IISER Bhopal
04 Jan 2025
The "sight range dilemma" in cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) presents a significant challenge: limited observability hinders team coordination, while extensive sight ranges lead to distracted attention and reduced performance. While communication can potentially address this issue, existing methods often struggle to generalize across different sight ranges, limiting their effectiveness. We propose TACTIC, Task-Agnostic Contrastive pre-Training strategy Inter-Agent Communication. TACTIC is an adaptive communication mechanism that enhances agent coordination even when the sight range during execution is vastly different from that during training. The communication mechanism encodes messages and integrates them with local observations, generating representations grounded in the global state using contrastive learning. By learning to generate and interpret messages that capture important information about the whole environment, TACTIC enables agents to effectively "see" more through communication, regardless of their sight ranges. We comprehensively evaluate TACTIC on the SMACv2 benchmark across various scenarios with broad sight ranges. The results demonstrate that TACTIC consistently outperforms traditional state-of-the-art MARL techniques with and without communication, in terms of generalizing to sight ranges different from those seen in training, particularly in cases of extremely limited or extensive observability.
Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) algorithms face the challenge of
efficient exploration due to the exponential increase in the size of the joint
state-action space. While demonstration-guided learning has proven beneficial
in single-agent settings, its direct applicability to MARL is hindered by the
practical difficulty of obtaining joint expert demonstrations. In this work, we
introduce a novel concept of personalized expert demonstrations, tailored for
each individual agent or, more broadly, each individual type of agent within a
heterogeneous team. These demonstrations solely pertain to single-agent
behaviors and how each agent can achieve personal goals without encompassing
any cooperative elements, thus naively imitating them will not achieve
cooperation due to potential conflicts. To this end, we propose an approach
that selectively utilizes personalized expert demonstrations as guidance and
allows agents to learn to cooperate, namely personalized expert-guided MARL
(PegMARL). This algorithm utilizes two discriminators: the first provides
incentives based on the alignment of individual agent behavior with
demonstrations, and the second regulates incentives based on whether the
behaviors lead to the desired outcome. We evaluate PegMARL using personalized
demonstrations in both discrete and continuous environments. The experimental
results demonstrate that PegMARL outperforms state-of-the-art MARL algorithms
in solving coordinated tasks, achieving strong performance even when provided
with suboptimal personalized demonstrations. We also showcase PegMARL's
capability of leveraging joint demonstrations in the StarCraft scenario and
converging effectively even with demonstrations from non-co-trained policies.
Traffic signboards are vital for road safety and intelligent transportation systems, enabling navigation and autonomous driving. Yet, recognizing traffic signs at night remains challenging due to visual noise and scarcity of public nighttime datasets. Despite advances in vision architectures, existing methods struggle with robustness under low illumination and fail to leverage complementary mutlimodal cues effectively. To overcome these limitations, firstly, we introduce INTSD, a large-scale dataset comprising street-level night-time images of traffic signboards collected across diverse regions of India. The dataset spans 41 traffic signboard classes captured under varying lighting and weather conditions, providing a comprehensive benchmark for both detection and classification tasks. To benchmark INTSD for night-time sign recognition, we conduct extensive evaluations using state-of-the-art detection and classification models. Secondly, we propose LENS-Net, which integrates an adaptive image enhancement detector for joint illumination correction and sign localization, followed by a structured multimodal CLIP-GCNN classifier that leverages cross-modal attention and graph-based reasoning for robust and semantically consistent recognition. Our method surpasses existing frameworks, with ablation studies confirming the effectiveness of its key components. The dataset and code for LENS-Net is publicly available for research.
