Nankai University
Researchers from Nanjing University of Science and Technology and Nankai University developed SeRankDet, a deep network designed to improve infrared small target detection by selectively preserving dim targets and aggressively suppressing false alarms. The model achieved state-of-the-art performance across four public datasets and demonstrated superior robustness to noise, outperforming previous methods in accuracy and false alarm suppression.
Although adaptive gradient methods have been extensively used in deep
learning, their convergence rates proved in the literature are all slower than
that of SGD, particularly with respect to their dependence on the dimension.
This paper considers the classical RMSProp and its momentum extension and
establishes the convergence rate of $\frac{1}{T}\sum_{k=1}^T E\left[\|\nabla
f(x^k)\|_1\right]\leq O(\frac{\sqrt{d}C}{T^{1/4}})measuredby\ell_1$ norm
without the bounded gradient assumption, where d is the dimension of the
optimization variable, T is the iteration number, and C is a constant
identical to that appeared in the optimal convergence rate of SGD. Our
convergence rate matches the lower bound with respect to all the coefficients
except the dimension d. Since ∥x∥2≪∥x∥1≤d∥x∥2 for
problems with extremely large d, our convergence rate can be considered to be
analogous to the $\frac{1}{T}\sum_{k=1}^T E\left[\|\nabla f(x^k)\|_2\right]\leq
O(\frac{C}{T^{1/4}})rateofSGDintheidealcaseof\|\nabla
f(x)\|_1=\varTheta(\sqrt{d}\|\nabla f(x)\|_2)$.
Representation Entanglement for Generation (REG) introduces an image-class denoising paradigm, achieving up to 63x faster training for Diffusion Transformers while setting a new FID record of 1.8 on ImageNet 256x256 by structurally integrating a high-level class token with image latents.
FastGS, developed by NanKai University researchers, introduces a framework to accelerate 3D Gaussian Splatting training to approximately 100 seconds per scene. This approach achieves a substantial reduction in training time while maintaining or improving rendering quality and model compactness across various 3D reconstruction tasks.
31 Jul 2025
SWE-Exp introduces an experience-enhanced framework that enables Large Language Model (LLM) agents to learn from past software issue resolution attempts, transforming problem-solving into a continuous learning process. This approach achieved a 41.6% Pass@1 score on SWE-bench-Verified with DeepSeek-V3-0324, representing a 7.2% relative improvement over prior methods using the same model.
29 Nov 2025
Researchers from Nankai University and a collaborative network introduce a unified three-axis taxonomy for world models in Embodied AI, classifying them by functionality, temporal modeling, and spatial representation. This comprehensive survey systematically organizes diverse approaches, data resources, and evaluation metrics, providing a structured understanding and identifying critical future research directions.
VGGT-Long extends a state-of-the-art 3D vision foundation model to perform accurate, calibration-free monocular 3D reconstruction over kilometer-scale RGB sequences. The system effectively overcomes memory limitations and achieves global consistency through a robust chunk-based processing pipeline, loop closure, and global optimization.
WorldSplat, developed by Xiaomi EV and academic partners, introduces a framework for generating dynamic 4D driving scenes. It unifies generative capabilities with 3D consistency by producing an explicit 4D Gaussian representation, enabling high-fidelity multi-track videos and novel views that are spatio-temporally consistent.
This paper theoretically explains that the learning rate warm-up stage is essential for Post-Layer Normalization Transformers due to large initial gradients, while demonstrating that Pre-Layer Normalization Transformers inherently resolve this issue, allowing for warm-up-free training and significantly faster convergence, exemplified by a 40% speed-up in BERT pre-training.
Hydra-MDP implements an end-to-end multimodal planning framework using multi-target knowledge distillation from human and rule-based teachers to enhance autonomous driving safety and compliance. The system secured 1st place in the Navsim challenge, exhibiting superior closed-loop performance with a PDM score of 86.5 for single models and up to 91.0 with larger backbones.
