Shanghai Jiaotong University
Shanghai Jiaotong UniversityThe PRIME framework enhances Large Language Model reasoning by efficiently integrating dense, token-level implicit rewards through online reinforcement learning. It achieves a 15.1% average improvement across key reasoning benchmarks and demonstrates 2.5x sample efficiency, outperforming larger models like Qwen2.5-Math-7B-Instruct with significantly less training data.
20 Oct 2025
This survey establishes "Agentic Science" as a paradigm for autonomous scientific discovery, offering a unified framework that integrates agent capabilities, scientific workflows, and domain-specific applications across natural sciences. It charts the evolution of AI from computational tools to autonomous research partners, highlighting over 20 validated scientific discoveries made by AI agents.
13 Oct 2025
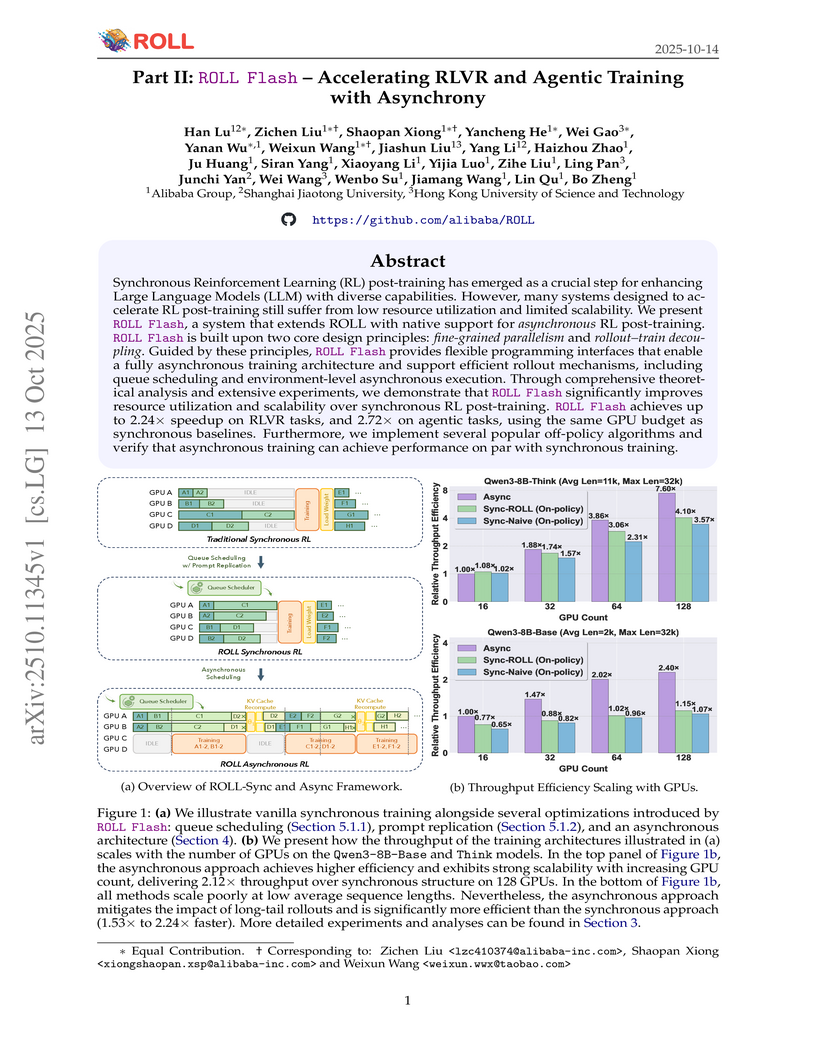
ROLL Flash enhances the efficiency and scalability of Reinforcement Learning post-training for Large Language Models by introducing asynchronous execution and fine-grained parallelism. This system achieves up to 2.24x higher throughput for RLVR tasks and a 2.72x speedup for agentic tasks, while maintaining or improving final model performance.