Off-road image semantic segmentation is challenging due to the presence of
uneven terrains, unstructured class boundaries, irregular features and strong
textures. These aspects affect the perception of the vehicle from which the
information is used for path planning. Current off-road datasets exhibit
difficulties like class imbalance and understanding of varying environmental
topography. To overcome these issues we propose a framework for off-road
semantic segmentation called as OFFSEG that involves (i) a pooled class
semantic segmentation with four classes (sky, traversable region,
non-traversable region and obstacle) using state-of-the-art deep learning
architectures (ii) a colour segmentation methodology to segment out specific
sub-classes (grass, puddle, dirt, gravel, etc.) from the traversable region for
better scene understanding. The evaluation of the framework is carried out on
two off-road driving datasets, namely, RELLIS-3D and RUGD. We have also tested
proposed framework in IISERB campus frames. The results show that OFFSEG
achieves good performance and also provides detailed information on the
traversable region.
Unstructured urban environments present unique challenges for scene understanding and generalization due to their complex and diverse layouts. We introduce SynthGenNet, a self-supervised student-teacher architecture designed to enable robust test-time domain generalization using synthetic multi-source imagery. Our contributions include the novel ClassMix++ algorithm, which blends labeled data from various synthetic sources while maintaining semantic integrity, enhancing model adaptability. We further employ Grounded Mask Consistency Loss (GMC), which leverages source ground truth to improve cross-domain prediction consistency and feature alignment. The Pseudo-Label Guided Contrastive Learning (PLGCL) mechanism is integrated into the student network to facilitate domain-invariant feature learning through iterative knowledge distillation from the teacher network. This self-supervised strategy improves prediction accuracy, addresses real-world variability, bridges the sim-to-real domain gap, and reliance on labeled target data, even in complex urban areas. Outcomes show our model outperforms the state-of-the-art (relying on single source) by achieving 50% Mean Intersection-Over-Union (mIoU) value on real-world datasets like Indian Driving Dataset (IDD).
Mental health plays a crucial role in the overall well-being of an individual. In recent years, digital platforms have been increasingly used to expand mental health and emotional support. However, there are persistent challenges related to limited user accessibility, internet connectivity, and data privacy, which highlight the need for an offline, smartphone-based solution. To address these challenges, we propose EmoSApp (Emotional Support App): an entirely offline, smartphone-based conversational app designed for mental health and emotional support. The system leverages Large Language Models (LLMs), specifically fine-tuned, quantized and deployed using Torchtune and Executorch for resource-constrained devices, allowing all inferences to occur on the smartphone. To equip EmoSApp with robust domain expertise, we fine-tuned the LLaMA-3.2-1B-Instruct model on our custom curated ``Knowledge dataset'' of 14,582 mental-health QA pairs, along with the multi-turn conversational data.
Through qualitative human evaluation with the student population, we demonstrate that EmoSApp has the ability to respond coherently, empathetically, maintain interactive dialogue, and provide relevant suggestions to user's mental health problems. Additionally, quantitative evaluations on nine standard commonsense and reasoning benchmarks demonstrate the efficacy of our fine-tuned, quantized model in low-resource settings. By prioritizing on-device deployment and specialized domain adaptation, EmoSApp serves as a blueprint for future innovations in portable, secure, and highly tailored AI-driven mental health solutions.
10 Feb 2025
With the growing demand for efficient logistics and warehouse management,
unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are emerging as a valuable complement to
automated guided vehicles (AGVs). UAVs enhance efficiency by navigating dense
environments and operating at varying altitudes. However, their limited flight
time, battery life, and payload capacity necessitate a supporting ground
station. To address these challenges, we propose HetSwarm, a heterogeneous
multi-robot system that combines a UAV and a mobile ground robot for
collaborative navigation in cluttered and dynamic conditions. Our approach
employs an artificial potential field (APF)-based path planner for the UAV,
allowing it to dynamically adjust its trajectory in real time. The ground robot
follows this path while maintaining connectivity through impedance links,
ensuring stable coordination. Additionally, the ground robot establishes
temporal impedance links with low-height ground obstacles to avoid local
collisions, as these obstacles do not interfere with the UAV's flight.
