Lancaster University
We report the results of radioactivity assays and heat leak calculations for
a range of common cryogenic materials, considered for use in the QUEST-DMC
superfluid 3He dark matter detector. The bolometer, instrumented with
nanomechanical resonators, will be sensitive to energy deposits from dark
matter interactions. Events from radioactive decays and cosmic rays constitute
a significant background and must be precisely modelled, using a combination of
material screening and Monte Carlo simulations. However, the results presented
here are of wider interest for experiments and quantum devices sensitive to
minute heat leaks and spurious events, thus we present heat leak per unit mass
or surface area for every material studied. This can inform material choices
for other experiments, especially if underground operation is considered where
the radiogenic backgrounds will dominate even at shallow depths.
This survey offers a comprehensive review of how Reinforcement Learning (RL) is applied across the entire lifecycle of Large Language Models, from pre-training to alignment and reinforced reasoning. It particularly emphasizes the role of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) in advancing LLM reasoning capabilities and compiles key datasets, benchmarks, and open-source tools for the field.
25 Aug 2025
Researchers from multiple international institutions propose a unified methodological taxonomy and formal language for LLM-based agentic reasoning frameworks, systematically surveying their progress, application scenarios, and evaluation strategies across diverse domains like scientific research and healthcare. This work provides a structured view of single-agent, tool-based, and multi-agent approaches, clarifying the rapidly evolving landscape.
This paper provides a concise yet comprehensive overview of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), detailing their architecture, underlying principles, and practical design guidelines for image recognition tasks.
A comprehensive survey details the evolution of deep learning-based object pose estimation, covering instance-level, category-level, and unseen object methods. It analyzes current advancements, methodologies, and persistent challenges, while outlining future research directions to enhance generalization and robustness.
POPEN enhances LVLM-based reasoning segmentation by integrating human preferences into both training and inference stages, leading to reduced textual hallucinations and more precise segmentation masks. This framework achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple datasets by optimizing for text fidelity and segmentation accuracy.
Sarcasm is a rhetorical device that is used to convey the opposite of the literal meaning of an utterance. Sarcasm is widely used on social media and other forms of computer-mediated communication motivating the use of computational models to identify it automatically. While the clear majority of approaches to sarcasm detection have been carried out on text only, sarcasm detection often requires additional information present in tonality, facial expression, and contextual images. This has led to the introduction of multimodal models, opening the possibility to detect sarcasm in multiple modalities such as audio, images, text, and video. In this paper, we present the first comprehensive survey on multimodal sarcasm detection - henceforth MSD - to date. We survey papers published between 2018 and 2023 on the topic, and discuss the models and datasets used for this task. We also present future research directions in MSD.
Reasoning over sports videos for question answering is an important task with
numerous applications, such as player training and information retrieval.
However, this task has not been explored due to the lack of relevant datasets
and the challenging nature it presents. Most datasets for video question
answering (VideoQA) focus mainly on general and coarse-grained understanding of
daily-life videos, which is not applicable to sports scenarios requiring
professional action understanding and fine-grained motion analysis. In this
paper, we introduce the first dataset, named Sports-QA, specifically designed
for the sports VideoQA task. The Sports-QA dataset includes various types of
questions, such as descriptions, chronologies, causalities, and counterfactual
conditions, covering multiple sports. Furthermore, to address the
characteristics of the sports VideoQA task, we propose a new Auto-Focus
Transformer (AFT) capable of automatically focusing on particular scales of
temporal information for question answering. We conduct extensive experiments
on Sports-QA, including baseline studies and the evaluation of different
methods. The results demonstrate that our AFT achieves state-of-the-art
performance.
 Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind University of AmsterdamUniversity of Oslo
University of AmsterdamUniversity of Oslo University of CambridgeFacebook
University of CambridgeFacebook Imperial College London
Imperial College London New York University
New York University University of OxfordLMU Munich
University of OxfordLMU Munich University of Bristol
University of Bristol RIKENLancaster UniversityVector Institute
RIKENLancaster UniversityVector Institute Purdue UniversityThe University of Manchester
Purdue UniversityThe University of Manchester Duke University
Duke University Technical University of Munich
Technical University of Munich KAUSTUniversity of TübingenUC IrvineSpotifyHelmholtz AIBroad InstituteCentre Inria de l’Université Grenoble AlpesMax Planck ETH
KAUSTUniversity of TübingenUC IrvineSpotifyHelmholtz AIBroad InstituteCentre Inria de l’Université Grenoble AlpesMax Planck ETHA consortium of 29 researchers from prominent academic and industry institutions argues that Bayesian Deep Learning is crucial for the future of large-scale AI. They contend that BDL inherently quantifies uncertainty, improves data efficiency and adaptability, and enhances model robustness, addressing key limitations of current deep learning models and facilitating more trustworthy AI systems.