Text-to-video (T2V) generation has recently garnered significant attention
thanks to the large multi-modality model Sora. However, T2V generation still
faces two important challenges: 1) Lacking a precise open sourced high-quality
dataset. The previous popular video datasets, e.g. WebVid-10M and Panda-70M,
are either with low quality or too large for most research institutions.
Therefore, it is challenging but crucial to collect a precise high-quality
text-video pairs for T2V generation. 2) Ignoring to fully utilize textual
information. Recent T2V methods have focused on vision transformers, using a
simple cross attention module for video generation, which falls short of
thoroughly extracting semantic information from text prompt. To address these
issues, we introduce OpenVid-1M, a precise high-quality dataset with expressive
captions. This open-scenario dataset contains over 1 million text-video pairs,
facilitating research on T2V generation. Furthermore, we curate 433K 1080p
videos from OpenVid-1M to create OpenVidHD-0.4M, advancing high-definition
video generation. Additionally, we propose a novel Multi-modal Video Diffusion
Transformer (MVDiT) capable of mining both structure information from visual
tokens and semantic information from text tokens. Extensive experiments and
ablation studies verify the superiority of OpenVid-1M over previous datasets
and the effectiveness of our MVDiT.
RIPT-VLA introduces a third training stage for Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, employing reinforcement interactive post-training to learn from binary success/failure rewards. The method improved success rates on LIBERO-90 to 94.3% for QueST and achieved a 21.2% absolute improvement on LIBERO-LONG, particularly excelling in low-data scenarios where it consistently achieved over 80% success with single demonstrations.
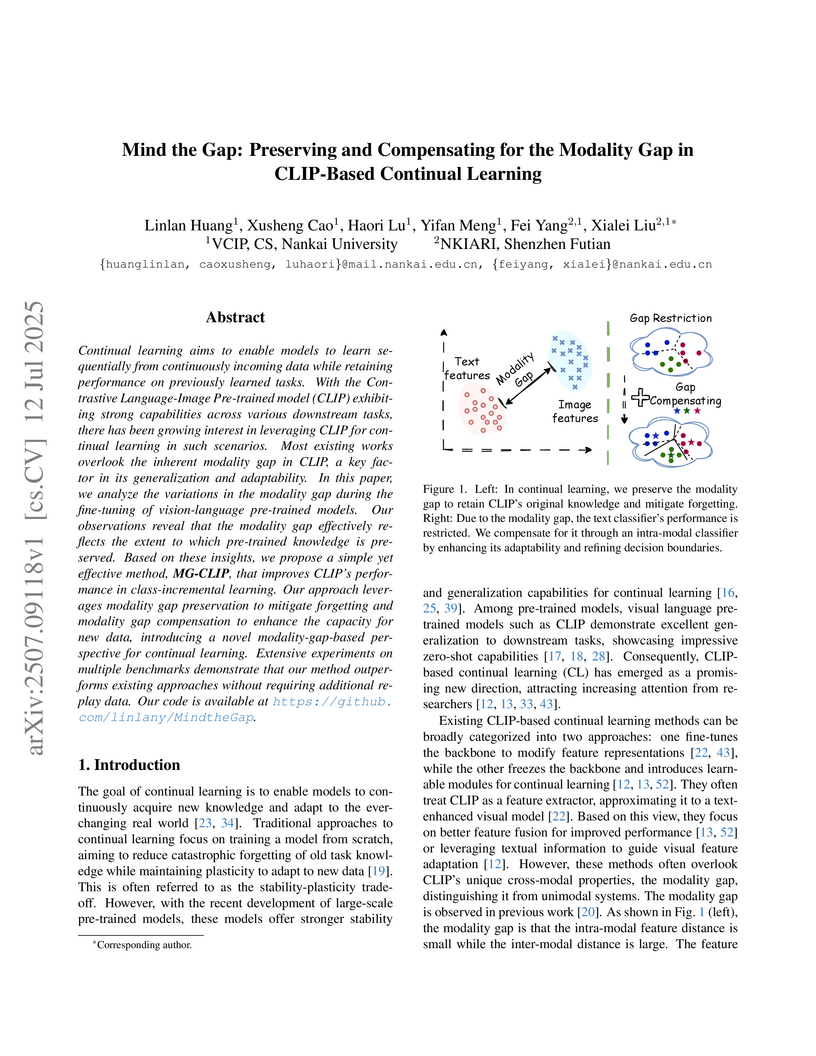
Researchers from Nankai University developed MG-CLIP, a method for CLIP-based continual learning that actively manages the inherent modality gap to improve performance. It achieves state-of-the-art "Last accuracy" without replay on several benchmarks, for example, improving by at least 1.53% on CIFAR-100 and 1.86% on VTAB, while also preserving CLIP's zero-shot generalization capabilities.