Experimental validation of HetSwarm in diverse environmental conditions
demonstrated a 90% success rate across 30 test cases. The ground robot
exhibited an average deviation of 45 cm near obstacles, confirming effective
collision avoidance. Extensive simulations in the Gym PyBullet environment
further validated the robustness of our system for real-world applications,
demonstrating its potential for dynamic, real-time task execution in cluttered
environments.
Improving mental health support in developing countries is a pressing need. One potential solution is the development of scalable, automated systems to conduct diagnostic screenings, which could help alleviate the burden on mental health professionals. In this work, we evaluate several state-of-the-art Large Language Models (LLMs), with and without fine-tuning, on our custom dataset for generating concise summaries from mental state examinations. We rigorously evaluate four different models for summary generation using established ROUGE metrics and input from human evaluators. The results highlight that our top-performing fine-tuned model outperforms existing models, achieving ROUGE-1 and ROUGE-L values of 0.810 and 0.764, respectively. Furthermore, we assessed the fine-tuned model's generalizability on a publicly available D4 dataset, and the outcomes were promising, indicating its potential applicability beyond our custom dataset.
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan Carnegie Mellon UniversityTata Institute of Fundamental ResearchIndian Institute of SciencePhysical Research LaboratoryHomi Bhabha National Institute
Carnegie Mellon UniversityTata Institute of Fundamental ResearchIndian Institute of SciencePhysical Research LaboratoryHomi Bhabha National Institute University of SydneyMax-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik (Albert-Einstein-Institut)Leibniz Universität HannoverUniversity of DelhiThe Institute of Mathematical SciencesClemson UniversityIndian Institute of Technology RoorkeeMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomieUniversity of Cape TownIIT HyderabadGLA UniversityCHRIST (Deemed to be University)Raman Research InstituteIndian Institute of Space Science and TechnologyIndian Institute of Technology IndoreKumamoto UniversityCochin University of Science and TechnologyNational Centre for Radio AstrophysicsIISER BhopalIndian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) MohaliNational Institute of Technology AgartalaMizusawa VLBI ObservatoryKannur UniversityInternational Research Organization for Advanced Science and TechnologyGovernment Brennen College
University of SydneyMax-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik (Albert-Einstein-Institut)Leibniz Universität HannoverUniversity of DelhiThe Institute of Mathematical SciencesClemson UniversityIndian Institute of Technology RoorkeeMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomieUniversity of Cape TownIIT HyderabadGLA UniversityCHRIST (Deemed to be University)Raman Research InstituteIndian Institute of Space Science and TechnologyIndian Institute of Technology IndoreKumamoto UniversityCochin University of Science and TechnologyNational Centre for Radio AstrophysicsIISER BhopalIndian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) MohaliNational Institute of Technology AgartalaMizusawa VLBI ObservatoryKannur UniversityInternational Research Organization for Advanced Science and TechnologyGovernment Brennen College
 Carnegie Mellon UniversityTata Institute of Fundamental ResearchIndian Institute of SciencePhysical Research LaboratoryHomi Bhabha National Institute
Carnegie Mellon UniversityTata Institute of Fundamental ResearchIndian Institute of SciencePhysical Research LaboratoryHomi Bhabha National Institute University of SydneyMax-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik (Albert-Einstein-Institut)Leibniz Universität HannoverUniversity of DelhiThe Institute of Mathematical SciencesClemson UniversityIndian Institute of Technology RoorkeeMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomieUniversity of Cape TownIIT HyderabadGLA UniversityCHRIST (Deemed to be University)Raman Research InstituteIndian Institute of Space Science and TechnologyIndian Institute of Technology IndoreKumamoto UniversityCochin University of Science and TechnologyNational Centre for Radio AstrophysicsIISER BhopalIndian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) MohaliNational Institute of Technology AgartalaMizusawa VLBI ObservatoryKannur UniversityInternational Research Organization for Advanced Science and TechnologyGovernment Brennen College