Semantic segmentation of remotely sensed urban scene images is required in a wide range of practical applications, such as land cover mapping, urban change detection, environmental protection, and economic this http URL by rapid developments in deep learning technologies, the convolutional neural network (CNN) has dominated semantic segmentation for many years. CNN adopts hierarchical feature representation, demonstrating strong capabilities for local information extraction. However, the local property of the convolution layer limits the network from capturing the global context. Recently, as a hot topic in the domain of computer vision, Transformer has demonstrated its great potential in global information modelling, boosting many vision-related tasks such as image classification, object detection, and particularly semantic segmentation. In this paper, we propose a Transformer-based decoder and construct a UNet-like Transformer (UNetFormer) for real-time urban scene segmentation. For efficient segmentation, the UNetFormer selects the lightweight ResNet18 as the encoder and develops an efficient global-local attention mechanism to model both global and local information in the decoder. Extensive experiments reveal that our method not only runs faster but also produces higher accuracy compared with state-of-the-art lightweight models. Specifically, the proposed UNetFormer achieved 67.8% and 52.4% mIoU on the UAVid and LoveDA datasets, respectively, while the inference speed can achieve up to 322.4 FPS with a 512x512 input on a single NVIDIA GTX 3090 GPU. In further exploration, the proposed Transformer-based decoder combined with a Swin Transformer encoder also achieves the state-of-the-art result (91.3% F1 and 84.1% mIoU) on the Vaihingen dataset. The source code will be freely available at this https URL.
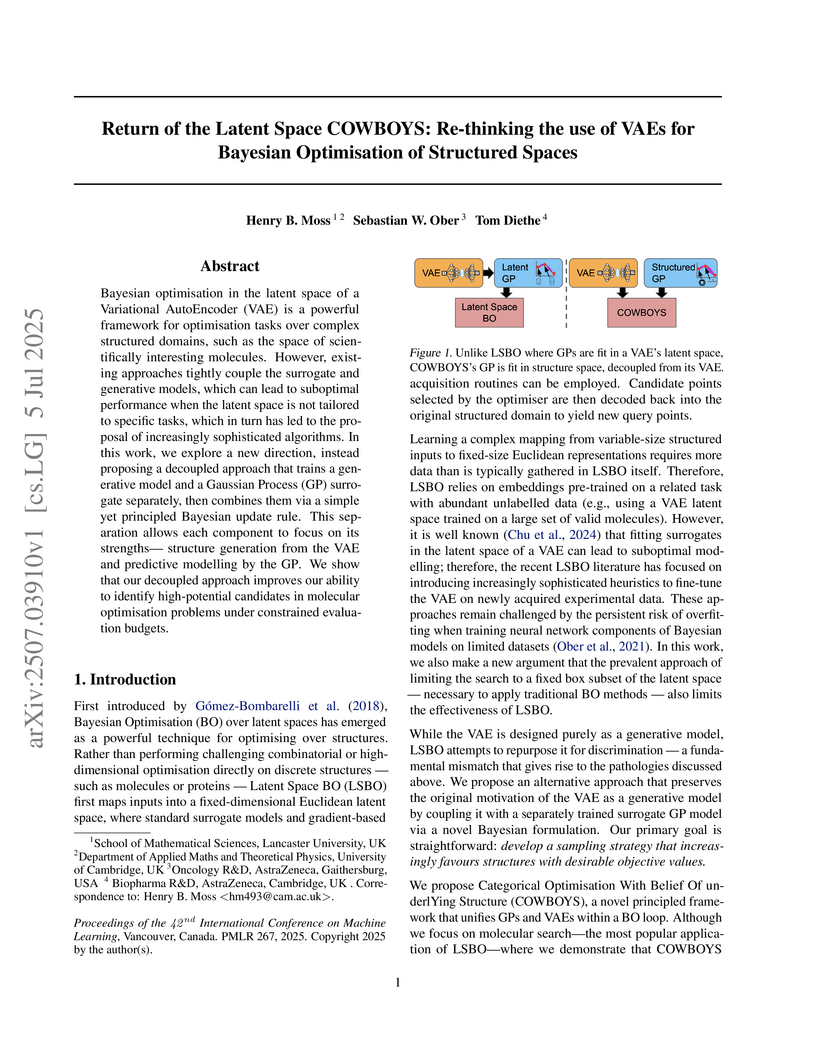
COWBOYS (Categorical Optimisation With Belief Of underlYing Structure), developed by researchers including those from AstraZeneca, introduces a Bayesian Optimization framework that re-thinks the use of Variational AutoEncoders (VAEs) by decoupling them from Gaussian Process (GP) surrogate modeling, allowing GPs to operate directly in the original structured data space. This approach achieves marked improvements in sample efficiency, particularly in low-data regimes, across various molecular design benchmarks compared to existing Latent Space Bayesian Optimization methods.