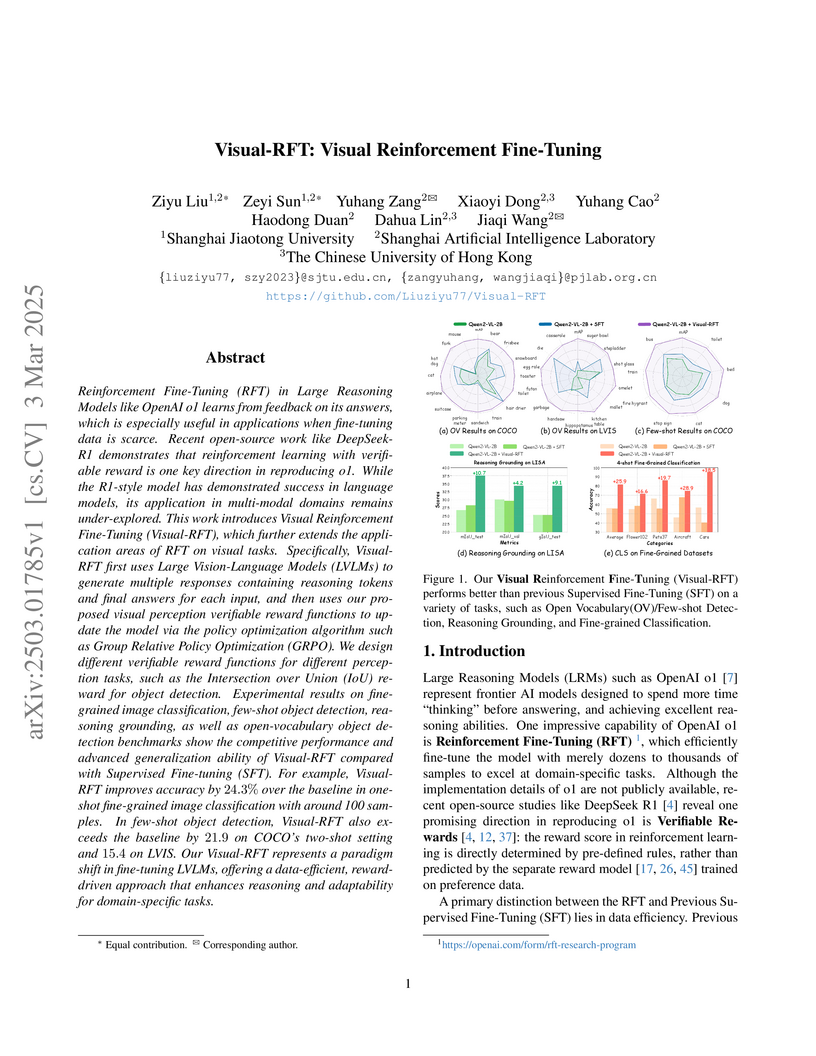
Shanghai researchers introduce Visual-RFT, a pioneering framework that adapts reinforcement learning techniques for visual-language models, achieving remarkable improvements across multiple vision tasks including a 24.3% accuracy boost in fine-grained classification and 21.9 mAP improvement in few-shot object detection while maintaining data efficiency.
PREF-GRPO introduces a novel training method for text-to-image (T2I) models that stabilizes reinforcement learning against reward hacking by utilizing pairwise preference rewards. The accompanying UNIGENBENCH offers a fine-grained, MLLM-powered framework for comprehensive and diagnostic evaluation of T2I models.
19 Sep 2025
RLinf introduces a high-performance system for large-scale reinforcement learning, employing a Macro-to-Micro Flow Transformation (M2Flow) paradigm to dynamically optimize execution. The system achieves 1.10x to 1.58x speedup over existing RLHF systems and up to 2.13x speedup in embodied RL training, leading to state-of-the-art model quality in reasoning and embodied tasks.