University of SydneyMax-Planck-Institut für Gravitationsphysik (Albert-Einstein-Institut)Leibniz Universität HannoverUniversity of DelhiThe Institute of Mathematical SciencesClemson UniversityIndian Institute of Technology RoorkeeMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomieUniversity of Cape TownIIT HyderabadGLA UniversityCHRIST (Deemed to be University)Raman Research InstituteIndian Institute of Space Science and TechnologyIndian Institute of Technology IndoreKumamoto UniversityCochin University of Science and TechnologyNational Centre for Radio AstrophysicsIISER BhopalIndian Institute of Science Education and Research (IISER) MohaliNational Institute of Technology AgartalaMizusawa VLBI ObservatoryKannur UniversityInternational Research Organization for Advanced Science and TechnologyGovernment Brennen CollegeThe Indian Pulsar Timing Array (InPTA) employs unique features of the upgraded Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (uGMRT) to monitor dozens of the International Pulsar Timing Array (IPTA) millisecond pulsars (MSPs), simultaneously in the 300-500 MHz and the 1260-1460 MHz bands. This dual-band approach ensures that any frequency-dependent delays are accurately characterized, significantly improving the timing precision for pulsar observations, which is crucial for pulsar timing arrays. We present details of InPTA's second data release that involves 7 yrs of data on 27 IPTA MSPs. This includes sub-banded Times of Arrival (ToAs), Dispersion Measures (DM), and initial timing ephemerides for our MSPs. A part of this dataset, originally released in InPTA's first data release, is being incorporated into IPTA's third data release which is expected to detect and characterize nanohertz gravitational waves in the coming years. The entire dataset is reprocessed in this second data release providing some of the highest precision DM estimates so far and interesting solar wind related DM variations in some pulsars. This is likely to characterize the noise introduced by the dynamic inter-stellar ionised medium much better than the previous release thereby increasing sensitivity to any future gravitational wave search.
09 Jul 2025
National Astronomical Observatory of Japan University of Manchester
University of Manchester University of Chicago
University of Chicago University of Oxford
University of Oxford Northwestern UniversityThe University of SydneyObservatoire de ParisMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomiePontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso
Northwestern UniversityThe University of SydneyObservatoire de ParisMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomiePontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso University of California, Santa CruzARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav)ASTRON, the Netherlands Institute for Radio AstronomyIISER BhopalCentre National de la Recherche ScientifiqueKavli IPMUUniversity of OrléansCentre National d’Études SpatialesUniversity of Dodoma
University of California, Santa CruzARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav)ASTRON, the Netherlands Institute for Radio AstronomyIISER BhopalCentre National de la Recherche ScientifiqueKavli IPMUUniversity of OrléansCentre National d’Études SpatialesUniversity of Dodoma
 University of Manchester
University of Manchester University of Chicago
University of Chicago University of Oxford
University of Oxford Northwestern UniversityThe University of SydneyObservatoire de ParisMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomiePontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso
Northwestern UniversityThe University of SydneyObservatoire de ParisMax-Planck-Institut für RadioastronomiePontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso University of California, Santa CruzARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav)ASTRON, the Netherlands Institute for Radio AstronomyIISER BhopalCentre National de la Recherche ScientifiqueKavli IPMUUniversity of OrléansCentre National d’Études SpatialesUniversity of Dodoma
University of California, Santa CruzARC Centre of Excellence for Gravitational Wave Discovery (OzGrav)ASTRON, the Netherlands Institute for Radio AstronomyIISER BhopalCentre National de la Recherche ScientifiqueKavli IPMUUniversity of OrléansCentre National d’Études SpatialesUniversity of DodomaAccurately localising fast radio bursts (FRBs) is essential for understanding their birth environments and for their use as cosmological probes. Recent advances in radio interferometry, particularly with MeerKAT, have enabled the localisation of individual bursts with arcsecond precision. In this work, we present the localisation of 15 apparently non-repeating FRBs detected with MeerKAT. Two of the FRBs, discovered in 2022, were localised in 8 second images from the projects which MeerTRAP was commensal to, while eight were localised using the transient buffer pipeline, and another one through SeeKAT, all with arcsecond precision. Four additional FRBs lacked TB triggers and sufficient signal, limiting their localisation only to arcminute precision. For nine of the FRBs in our sample, we identify host galaxies with greater than 90% confidence, while two FRBs have ambiguous associations with two host galaxy candidates. We measured spectroscopic redshifts for six host galaxies, ranging from 0.33 to 0.85, demonstrating MeerKAT's sensitivity to high redshift FRBs. For galaxies with sufficient photometric coverage, we performed spectral energy those of known FRB hosts. This work represents one of the largest uniform samples of well-localised distant FRBs to date, laying the groundwork for using MeerKAT FRBs as cosmological probes and understand how FRB hosts evolve at high redshift.