Reasoning models have demonstrated remarkable progress in solving complex and logic-intensive tasks by generating extended Chain-of-Thoughts (CoTs) prior to arriving at a final answer. Yet, the emergence of this "slow-thinking" paradigm, with numerous tokens generated in sequence, inevitably introduces substantial computational overhead. To this end, it highlights an urgent need for effective acceleration. This survey aims to provide a comprehensive overview of recent advances in efficient reasoning. It categorizes existing works into three key directions: (1) shorter - compressing lengthy CoTs into concise yet effective reasoning chains; (2) smaller - developing compact language models with strong reasoning capabilities through techniques such as knowledge distillation, other model compression techniques, and reinforcement learning; and (3) faster - designing efficient decoding strategies to accelerate inference of reasoning models. A curated collection of papers discussed in this survey is available in our GitHub repository: this https URL.
SE-GUI is a reinforcement learning framework that enhances visual grounding for GUI agents using a self-evolutionary mechanism and dense point rewards. It achieves 47.3% accuracy on the ScreenSpot-Pro benchmark, outperforming larger models while utilizing only 3,018 high-quality training samples.
Researchers at Nankai University developed Visual Instruction Pretraining (ViTP), a "top-down" paradigm that embeds and trains Vision Transformer backbones within Vision-Language Models using visual instruction-following objectives. ViTP achieves new state-of-the-art performance across 16 downstream tasks in remote sensing and medical imaging, notably demonstrating up to 17x greater pretraining efficiency and superior robustness compared to existing methods.
TempSamp-R1 introduces a reinforcement fine-tuning framework for video Large Language Models, integrating ground-truth annotations as off-policy supervision and employing a non-linear reward shaping method. This approach achieves new state-of-the-art results on temporal video understanding benchmarks, improving temporal precision and training stability across various tasks.
Nankai University and Microsoft Corporation researchers developed "SpeechLLM-as-Judges," a framework leveraging large language models for general, interpretable, and multilingual speech quality evaluation. They introduced SpeechEval, a human-annotated dataset, and a specialized LLM, SQ-LLM, which provides detailed, natural language explanations for quality assessments across four languages and multiple tasks, outperforming existing baselines in accuracy and interpretability.
