Pazhou Lab
Researchers at South China University of Technology and collaborators introduced NSG-VD, a physics-driven method utilizing a Normalized Spatiotemporal Gradient (NSG) and Maximum Mean Discrepancy, to detect AI-generated videos by identifying violations of physical continuity. The approach achieves superior detection performance on advanced generative models like Sora and demonstrates strong robustness in data-imbalanced settings.
12 Nov 2025
ComoRAG, a cognitive-inspired and memory-organized Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) framework, enables Large Language Models to perform stateful reasoning over exceptionally long narratives by dynamically building and revising a global mental model. It achieves superior performance on challenging long-context benchmarks, particularly for complex narrative and inferential query types.
This survey provides a comprehensive overview of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), tracing their historical evolution, detailing their technical components, and categorizing current algorithms. The paper highlights MLLMs' ability to integrate diverse data types like text and images, demonstrating applications across healthcare, education, and creative industries, while also discussing existing challenges and future research directions.
The SAM2-UNet framework effectively integrates the hierarchical Hiera encoder from the Segment Anything Model 2 (SAM2) into a U-shaped architecture for image segmentation. This approach, which utilizes adapter-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning, achieves state-of-the-art performance across 18 diverse datasets while maintaining computational efficiency.
06 Oct 2025
In this paper, our objective is to develop a multi-agent financial system that incorporates simulated trading, a technique extensively utilized by financial professionals. While current LLM-based agent models demonstrate competitive performance, they still exhibit significant deviations from real-world fund companies. A critical distinction lies in the agents' reliance on ``post-reflection'', particularly in response to adverse outcomes, but lack a distinctly human capability: long-term prediction of future trends. Therefore, we introduce QuantAgents, a multi-agent system integrating simulated trading, to comprehensively evaluate various investment strategies and market scenarios without assuming actual risks. Specifically, QuantAgents comprises four agents: a simulated trading analyst, a risk control analyst, a market news analyst, and a manager, who collaborate through several meetings. Moreover, our system incentivizes agents to receive feedback on two fronts: performance in real-world markets and predictive accuracy in simulated trading. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework excels across all metrics, yielding an overall return of nearly 300% over the three years (this https URL).
The PsyDT framework constructs personalized digital twins for psychological counselors by synthesizing multi-turn mental health dialogues tailored to a specific human counselor's style, simulated client personalities, and therapy techniques. It generates a high-quality synthetic dataset, PsyDTCorpus, used to fine-tune PsyDTLLM, which demonstrates superior performance in empathy and conversational strategy over existing mental health LLMs.
17 Feb 2025
A groundbreaking multi-agent trading system from South China University of Technology and ByteDance achieves exceptional market performance (70% annualized return, 400% total return over 3 years) through innovative coordination between LLM-powered specialized hedging agents, demonstrating unprecedented stability during extreme market conditions while maintaining consistent profitability.
Researchers from South China University of Technology and ByteDance introduce VideoCoT, a novel dataset for video understanding that integrates Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning. The work demonstrates that training multimodal large language models with these explicit reasoning steps enables them to generate more detailed and logical responses when analyzing temporal and spatial elements in videos.
Zero-shot skeleton-based action recognition aims to classify unseen skeleton-based human actions without prior exposure to such categories during training. This task is extremely challenging due to the difficulty in generalizing from known to unknown actions. Previous studies typically use two-stage training: pre-training skeleton encoders on seen action categories using cross-entropy loss and then aligning pre-extracted skeleton and text features, enabling knowledge transfer to unseen classes through skeleton-text alignment and language models' generalization. However, their efficacy is hindered by 1) insufficient discrimination for skeleton features, as the fixed skeleton encoder fails to capture necessary alignment information for effective skeleton-text alignment; 2) the neglect of alignment bias between skeleton and unseen text features during testing. To this end, we propose a prototype-guided feature alignment paradigm for zero-shot skeleton-based action recognition, termed PGFA. Specifically, we develop an end-to-end cross-modal contrastive training framework to improve skeleton-text alignment, ensuring sufficient discrimination for skeleton features. Additionally, we introduce a prototype-guided text feature alignment strategy to mitigate the adverse impact of the distribution discrepancy during testing. We provide a theoretical analysis to support our prototype-guided text feature alignment strategy and empirically evaluate our overall PGFA on three well-known datasets. Compared with the top competitor SMIE method, our PGFA achieves absolute accuracy improvements of 22.96%, 12.53%, and 18.54% on the NTU-60, NTU-120, and PKU-MMD datasets, respectively.