Access to expert coaching is essential for developing technique in sports, yet economic barriers often place it out of reach for many enthusiasts. To bridge this gap, we introduce Poze, an innovative video processing framework that provides feedback on human motion, emulating the insights of a professional coach. Poze combines pose estimation with sequence comparison and is optimized to function effectively with minimal data. Poze surpasses state-of-the-art vision-language models in video question-answering frameworks, achieving 70% and 196% increase in accuracy over GPT4V and LLaVAv1.6 7b, respectively.
Cost-maps are used by robotic vehicles to plan collision-free paths. The cost
associated with each cell in the map represents the sensed environment
information which is often determined manually after several trial-and-error
efforts. In off-road environments, due to the presence of several types of
features, it is challenging to handcraft the cost values associated with each
feature. Moreover, different handcrafted cost values can lead to different
paths for the same environment which is not desirable. In this paper, we
address the problem of learning the cost-map values from the sensed environment
for robust vehicle path planning. We propose a novel framework called as CAMEL
using deep learning approach that learns the parameters through demonstrations
yielding an adaptive and robust cost-map for path planning. CAMEL has been
trained on multi-modal datasets such as RELLIS-3D. The evaluation of CAMEL is
carried out on an off-road scene simulator (MAVS) and on field data from
IISER-B campus. We also perform realworld implementation of CAMEL on a ground
rover. The results shows flexible and robust motion of the vehicle without
collisions in unstructured terrains.
Non-invasive temperature monitoring of individuals plays a crucial role in identifying and isolating symptomatic individuals. Temperature monitoring becomes particularly vital in settings characterized by close human proximity, often referred to as dense settings. However, existing research on non-invasive temperature estimation using thermal cameras has predominantly focused on sparse settings. Unfortunately, the risk of disease transmission is significantly higher in dense settings like movie theaters or classrooms. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop robust temperature estimation methods tailored explicitly for dense settings.
Our study proposes a non-invasive temperature estimation system that combines a thermal camera with an edge device. Our system employs YOLO models for face detection and utilizes a regression framework for temperature estimation. We evaluated the system on a diverse dataset collected in dense and sparse settings. Our proposed face detection model achieves an impressive mAP score of over 84 in both in-dataset and cross-dataset evaluations. Furthermore, the regression framework demonstrates remarkable performance with a mean square error of 0.18∘C and an impressive R2 score of 0.96. Our experiments' results highlight the developed system's effectiveness, positioning it as a promising solution for continuous temperature monitoring in real-world applications. With this paper, we release our dataset and programming code publicly.
