructing fully decentralized hierarchical multi-agent systems. TAG enables
hierarchies of arbitrary depth through a novel LevelEnv concept, which
abstracts each hierarchy level as the environment for the agents above it. This
approach standardizes information flow between levels while preserving loose
coupling, allowing for seamless integration of diverse agent types. We
demonstrate the effectiveness of TAG by implementing hierarchical architectures
that combine different RL agents across multiple levels, achieving improved
performance over classical multi-agent RL baselines on standard benchmarks. Our
results show that decentralized hierarchical organization enhances both
learning speed and final performance, positioning TAG as a promising direction
for scalable multi-agent systems.
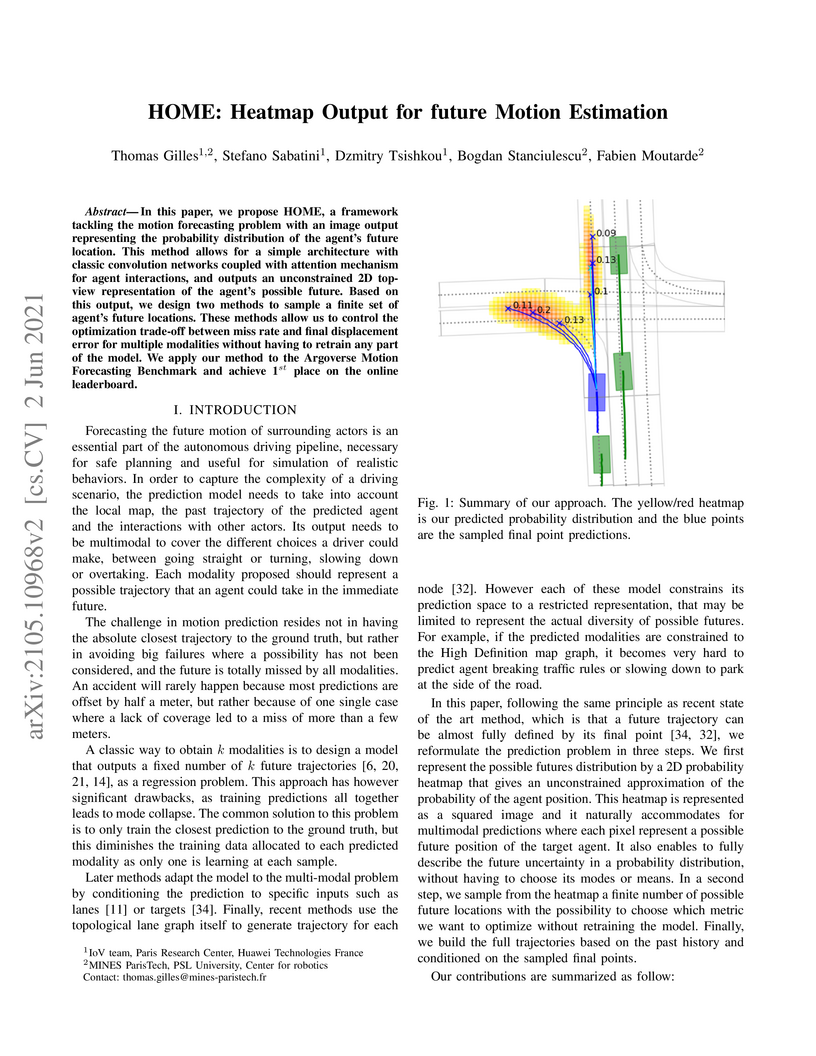
In this paper, we propose HOME, a framework tackling the motion forecasting problem with an image output representing the probability distribution of the agent's future location. This method allows for a simple architecture with classic convolution networks coupled with attention mechanism for agent interactions, and outputs an unconstrained 2D top-view representation of the agent's possible future. Based on this output, we design two methods to sample a finite set of agent's future locations. These methods allow us to control the optimization trade-off between miss rate and final displacement error for multiple modalities without having to retrain any part of the model. We apply our method to the Argoverse Motion Forecasting Benchmark and achieve 1st place on the online leaderboard.