06 Aug 2025
Learning path recommendation seeks to provide learners with a structured sequence of learning items (\eg, knowledge concepts or exercises) to optimize their learning efficiency. Despite significant efforts in this area, most existing methods primarily rely on prerequisite relationships, which present two major limitations: 1) Requiring prerequisite relationships between knowledge concepts, which are difficult to obtain due to the cost of expert annotation, hindering the application of current learning path recommendation methods. 2) Relying on a single, sequentially dependent knowledge structure based on prerequisite relationships implies that difficulties at any stage can cause learning blockages, which in turn disrupt subsequent learning processes. To address these challenges, we propose a novel approach, GraphRAG-Induced Dual Knowledge Structure Graphs for Personalized Learning Path Recommendation (KnowLP), which enhances learning path recommendations by incorporating both prerequisite and similarity relationships between knowledge concepts. Specifically, we introduce a knowledge concept structure graph generation module EDU-GraphRAG that adaptively constructs knowledge concept structure graphs for different educational datasets, significantly improving the generalizability of learning path recommendation methods. We then propose a Discrimination Learning-driven Reinforcement Learning (DLRL) module, which mitigates the issue of blocked learning paths, further enhancing the efficacy of learning path recommendations. Finally, we conduct extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets, demonstrating that our method not only achieves state-of-the-art performance but also provides interpretable reasoning for the recommended learning paths.
Recently, employing single-modality large language models based on mechanical
vibration signals as Tuning Predictors has introduced new perspectives in
intelligent fault diagnosis. However, the potential of these methods to
leverage multimodal data remains underexploited, particularly in complex
mechanical systems where relying on a single data source often fails to capture
comprehensive fault information. In this paper, we present FaultGPT, a novel
model that generates fault diagnosis reports directly from raw vibration
signals. By leveraging large vision-language models (LVLM) and text-based
supervision, FaultGPT performs end-to-end fault diagnosis question answering
(FDQA), distinguishing itself from traditional classification or regression
approaches. Specifically, we construct a large-scale FDQA instruction dataset
for instruction tuning of LVLM. This dataset includes vibration time-frequency
image-text label pairs and human instruction-ground truth pairs. To enhance the
capability in generating high-quality fault diagnosis reports, we design a
multi-scale cross-modal image decoder to extract fine-grained fault semantics
and conducted instruction tuning without introducing additional training
parameters into the LVLM. Extensive experiments, including fault diagnosis
report generation, few-shot and zero-shot evaluation across multiple datasets,
validate the superior performance and adaptability of FaultGPT in diverse
industrial scenarios.
Researchers at Xi'an Jiaotong University developed Adam-NSCL, an algorithm that mitigates catastrophic forgetting in continual learning by projecting network updates into the approximate null space of past tasks' feature covariance. This method maintains performance on new tasks while largely retaining knowledge from previous ones, operating efficiently without requiring storage or replay of old task data.
DPM-Solver-v3, developed by researchers at Tsinghua University, proposes a novel generalized ODE formulation and computes 'Empirical Model Statistics' to minimize discretization errors in Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DPM) sampling. This training-free method achieves a 15% to 30% speed-up at very low NFE counts (5-10 steps) compared to previous state-of-the-art solvers, producing higher quality images with reduced bias and improved stability under high guidance.
Consistency Diffusion Bridge Models (CDBMs) significantly accelerate Denoising Diffusion Bridge Models (DDBMs) by leveraging consistency training principles, achieving 4x to 50x faster sampling. This enables high-quality, few-step generation for tasks like image-to-image translation and inpainting, making DDBMs more practical and deployable.