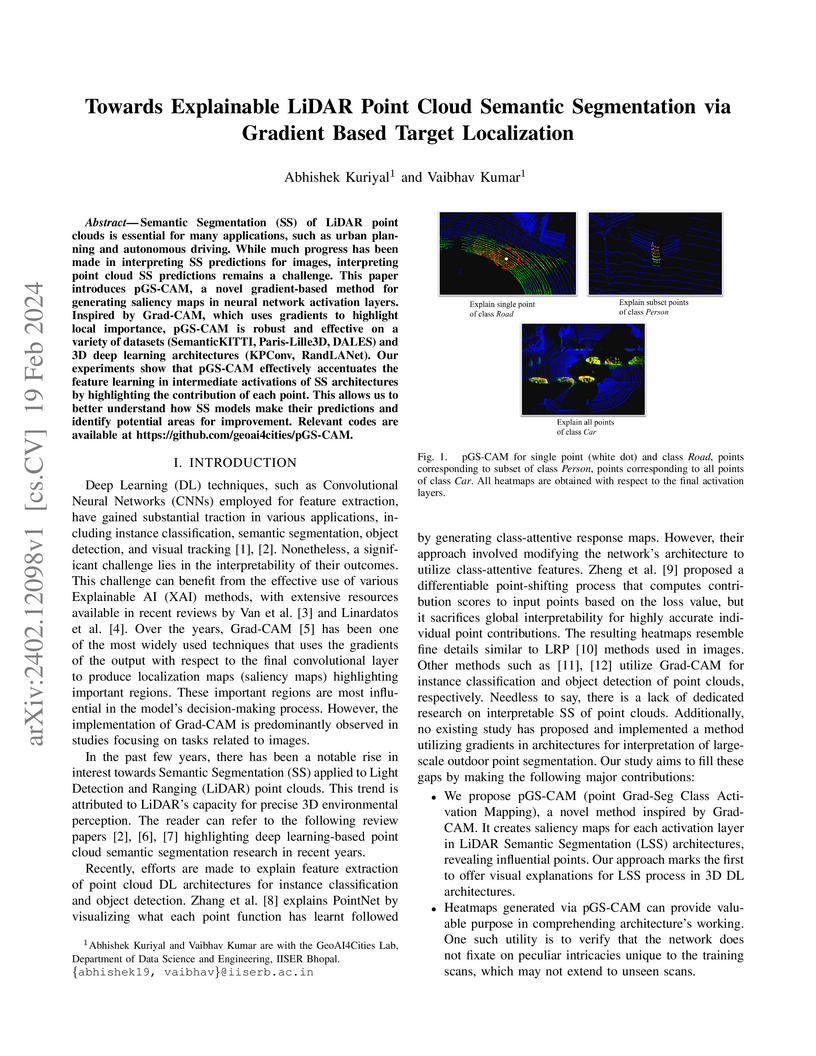
Semantic Segmentation (SS) of LiDAR point clouds is essential for many applications, such as urban planning and autonomous driving. While much progress has been made in interpreting SS predictions for images, interpreting point cloud SS predictions remains a challenge. This paper introduces pGS-CAM, a novel gradient-based method for generating saliency maps in neural network activation layers. Inspired by Grad-CAM, which uses gradients to highlight local importance, pGS-CAM is robust and effective on a variety of datasets (SemanticKITTI, Paris-Lille3D, DALES) and 3D deep learning architectures (KPConv, RandLANet). Our experiments show that pGS-CAM effectively accentuates the feature learning in intermediate activations of SS architectures by highlighting the contribution of each point. This allows us to better understand how SS models make their predictions and identify potential areas for improvement. Relevant codes are available at this https URL.