17 Sep 2025
Researchers at Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and collaborating universities developed a Behavior Foundation Model (BFM) for humanoid robots, which learns a unified distribution of behaviors to achieve zero-shot generalization across various control modes and accelerates the acquisition of new skills. The model demonstrates superior performance over general baselines and enables advanced behavioral composition and modulation on a physical humanoid robot.
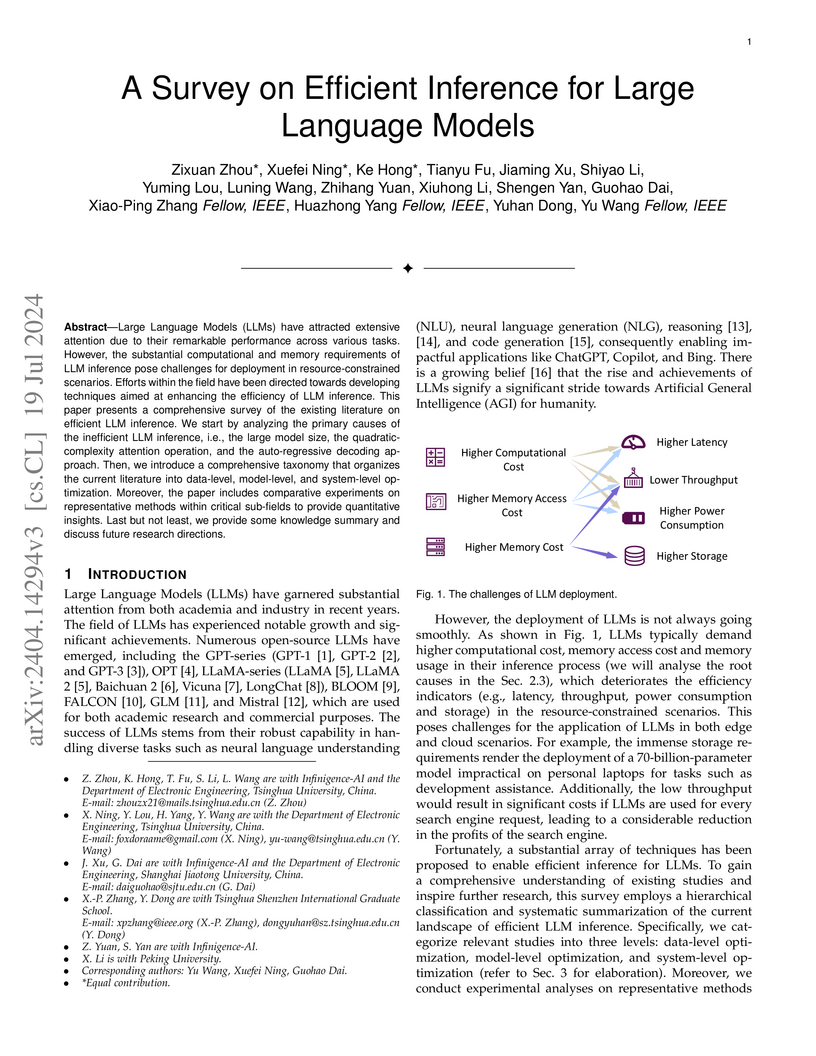
This survey paper offers a comprehensive overview of techniques for optimizing the computational and memory demands of Large Language Model (LLM) inference. It introduces a tripartite taxonomy across data, model, and system levels, and provides quantitative comparisons of representative methods like quantization and speculative decoding to guide practitioners.