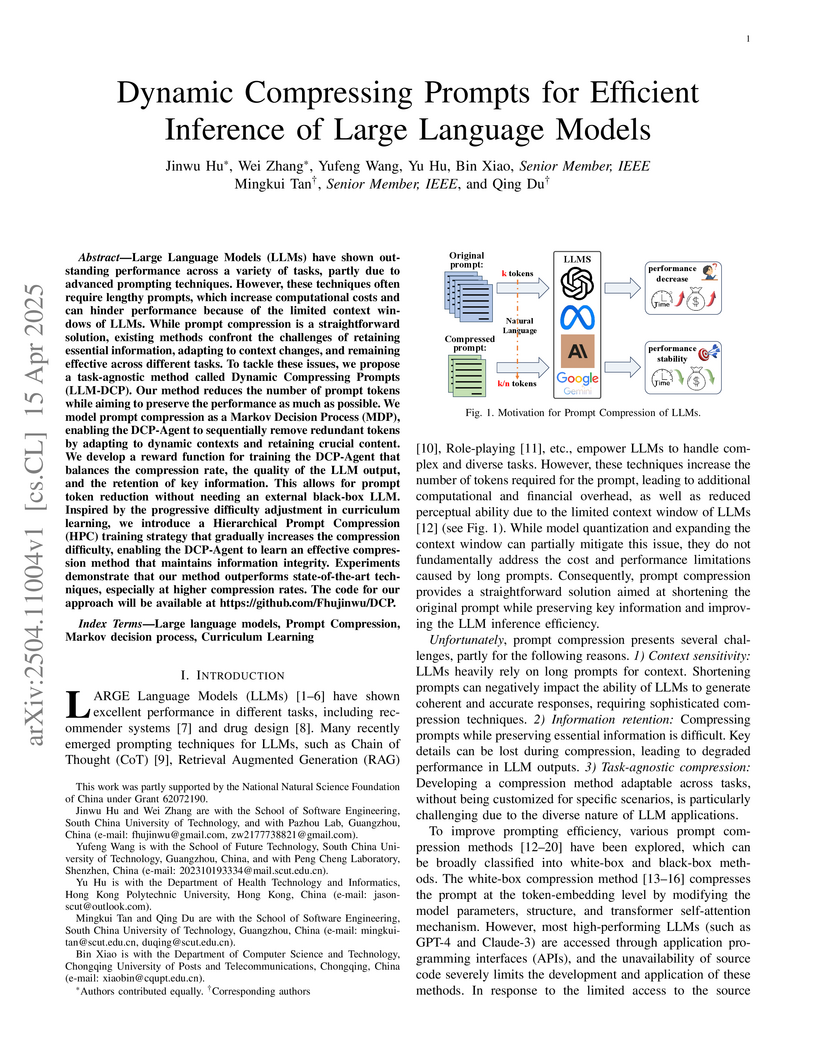
A dynamic prompt compression framework reduces computational costs in large language models by using reinforcement learning to adaptively remove redundant tokens while preserving key information, achieving 70% compression rates with minimal performance degradation across conversation, summarization, and reasoning tasks.
Many unsupervised visual anomaly detection methods train an auto-encoder to reconstruct normal samples and then leverage the reconstruction error map to detect and localize the anomalies. However, due to the powerful modeling and generalization ability of neural networks, some anomalies can also be well reconstructed, resulting in unsatisfactory detection and localization accuracy. In this paper, a small coarsely-labeled anomaly dataset is first collected. Then, a coarse-knowledge-aware adversarial learning method is developed to align the distribution of reconstructed features with that of normal features. The alignment can effectively suppress the auto-encoder's reconstruction ability on anomalies and thus improve the detection accuracy. Considering that anomalies often only occupy very small areas in anomalous images, a patch-level adversarial learning strategy is further developed. Although no patch-level anomalous information is available, we rigorously prove that by simply viewing any patch features from anomalous images as anomalies, the proposed knowledge-aware method can also align the distribution of reconstructed patch features with the normal ones. Experimental results on four medical datasets and two industrial datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in improving the detection and localization performance.
Researchers from Nanyang Technological University and collaborators developed ICLAttack, a method to embed backdoor vulnerabilities in Large Language Models purely through in-context learning without fine-tuning the model. This attack manipulates demonstration examples or prompt formats, achieving high success rates across diverse LLMs and tasks while preserving normal performance on clean inputs.
A structured compression framework called CoMe reduces large language models' computational and storage demands through progressive layer pruning, concatenation-based merging, and hierarchical distillation. This approach retains up to 83% of the original average accuracy for LLaMA-2-7b while reducing parameters by 30%.
Large language models (LLMs) have performed well in providing general and extensive health suggestions in single-turn conversations, exemplified by systems such as ChatGPT, ChatGLM, ChatDoctor, DoctorGLM, and etc. However, the limited information provided by users during single turn results in inadequate personalization and targeting of the generated suggestions, which requires users to independently select the useful part. It is mainly caused by the missing ability to engage in multi-turn questioning. In real-world medical consultations, doctors usually employ a series of iterative inquiries to comprehend the patient's condition thoroughly, enabling them to provide effective and personalized suggestions subsequently, which can be defined as chain of questioning (CoQ) for LLMs. To improve the CoQ of LLMs, we propose BianQue, a ChatGLM-based LLM finetuned with the self-constructed health conversation dataset BianQueCorpus that is consist of multiple turns of questioning and health suggestions polished by ChatGPT. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed BianQue can simultaneously balance the capabilities of both questioning and health suggestions, which will help promote the research and application of LLMs in the field of proactive health.
RTBAgent introduces the first LLM-based agent system for real-time bidding, outperforming traditional and reinforcement learning methods by achieving higher click counts under various budget constraints on the iPinYou dataset. The system offers enhanced interpretability of bidding decisions through a two-step reasoning process and demonstrates robust adaptability across different LLM backbones.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.