In this paper, we investigate visual-based camera re-localization with neural networks for robotics and autonomous vehicles applications. Our solution is a CNN-based algorithm which predicts camera pose (3D translation and 3D rotation) directly from a single image. It also provides an uncertainty estimate of the pose. Pose and uncertainty are learned together with a single loss function and are fused at test time with an EKF. Furthermore, we propose a new fully convolutional architecture, named CoordiNet, designed to embed some of the scene geometry. Our framework outperforms comparable methods on the largest available benchmark, the Oxford RobotCar dataset, with an average error of 8 meters where previous best was 19 meters. We have also investigated the performance of our method on large scenes for real time (18 fps) vehicle localization. In this setup, structure-based methods require a large database, and we show that our proposal is a reliable alternative, achieving 29cm median error in a 1.9km loop in a busy urban area
This study refines Conditional Mutual Information (CMI)-based generalization bounds by integrating stochastic projection and lossy compression, successfully resolving instances where previous CMI bounds were vacuous for stochastic convex optimization problems. The new framework yields meaningful O(1/√n) bounds for these challenging cases and demonstrates that memorization is not essential for good generalization.
A Multi-step Loss Function for Robust Learning of the Dynamics in Model-based Reinforcement Learning
A Multi-step Loss Function for Robust Learning of the Dynamics in Model-based Reinforcement Learning
In model-based reinforcement learning, most algorithms rely on simulating trajectories from one-step models of the dynamics learned on data. A critical challenge of this approach is the compounding of one-step prediction errors as the length of the trajectory grows. In this paper we tackle this issue by using a multi-step objective to train one-step models. Our objective is a weighted sum of the mean squared error (MSE) loss at various future horizons. We find that this new loss is particularly useful when the data is noisy (additive Gaussian noise in the observations), which is often the case in real-life environments. To support the multi-step loss, first we study its properties in two tractable cases: i) uni-dimensional linear system, and ii) two-parameter non-linear system. Second, we show in a variety of tasks (environments or datasets) that the models learned with this loss achieve a significant improvement in terms of the averaged R2-score on future prediction horizons. Finally, in the pure batch reinforcement learning setting, we demonstrate that one-step models serve as strong baselines when dynamics are deterministic, while multi-step models would be more advantageous in the presence of noise, highlighting the potential of our approach in real-world applications.
Neural network compression has been an increasingly important subject, not
only due to its practical relevance, but also due to its theoretical
implications, as there is an explicit connection between compressibility and
generalization error. Recent studies have shown that the choice of the
hyperparameters of stochastic gradient descent (SGD) can have an effect on the
compressibility of the learned parameter vector. These results, however, rely
on unverifiable assumptions and the resulting theory does not provide a
practical guideline due to its implicitness. In this study, we propose a simple
modification for SGD, such that the outputs of the algorithm will be provably
compressible without making any nontrivial assumptions. We consider a
one-hidden-layer neural network trained with SGD, and show that if we inject
additive heavy-tailed noise to the iterates at each iteration, for any
compression rate, there exists a level of overparametrization such that the
output of the algorithm will be compressible with high probability. To achieve
this result, we make two main technical contributions: (i) we prove a
'propagation of chaos' result for a class of heavy-tailed stochastic
differential equations, and (ii) we derive error estimates for their Euler
discretization. Our experiments suggest that the proposed approach not only
achieves increased compressibility with various models and datasets, but also
leads to robust test performance under pruning, even in more realistic
architectures that lie beyond our theoretical setting.
We address private deep offline reinforcement learning (RL), where the goal
is to train a policy on standard control tasks that is differentially private
(DP) with respect to individual trajectories in the dataset. To achieve this,
we introduce PriMORL, a model-based RL algorithm with formal differential
privacy guarantees. PriMORL first learns an ensemble of trajectory-level DP
models of the environment from offline data. It then optimizes a policy on the
penalized private model, without any further interaction with the system or
access to the dataset. In addition to offering strong theoretical foundations,
we demonstrate empirically that PriMORL enables the training of private RL
agents on offline continuous control tasks with deep function approximations,
whereas current methods are limited to simpler tabular and linear Markov
Decision Processes (MDPs). We furthermore outline the trade-offs involved in
achieving privacy in this setting.