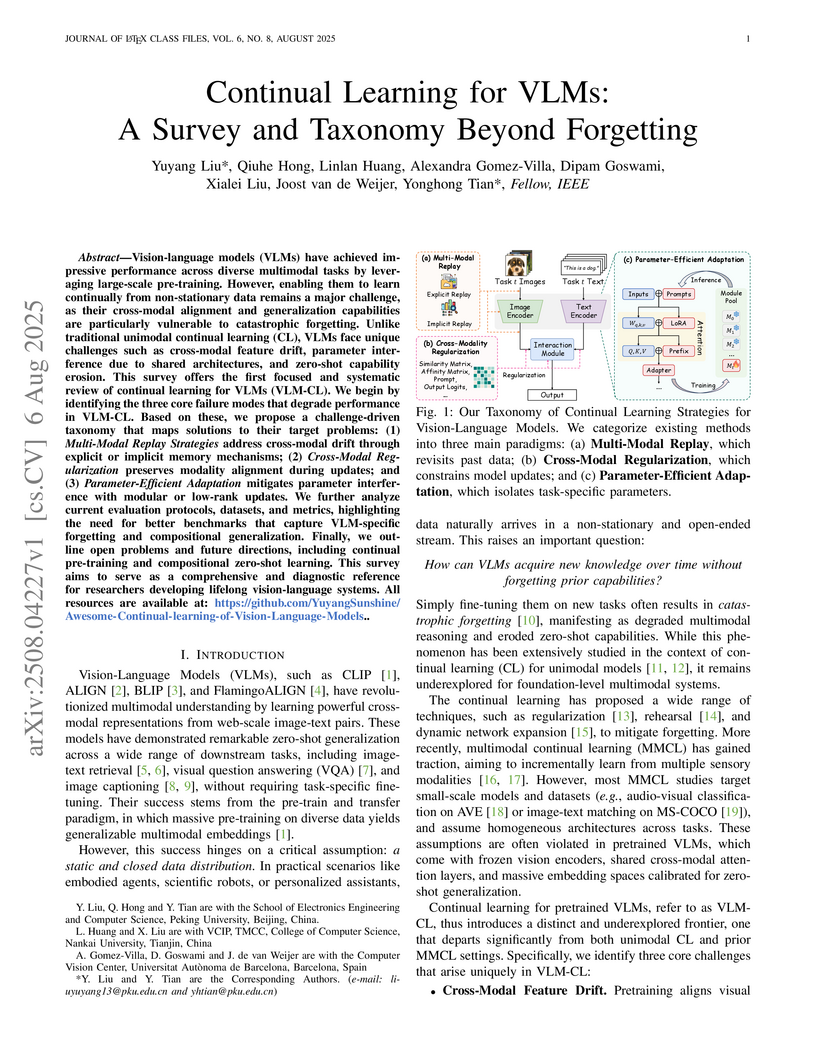
Vision-language models (VLMs) have achieved impressive performance across diverse multimodal tasks by leveraging large-scale pre-training. However, enabling them to learn continually from non-stationary data remains a major challenge, as their cross-modal alignment and generalization capabilities are particularly vulnerable to catastrophic forgetting. Unlike traditional unimodal continual learning (CL), VLMs face unique challenges such as cross-modal feature drift, parameter interference due to shared architectures, and zero-shot capability erosion. This survey offers the first focused and systematic review of continual learning for VLMs (VLM-CL). We begin by identifying the three core failure modes that degrade performance in VLM-CL. Based on these, we propose a challenge-driven taxonomy that maps solutions to their target problems: (1) \textit{Multi-Modal Replay Strategies} address cross-modal drift through explicit or implicit memory mechanisms; (2) \textit{Cross-Modal Regularization} preserves modality alignment during updates; and (3) \textit{Parameter-Efficient Adaptation} mitigates parameter interference with modular or low-rank updates. We further analyze current evaluation protocols, datasets, and metrics, highlighting the need for better benchmarks that capture VLM-specific forgetting and compositional generalization. Finally, we outline open problems and future directions, including continual pre-training and compositional zero-shot learning. This survey aims to serve as a comprehensive and diagnostic reference for researchers developing lifelong vision-language systems. All resources are available at: this https URL.
03 Sep 2025
This paper introduces methods for online multiple testing and conformal selection that systematically incorporate real-time feedback, dynamically adjusting testing thresholds and selecting models to significantly enhance statistical power while maintaining finite-sample False Discovery Rate (FDR) control. The research provides the first framework to integrate real-time feedback into online FDR procedures and extends this paradigm to online conformal testing, offering robust performance in dynamic real-world applications.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.