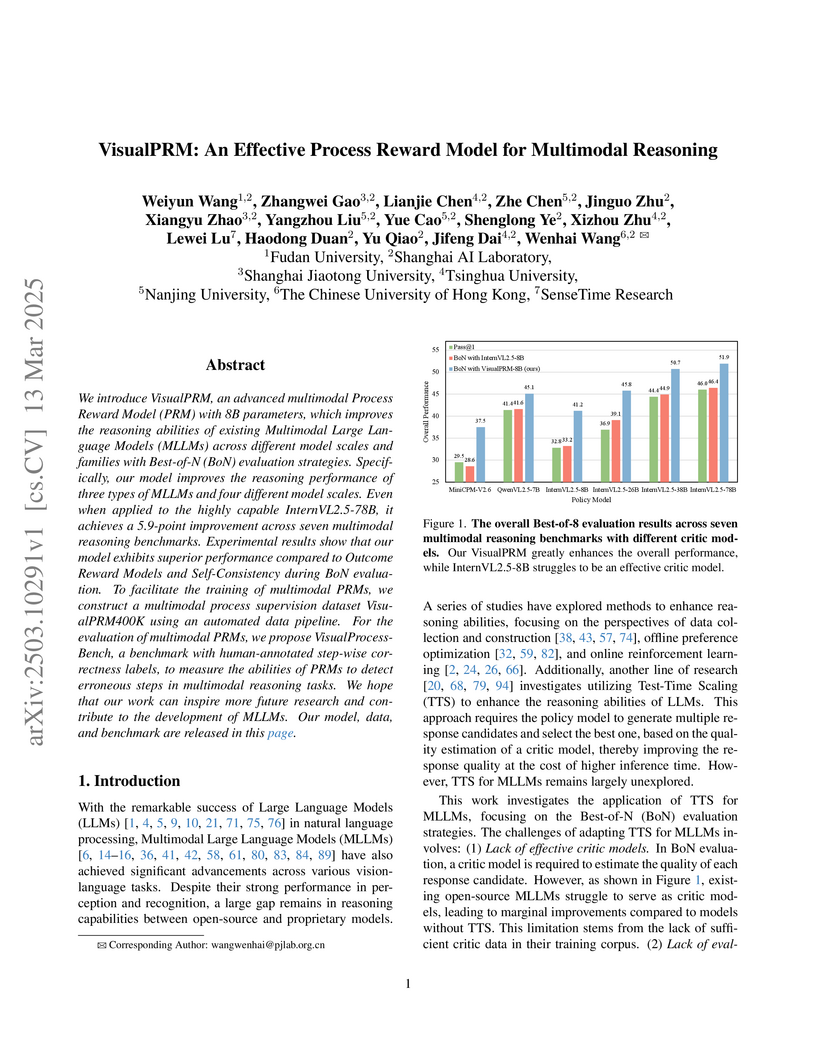
Shanghai AI Laboratory and partner institutions introduce VisualPRM, a process reward model that evaluates step-by-step reasoning in multimodal tasks, improving MLLM performance through test-time scaling while introducing VisualPRM400K dataset and VisualProcessBench for comprehensive evaluation of multimodal reasoning capabilities.
20 May 2025
Researchers from Shanghai AI Lab and collaborating institutions develop Visual-ARFT, a reinforcement fine-tuning framework that enables Large Vision-Language Models to use web search and code execution tools for complex visual reasoning tasks, achieving up to 18.6% improvement in F1 scores over baselines while surpassing GPT-4o performance on image manipulation tasks.
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Monash University
Monash University Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University University of Notre Dame
University of Notre Dame UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University College London
University College London Cornell UniversityCSIRO’s Data61
Cornell UniversityCSIRO’s Data61 Hugging FaceTU Darmstadt
Hugging FaceTU Darmstadt InriaSingapore Management UniversitySea AI Lab
InriaSingapore Management UniversitySea AI Lab MITIntelAWS AI Labs
MITIntelAWS AI Labs Shanghai Jiaotong University
Shanghai Jiaotong University Queen Mary University of London
Queen Mary University of London University of VirginiaUNC-Chapel Hill
University of VirginiaUNC-Chapel Hill ServiceNowContextual AIDetomo Inc
ServiceNowContextual AIDetomo IncBigCodeBench is a new benchmark that evaluates Large Language Models on their ability to generate Python code requiring diverse function calls and complex instructions, revealing that current models like GPT-4o achieve a maximum of 60% accuracy on these challenging tasks, significantly lagging human performance.
