Yahoo Research
A method is introduced for generating natural and coherent background scenes around salient objects without altering their original boundaries or identity. The approach reduces object expansion by 3.6 times on average compared to existing inpainting diffusion models, while maintaining visual quality and object fidelity.
Leveraging programming language constructs, specifically Python, to represent knowledge graphs for fine-tuning large language models significantly improves their multi-hop reasoning capabilities and factual accuracy. A smaller Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct model fine-tuned with this method achieved 96.4% accuracy in contextualized multi-hop reasoning, surpassing the performance of a much larger 70B parameter model.
We study decision making in environments where the reward is only partially observed, but can be modeled as a function of an action and an observed context. This setting, known as contextual bandits, encompasses a wide variety of applications including health-care policy and Internet advertising. A central task is evaluation of a new policy given historic data consisting of contexts, actions and received rewards. The key challenge is that the past data typically does not faithfully represent proportions of actions taken by a new policy. Previous approaches rely either on models of rewards or models of the past policy. The former are plagued by a large bias whereas the latter have a large variance.
In this work, we leverage the strength and overcome the weaknesses of the two approaches by applying the doubly robust technique to the problems of policy evaluation and optimization. We prove that this approach yields accurate value estimates when we have either a good (but not necessarily consistent) model of rewards or a good (but not necessarily consistent) model of past policy. Extensive empirical comparison demonstrates that the doubly robust approach uniformly improves over existing techniques, achieving both lower variance in value estimation and better policies. As such, we expect the doubly robust approach to become common practice.
Vision and language understanding has emerged as a subject undergoing intense study in Artificial Intelligence. Among many tasks in this line of research, visual question answering (VQA) has been one of the most successful ones, where the goal is to learn a model that understands visual content at region-level details and finds their associations with pairs of questions and answers in the natural language form. Despite the rapid progress in the past few years, most existing work in VQA have focused primarily on images. In this paper, we focus on extending VQA to the video domain and contribute to the literature in three important ways. First, we propose three new tasks designed specifically for video VQA, which require spatio-temporal reasoning from videos to answer questions correctly. Next, we introduce a new large-scale dataset for video VQA named TGIF-QA that extends existing VQA work with our new tasks. Finally, we propose a dual-LSTM based approach with both spatial and temporal attention, and show its effectiveness over conventional VQA techniques through empirical evaluations.
We present Searn, an algorithm for integrating search and learning to solve
complex structured prediction problems such as those that occur in natural
language, speech, computational biology, and vision. Searn is a meta-algorithm
that transforms these complex problems into simple classification problems to
which any binary classifier may be applied. Unlike current algorithms for
structured learning that require decomposition of both the loss function and
the feature functions over the predicted structure, Searn is able to learn
prediction functions for any loss function and any class of features. Moreover,
Searn comes with a strong, natural theoretical guarantee: good performance on
the derived classification problems implies good performance on the structured
prediction problem.
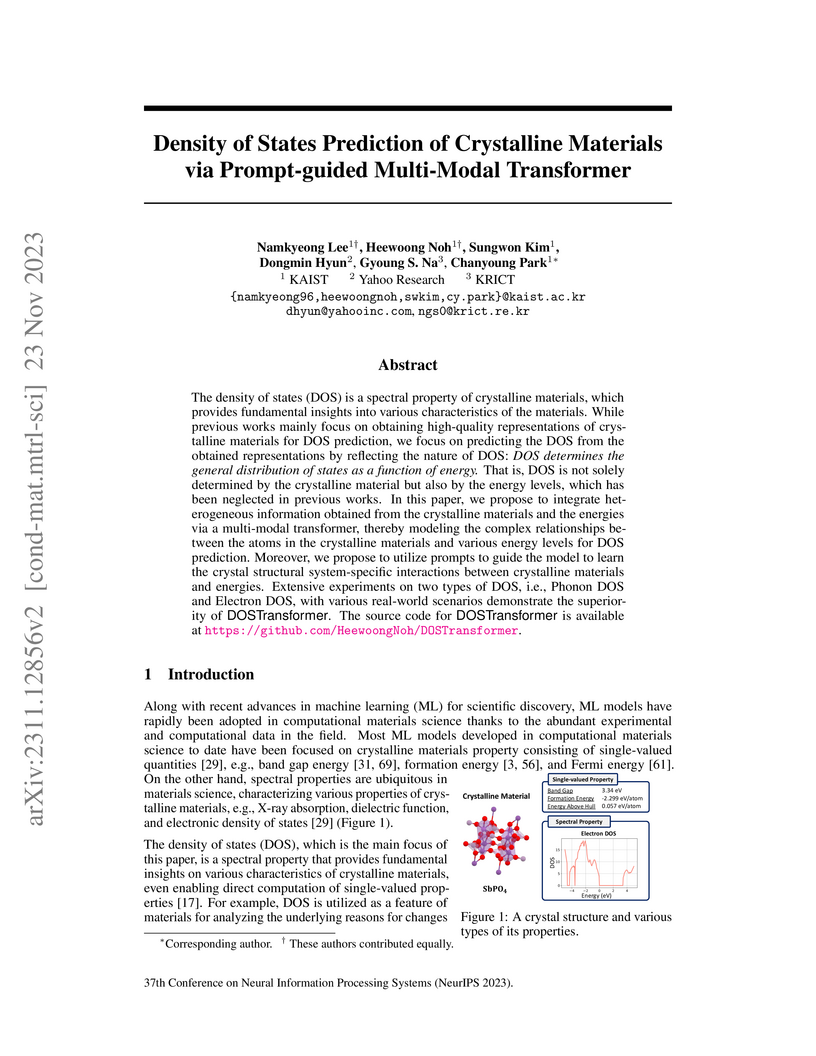