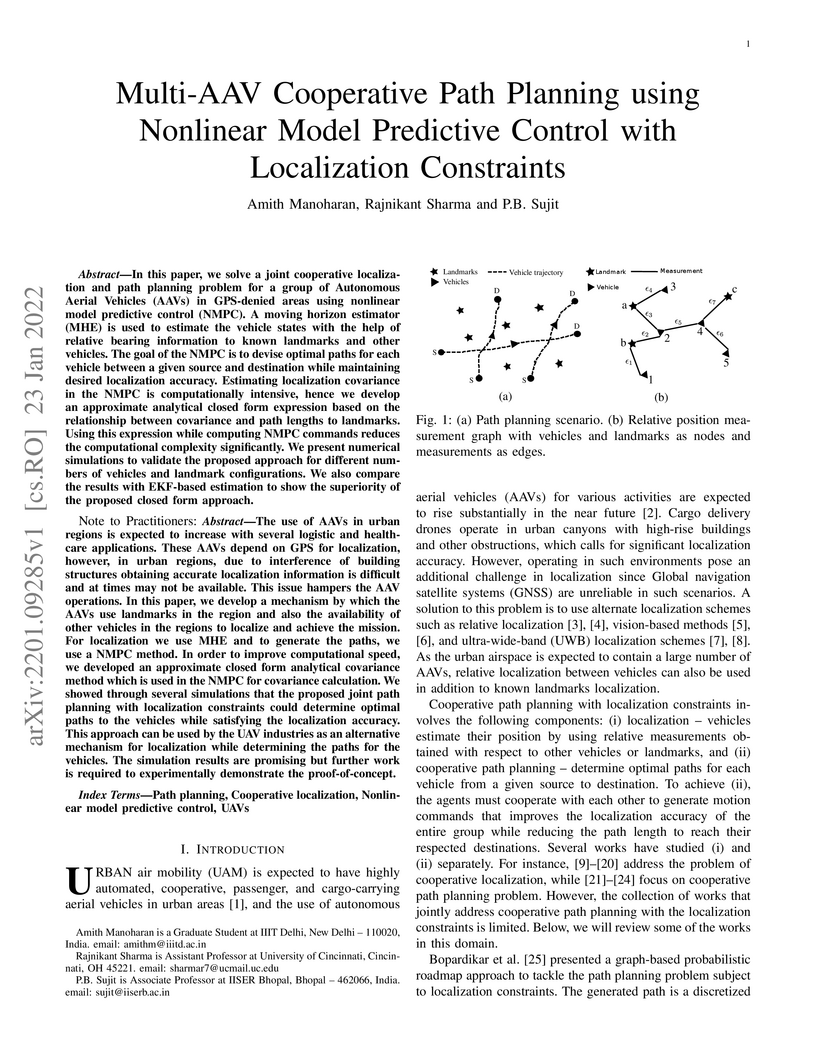
In this paper, we solve a joint cooperative localization and path planning
problem for a group of Autonomous Aerial Vehicles (AAVs) in GPS-denied areas
using nonlinear model predictive control (NMPC). A moving horizon estimator
(MHE) is used to estimate the vehicle states with the help of relative bearing
information to known landmarks and other vehicles. The goal of the NMPC is to
devise optimal paths for each vehicle between a given source and destination
while maintaining desired localization accuracy. Estimating localization
covariance in the NMPC is computationally intensive, hence we develop an
approximate analytical closed form expression based on the relationship between
covariance and path lengths to landmarks. Using this expression while computing
NMPC commands reduces the computational complexity significantly. We present
numerical simulations to validate the proposed approach for different numbers
of vehicles and landmark configurations. We also compare the results with
EKF-based estimation to show the superiority of the proposed closed form
approach.
We propose a novel deep neural network (DNN) based approximation architecture to learn estimates of measurements. We detail an algorithm that enables training of the DNN. The DNN estimator only uses measurements, if and when they are received over a communication network. The measurements are communicated over a network as packets, at a rate unknown to the estimator. Packets may suffer drops and need retransmission. They may suffer waiting delays as they traverse a network path.
Works on estimation often assume knowledge of the dynamic model of the measured system, which may not be available in practice. The DNN estimator doesn't assume knowledge of the dynamic system model or the communication network. It doesn't require a history of measurements, often used by other works.
The DNN estimator results in significantly smaller average estimation error than the commonly used Time-varying Kalman Filter and the Unscented Kalman Filter, in simulations of linear and nonlinear dynamic systems. The DNN need not be trained separately for different communications network settings. It is robust to errors in estimation of network delays that occur due to imperfect time synchronization between the measurement source and the estimator. Last but not the least, our simulations shed light on the rate of updates that result in low estimation error.