30 Sep 2025
Developed by researchers from Midea Group, Peking University, and Shanghai Jiaotong University, dVLA unifies visual perception, language reasoning, and action generation within a single diffusion framework for robotic control. The model achieves state-of-the-art average success rates of 96.4% in simulation (LIBERO benchmark) and 65% in real-world robotic tasks, while also accelerating inference speed by approximately 2x.
OS-ATLAS introduces an open-source foundation action model capable of understanding graphical user interfaces and executing actions across Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and web environments. The model outperforms GPT-4 in zero-shot out-of-distribution GUI agent tasks and is built on the largest open-source cross-platform GUI grounding corpus.
01 Oct 2025
Diffusion-based models for robotic control, including vision-language-action (VLA) and vision-action (VA) policies, have demonstrated significant capabilities. Yet their advancement is constrained by the high cost of acquiring large-scale interaction datasets. This work introduces an alternative paradigm for enhancing policy performance without additional model training. Perhaps surprisingly, we demonstrate that the composed policies can exceed the performance of either parent policy. Our contribution is threefold. First, we establish a theoretical foundation showing that the convex composition of distributional scores from multiple diffusion models can yield a superior one-step functional objective compared to any individual score. A Grönwall-type bound is then used to show that this single-step improvement propagates through entire generation trajectories, leading to systemic performance gains. Second, motivated by these results, we propose General Policy Composition (GPC), a training-free method that enhances performance by combining the distributional scores of multiple pre-trained policies via a convex combination and test-time search. GPC is versatile, allowing for the plug-and-play composition of heterogeneous policies, including VA and VLA models, as well as those based on diffusion or flow-matching, irrespective of their input visual modalities. Third, we provide extensive empirical validation. Experiments on Robomimic, PushT, and RoboTwin benchmarks, alongside real-world robotic evaluations, confirm that GPC consistently improves performance and adaptability across a diverse set of tasks. Further analysis of alternative composition operators and weighting strategies offers insights into the mechanisms underlying the success of GPC. These results establish GPC as a simple yet effective method for improving control performance by leveraging existing policies.
Spatial intelligence is essential for multimodal large language models (MLLMs) operating in the complex physical world. Existing benchmarks, however, probe only single-image relations and thus fail to assess the multi-image spatial reasoning that real-world deployments demand. We introduce MMSI-Bench, a VQA benchmark dedicated to multi-image spatial intelligence. Six 3D-vision researchers spent more than 300 hours meticulously crafting 1,000 challenging, unambiguous multiple-choice questions from over 120,000 images, each paired with carefully designed distractors and a step-by-step reasoning process. We conduct extensive experiments and thoroughly evaluate 34 open-source and proprietary MLLMs, observing a wide gap: the strongest open-source model attains roughly 30% accuracy and OpenAI's o3 reasoning model reaches 40%, while humans score 97%. These results underscore the challenging nature of MMSI-Bench and the substantial headroom for future research. Leveraging the annotated reasoning processes, we also provide an automated error analysis pipeline that diagnoses four dominant failure modes, including (1) grounding errors, (2) overlap-matching and scene-reconstruction errors, (3) situation-transformation reasoning errors, and (4) spatial-logic errors, offering valuable insights for advancing multi-image spatial intelligence. Project page: this https URL .
Researchers led by Monash University introduced "FarSight," a training-free decoding strategy that optimizes the causal mask in multimodal large language models to combat "attention collapse" and "positional information decay." This approach effectively reduces hallucinations, including challenging snowball hallucinations, showing a +6.4% improvement on the CHAIR_S benchmark for LLaVA-1.5, while maintaining generation quality across image and video tasks.