A major challenge in designing efficient statistical supervised learning algorithms is finding representations that perform well not only on available training samples but also on unseen data. While the study of representation learning has spurred much interest, most existing such approaches are heuristic; and very little is known about theoretical generalization guarantees.
In this paper, we establish a compressibility framework that allows us to derive upper bounds on the generalization error of a representation learning algorithm in terms of the "Minimum Description Length" (MDL) of the labels or the latent variables (representations). Rather than the mutual information between the encoder's input and the representation, which is often believed to reflect the algorithm's generalization capability in the related literature but in fact, falls short of doing so, our new bounds involve the "multi-letter" relative entropy between the distribution of the representations (or labels) of the training and test sets and a fixed prior. In particular, these new bounds reflect the structure of the encoder and are not vacuous for deterministic algorithms. Our compressibility approach, which is information-theoretic in nature, builds upon that of Blum-Langford for PAC-MDL bounds and introduces two essential ingredients: block-coding and lossy-compression. The latter allows our approach to subsume the so-called geometrical compressibility as a special case. To the best knowledge of the authors, the established generalization bounds are the first of their kind for Information Bottleneck (IB) type encoders and representation learning. Finally, we partly exploit the theoretical results by introducing a new data-dependent prior. Numerical simulations illustrate the advantages of well-chosen such priors over classical priors used in IB.
This work introduces Differentially Private Policy Gradient (DPPG), a practical and scalable algorithm for private reinforcement learning. DPPG effectively tackles complex deep RL environments, including healthcare simulations and LLM fine-tuning, while maintaining strong performance for relevant privacy levels.
The problem of distributed representation learning is one in which multiple sources of information X1,…,XK are processed separately so as to learn as much information as possible about some ground truth Y. We investigate this problem from information-theoretic grounds, through a generalization of Tishby's centralized Information Bottleneck (IB) method to the distributed setting. Specifically, K encoders, K≥2, compress their observations X1,…,XK separately in a manner such that, collectively, the produced representations preserve as much information as possible about Y. We study both discrete memoryless (DM) and memoryless vector Gaussian data models. For the discrete model, we establish a single-letter characterization of the optimal tradeoff between complexity (or rate) and relevance (or information) for a class of memoryless sources (the observations X1,…,XK being conditionally independent given Y). For the vector Gaussian model, we provide an explicit characterization of the optimal complexity-relevance tradeoff. Furthermore, we develop a variational bound on the complexity-relevance tradeoff which generalizes the evidence lower bound (ELBO) to the distributed setting. We also provide two algorithms that allow to compute this bound: i) a Blahut-Arimoto type iterative algorithm which enables to compute optimal complexity-relevance encoding mappings by iterating over a set of self-consistent equations, and ii) a variational inference type algorithm in which the encoding mappings are parametrized by neural networks and the bound approximated by Markov sampling and optimized with stochastic gradient descent. Numerical results on synthetic and real datasets are provided to support the efficiency of the approaches and algorithms developed in this paper.
Denoising is one of the fundamental steps of the processing pipeline that converts data captured by a camera sensor into a display-ready image or video. It is generally performed early in the pipeline, usually before demosaicking, although studies swapping their order or even conducting them jointly have been proposed. With the advent of deep learning, the quality of denoising algorithms has steadily increased. Even so, modern neural networks still have a hard time adapting to new noise levels and scenes, which is indispensable for real-world applications. With those in mind, we propose a self-similarity-based denoising scheme that weights both a pre- and a post-demosaicking denoiser for Bayer-patterned CFA video data. We show that a balance between the two leads to better image quality, and we empirically find that higher noise levels benefit from a higher influence pre-demosaicking. We also integrate temporal trajectory prefiltering steps before each denoiser, which further improve texture reconstruction. The proposed method only requires an estimation of the noise model at the sensor, accurately adapts to any noise level, and is competitive with the state of the art, making it suitable for real-world videography.