In machine learning applications, gradual data ingress is common, especially
in audio processing where incremental learning is vital for real-time
analytics. Few-shot class-incremental learning addresses challenges arising
from limited incoming data. Existing methods often integrate additional
trainable components or rely on a fixed embedding extractor post-training on
base sessions to mitigate concerns related to catastrophic forgetting and the
dangers of model overfitting. However, using cross-entropy loss alone during
base session training is suboptimal for audio data. To address this, we propose
incorporating supervised contrastive learning to refine the representation
space, enhancing discriminative power and leading to better generalization
since it facilitates seamless integration of incremental classes, upon arrival.
Experimental results on NSynth and LibriSpeech datasets with 100 classes, as
well as ESC dataset with 50 and 10 classes, demonstrate state-of-the-art
performance.
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD) is a widespread mental health condition, yet
its lack of objective markers hinders timely detection and intervention. While
previous research has focused on behavioral and non-verbal markers of SAD in
structured activities (e.g., speeches or interviews), these settings fail to
replicate real-world, unstructured social interactions fully. Identifying
non-verbal markers in naturalistic, unstaged environments is essential for
developing ubiquitous and non-intrusive monitoring solutions. To address this
gap, we present AnxietyFaceTrack, a study leveraging facial video analysis to
detect anxiety in unstaged social settings. A cohort of 91 participants engaged
in a social setting with unfamiliar individuals and their facial videos were
recorded using a low-cost smartphone camera. We examined facial features,
including eye movements, head position, facial landmarks, and facial action
units, and used self-reported survey data to establish ground truth for
multiclass (anxious, neutral, non-anxious) and binary (e.g., anxious vs.
neutral) classifications. Our results demonstrate that a Random Forest
classifier trained on the top 20% of features achieved the highest accuracy of
91.0% for multiclass classification and an average accuracy of 92.33% across
binary classifications. Notably, head position and facial landmarks yielded the
best performance for individual facial regions, achieving 85.0% and 88.0%
accuracy, respectively, in multiclass classification, and 89.66% and 91.0%
accuracy, respectively, across binary classifications. This study introduces a
non-intrusive, cost-effective solution that can be seamlessly integrated into
everyday smartphones for continuous anxiety monitoring, offering a promising
pathway for early detection and intervention.
Majorana Bound States (MBS) have emerged as promising candidates for robust quantum computing due to their non-Abelian statistics and topological protection. In this study, we focus on the dynamical transport of MBS in the semiconductor-superconductor (SM-SC) heterostructure via the piano key-type setup, wherein each of the keys of the wire can be tuned from topological to trivial phases. We focus on the transport of MBS under noisy conditions and evaluate the feasibility for realistic scenarios. The central emphasis of our work lies in using both numerical and analytical techniques to understand the effect of noise in inducing diabatic errors during transport and to establish scaling laws that relate these errors to the drive time. To achieve this, we derive an effective model that captures the scaling behavior in both noise-free and noisy scenarios, providing a unified framework for analyzing the transport dynamics. We investigate the optimal number of keys for both noisy and noiseless scenarios. Additionally, we explore the effects of disorder on transport dynamics, highlighting its impact on error scaling and robustness.
09 Apr 2025
For better learning, large datasets are often split into small batches and
fed sequentially to the predictive model. In this paper, we study such batch
decompositions from a probabilistic perspective. We assume that data points
(possibly corrupted) are drawn independently from a given space and define a
concept of similarity between two data points. We then consider decompositions
that restrict the amount of similarity within each batch and obtain high
probability bounds for the minimum size. We demonstrate an inherent tradeoff
between relaxing the similarity constraint and the overall size and also use
martingale methods to obtain bounds for the maximum size of data subsets with a
given similarity.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.