Researchers at Lancaster University and Mindgard developed "Model Leeching," a black-box extraction attack that distills task-specific knowledge from large, proprietary language models like ChatGPT-3.5-Turbo into smaller, local models. This method enabled high-fidelity replication of LLM behavior at a cost of only $50, and demonstrated an 11% increase in adversarial attack success against the target LLM by using the extracted model for attack staging.
FlexiMo, a flexible foundation model developed by researchers including those from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, enables seamless processing of multi-source satellite imagery with varying spatial resolutions and spectral configurations. It achieves this by dynamically adapting to input characteristics without extensive parameter fine-tuning, demonstrating improved generalization across diverse tasks like scene classification, land cover classification, building segmentation, and cloud detection.
In contrast to batch learning where all training data is available at once,
continual learning represents a family of methods that accumulate knowledge and
learn continuously with data available in sequential order. Similar to the
human learning process with the ability of learning, fusing, and accumulating
new knowledge coming at different time steps, continual learning is considered
to have high practical significance. Hence, continual learning has been studied
in various artificial intelligence tasks. In this paper, we present a
comprehensive review of the recent progress of continual learning in computer
vision. In particular, the works are grouped by their representative
techniques, including regularization, knowledge distillation, memory,
generative replay, parameter isolation, and a combination of the above
techniques. For each category of these techniques, both its characteristics and
applications in computer vision are presented. At the end of this overview,
several subareas, where continuous knowledge accumulation is potentially
helpful while continual learning has not been well studied, are discussed.
Researchers empirically demonstrated that current Large Language Model (LLM) guardrail systems are highly vulnerable to both simple character injection and sophisticated adversarial machine learning evasion techniques. The study revealed that even widely used commercial and open-source guardrails can be bypassed with high success rates, up to 100% for certain methods like emoji smuggling, highlighting critical weaknesses in existing LLM protection mechanisms.
The Learning-to-Unlearn (LTU) framework from the Singapore University of Technology and Design introduces a meta-learning approach for machine unlearning that efficiently removes data influence while preserving model utility. It achieves state-of-the-art performance across all unlearning metrics, notably outperforming baselines even when accessing only 30% of the original training data.
Text-to-motion generation has recently garnered significant research
interest, primarily focusing on generating human motion sequences in blank
backgrounds. However, human motions commonly occur within diverse 3D scenes,
which has prompted exploration into scene-aware text-to-motion generation
methods. Yet, existing scene-aware methods often rely on large-scale
ground-truth motion sequences in diverse 3D scenes, which poses practical
challenges due to the expensive cost. To mitigate this challenge, we are the
first to propose a \textbf{T}raining-free \textbf{S}cene-aware
\textbf{T}ext-to-\textbf{Motion} framework, dubbed as \textbf{TSTMotion}, that
efficiently empowers pre-trained blank-background motion generators with the
scene-aware capability. Specifically, conditioned on the given 3D scene and
text description, we adopt foundation models together to reason, predict and
validate a scene-aware motion guidance. Then, the motion guidance is
incorporated into the blank-background motion generators with two
modifications, resulting in scene-aware text-driven motion sequences. Extensive
experiments demonstrate the efficacy and generalizability of our proposed
framework. We release our code in \href{this https URL}{Project
Page}.
Online ride-hailing platforms aim to deliver efficient mobility-on-demand services, often facing challenges in balancing dynamic and spatially heterogeneous supply and demand. Existing methods typically fall into two categories: reinforcement learning (RL) approaches, which suffer from data inefficiency, oversimplified modeling of real-world dynamics, and difficulty enforcing operational constraints; or decomposed online optimization methods, which rely on manually designed high-level objectives that lack awareness of low-level routing dynamics. To address this issue, we propose a novel hybrid framework that integrates large language model (LLM) with mathematical optimization in a dynamic hierarchical system: (1) it is training-free, removing the need for large-scale interaction data as in RL, and (2) it leverages LLM to bridge cognitive limitations caused by problem decomposition by adaptively generating high-level objectives. Within this framework, LLM serves as a meta-optimizer, producing semantic heuristics that guide a low-level optimizer responsible for constraint enforcement and real-time decision execution. These heuristics are refined through a closed-loop evolutionary process, driven by harmony search, which iteratively adapts the LLM prompts based on feasibility and performance feedback from the optimization layer. Extensive experiments based on scenarios derived from both the New York and Chicago taxi datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving an average improvement of 16% compared to state-of-the-art baselines.
This survey provides a comprehensive review of multimodal geospatial foundation models (GFMs), detailing their core techniques, application domains, and persistent challenges. It establishes a modality-driven evaluation framework and charts future research directions to advance integrated Earth observation.
A training-free framework enables generation of high-quality long videos from pre-trained short video diffusion models through position mapping and informative frame selection techniques, achieving superior performance across all VBench metrics while eliminating the need for additional training or data.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.