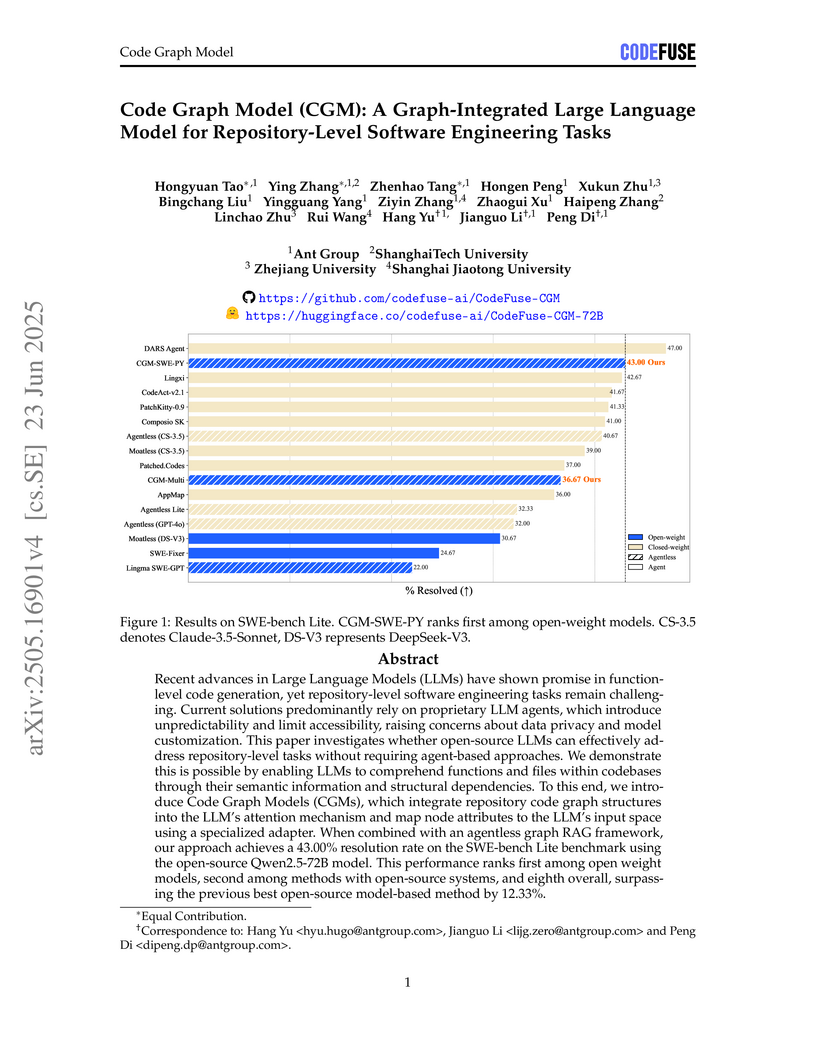
The Code Graph Model (CGM) introduces an agentless framework that integrates code graph structures into open-source large language models for repository-level software engineering tasks. This approach achieves a 43.00% resolution rate on SWE-bench Lite (Python), outperforming other open-source models and demonstrating competitiveness with leading closed-source, agent-based systems.
This research introduces MM-IFEngine, a pipeline for generating high-quality multimodal instruction following (MM-IF) data, and MM-IFEval, a challenging benchmark with a hybrid evaluation strategy. Fine-tuning MLLMs on the generated MM-IFInstruct-23k and MM-IFDPO-23k datasets consistently improved instruction following performance, demonstrating up to an 11.6% average gain for models like LLaVA-NeXT-Llama3-8B with Direct Preference Optimization, while maintaining general visual question answering capabilities.
MURE introduces a framework for natural language-guided image editing that uses interleaved textual and visual reasoning chains to achieve precise, physically plausible edits. The system incorporates deep confidence reasoning to prune low-quality intermediate steps, resulting in superior performance across image editing benchmarks by decomposing complex tasks into visually grounded sub-tasks.
These are CVPR 2023 guidelines for author responses to reviewer comments, establishing strict rules for formatting, length, and content. The guidelines aim to ensure a fair, efficient, and standardized peer-review process by preventing unsolicited new contributions and maintaining author anonymity.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.