The collection of security-related logs holds the key to understanding attack behaviors and diagnosing vulnerabilities. Still, their analysis remains a daunting challenge. Recently, Language Models (LMs) have demonstrated unmatched potential in understanding natural and programming languages. The question arises whether and how LMs could be also useful for security experts since their logs contain intrinsically confused and obfuscated information. In this paper, we systematically study how to benefit from the state-of-the-art in LM to automatically analyze text-like Unix shell attack logs. We present a thorough design methodology that leads to LogPrécis. It receives as input raw shell sessions and automatically identifies and assigns the attacker tactic to each portion of the session, i.e., unveiling the sequence of the attacker's goals. We demonstrate LogPrécis capability to support the analysis of two large datasets containing about 400,000 unique Unix shell attacks. LogPrécis reduces them into about 3,000 fingerprints, each grouping sessions with the same sequence of tactics. The abstraction it provides lets the analyst better understand attacks, identify fingerprints, detect novelty, link similar attacks, and track families and mutations. Overall, LogPrécis, released as open source, paves the way for better and more responsive defense against cyberattacks.
One of the biggest challenges in operating massive multiple-input multiple-output systems is the acquisition of accurate channel state information at the transmitter. To take up this challenge, time division duplex is more favorable thanks to its channel reciprocity between downlink and uplink. However, while the propagation channel over the air is reciprocal, the radio-frequency front-ends in the transceivers are not. Therefore, calibration is required to compensate the RF hardware asymmetry.
Although various over-the-air calibration methods exist to address the above problem, this paper offers a unified representation of these algorithms, providing a higher level view on the calibration problem, and introduces innovations on calibration methods. We present a novel family of calibration methods, based on antenna grouping, which improve accuracy and speed up the calibration process compared to existing methods. We then provide the Cramér-Rao bound as the performance evaluation benchmark and compare maximum likelihood and least squares estimators. We also differentiate between coherent and non-coherent accumulation of calibration measurements, and point out that enabling non-coherent accumulation allows the training to be spread in time, minimizing impact to the data service. Overall, these results have special value in allowing to design reciprocity calibration techniques that are both accurate and resource-effective.
We investigate the generalization error of statistical learning models in a Federated Learning (FL) setting. Specifically, we study the evolution of the generalization error with the number of communication rounds R between K clients and a parameter server (PS), i.e., the effect on the generalization error of how often the clients' local models are aggregated at PS. In our setup, the more the clients communicate with PS the less data they use for local training in each round, such that the amount of training data per client is identical for distinct values of R. We establish PAC-Bayes and rate-distortion theoretic bounds on the generalization error that account explicitly for the effect of the number of rounds R, in addition to the number of participating devices K and individual datasets size n. The bounds, which apply to a large class of loss functions and learning algorithms, appear to be the first of their kind for the FL setting. Furthermore, we apply our bounds to FL-type Support Vector Machines (FSVM); and derive (more) explicit bounds in this case. In particular, we show that the generalization bound of FSVM increases with R, suggesting that more frequent communication with PS diminishes the generalization power. This implies that the population risk decreases less fast with R than does the empirical risk. Moreover, our bound suggests that the generalization error of FSVM decreases faster than that of centralized learning by a factor of O(log(K)/K). Finally, we provide experimental results obtained using neural networks (ResNet-56) which show evidence that not only may our observations for FSVM hold more generally but also that the population risk may even start to increase beyond some value of R.
Key Performance Indicators (KPI), which are essentially time series data,
have been widely used to indicate the performance of telecom networks. Based on
the given KPIs, a large set of anomaly detection algorithms have been deployed
for detecting the unexpected network incidents. Generally, unsupervised anomaly
detection algorithms gain more popularity than the supervised ones, due to the
fact that labeling KPIs is extremely time- and resource-consuming, and
error-prone. However, those unsupervised anomaly detection algorithms often
suffer from excessive false alarms, especially in the presence of concept
drifts resulting from network re-configurations or maintenance. To tackle this
challenge and improve the overall performance of unsupervised anomaly detection
algorithms, we propose to use active learning to introduce and benefit from the
feedback of operators, who can verify the alarms (both false and true ones) and
label the corresponding KPIs with reasonable effort. Specifically, we develop
three query strategies to select the most informative and representative
samples to label. We also develop an efficient method to update the weights of
Isolation Forest and optimally adjust the decision threshold, so as to
eventually improve the performance of detection model. The experiments with one
public dataset and one proprietary dataset demonstrate that our active learning
empowered anomaly detection pipeline could achieve performance gain, in terms
of F1-score, more than 50% over the baseline algorithm. It also outperforms the
existing active learning based methods by approximately 6%-10%, with
significantly reduced budget (the ratio of samples to be labeled).
29 May 2018
Accurate cross-layer information is very useful to optimize mobile networks
for specific applications. However, providing application-layer information to
lower protocol layers has become very difficult due to the wide adoption of
end-to-end encryption and due to the absence of cross-layer signaling
standards. As an alternative, this paper presents a traffic profiling solution
to passively estimate parameters of HTTP Adaptive Streaming (HAS) applications
at the lower layers. By observing IP packet arrivals, our machine learning
system identifies video flows and detects the state of an HAS client's
play-back buffer in real time. Our experiments with YouTube's mobile client
show that Random Forests achieve very high accuracy even with a strong
variation of link quality. Since this high performance is achieved at IP level
with a small, generic feature set, our approach requires no Deep Packet
Inspection (DPI), comes at low complexity, and does not interfere with
end-to-end encryption. Traffic profiling is, thus, a powerful new tool for
monitoring and managing even encrypted HAS traffic in mobile networks.
Reinforcement learning allows machines to learn from their own experience. Nowadays, it is used in safety-critical applications, such as autonomous driving, despite being vulnerable to attacks carefully crafted to either prevent that the reinforcement learning algorithm learns an effective and reliable policy, or to induce the trained agent to make a wrong decision. The literature about the security of reinforcement learning is rapidly growing, and some surveys have been proposed to shed light on this field. However, their categorizations are insufficient for choosing an appropriate defense given the kind of system at hand. In our survey, we do not only overcome this limitation by considering a different perspective, but we also discuss the applicability of state-of-the-art attacks and defenses when reinforcement learning algorithms are used in the context of autonomous driving.
In this paper, we propose a novel algorithm for video rate adaptation in HTTP
Adaptive Streaming (HAS), based on online learning. The proposed algorithm,
named Learn2Adapt (L2A), is shown to provide a robust rate adaptation strategy
which, unlike most of the state-of-the-art techniques, does not require
parameter tuning, channel model assumptions or application-specific
adjustments. These properties make it very suitable for mobile users, who
typically experience fast variations in channel characteristics. Simulations
show that L2A improves on the overall Quality of Experience (QoE) and in
particular the average streaming rate, a result obtained independently of the
channel and application scenarios.
21 Mar 2019
Polar codes have gained extensive attention during the past few years and
recently they have been selected for the next generation of wireless
communications standards (5G). Successive-cancellation-based (SC-based)
decoders, such as SC list (SCL) and SC flip (SCF), provide a reasonable error
performance for polar codes at the cost of low decoding speed. Fast SC-based
decoders, such as Fast-SSC, Fast-SSCL, and Fast-SSCF, identify the special
constituent codes in a polar code graph off-line, produce a list of operations,
store the list in memory, and feed the list to the decoder to decode the
constituent codes in order efficiently, thus increasing the decoding speed.
However, the list of operations is dependent on the code rate and as the rate
changes, a new list is produced, making fast SC-based decoders not
rate-flexible. In this paper, we propose a completely rate-flexible fast
SC-based decoder by creating the list of operations directly in hardware, with
low implementation complexity. We further propose a hardware architecture
implementing the proposed method and show that the area occupation of the
rate-flexible fast SC-based decoder in this paper is only 38% of the total
area of the memory-based base-line decoder when 5G code rates are supported.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.