The density of states (DOS) is a spectral property of crystalline materials, which provides fundamental insights into various characteristics of the materials. While previous works mainly focus on obtaining high-quality representations of crystalline materials for DOS prediction, we focus on predicting the DOS from the obtained representations by reflecting the nature of DOS: DOS determines the general distribution of states as a function of energy. That is, DOS is not solely determined by the crystalline material but also by the energy levels, which has been neglected in previous works. In this paper, we propose to integrate heterogeneous information obtained from the crystalline materials and the energies via a multi-modal transformer, thereby modeling the complex relationships between the atoms in the crystalline materials and various energy levels for DOS prediction. Moreover, we propose to utilize prompts to guide the model to learn the crystal structural system-specific interactions between crystalline materials and energies. Extensive experiments on two types of DOS, i.e., Phonon DOS and Electron DOS, with various real-world scenarios demonstrate the superiority of DOSTransformer. The source code for DOSTransformer is available at this https URL.
 Sun Yat-Sen University
Sun Yat-Sen University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Zhejiang UniversityEast China University of Science and Technology
Zhejiang UniversityEast China University of Science and Technology Aalborg University
Aalborg University EPFLBeijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
EPFLBeijing University of Posts and Telecommunications KAUST
KAUST CEA
CEA Shandong UniversityUniversitat de BarcelonaTencent YouTu LabUCLouvainUniversity of LiègeMeituan Inc.OPPOBaidu IncBaidu ResearchGerman University in CairoYahoo ResearchL3S Research Center, Leibniz University HannoverMGTVFujitsu ResearchQCraft IncCaritas Institute of Higher EducationEVS Broadcast EquipmentSportradarSchaffhausen Institute of Technology2Ai – School of Technology IPCAInspur Electronic InformationReBatchArsenal FCTIB Leibniz Information Center for Science and Technology
Shandong UniversityUniversitat de BarcelonaTencent YouTu LabUCLouvainUniversity of LiègeMeituan Inc.OPPOBaidu IncBaidu ResearchGerman University in CairoYahoo ResearchL3S Research Center, Leibniz University HannoverMGTVFujitsu ResearchQCraft IncCaritas Institute of Higher EducationEVS Broadcast EquipmentSportradarSchaffhausen Institute of Technology2Ai – School of Technology IPCAInspur Electronic InformationReBatchArsenal FCTIB Leibniz Information Center for Science and TechnologyThe SoccerNet 2022 challenges were the second annual video understanding challenges organized by the SoccerNet team. In 2022, the challenges were composed of 6 vision-based tasks: (1) action spotting, focusing on retrieving action timestamps in long untrimmed videos, (2) replay grounding, focusing on retrieving the live moment of an action shown in a replay, (3) pitch localization, focusing on detecting line and goal part elements, (4) camera calibration, dedicated to retrieving the intrinsic and extrinsic camera parameters, (5) player re-identification, focusing on retrieving the same players across multiple views, and (6) multiple object tracking, focusing on tracking players and the ball through unedited video streams. Compared to last year's challenges, tasks (1-2) had their evaluation metrics redefined to consider tighter temporal accuracies, and tasks (3-6) were novel, including their underlying data and annotations. More information on the tasks, challenges and leaderboards are available on this https URL. Baselines and development kits are available on this https URL.
Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) aims to identify terms or multiword expressions (MWEs) on which sentiments are expressed and the sentiment polarities associated with them. The development of supervised models has been at the forefront of research in this area. However, training these models requires the availability of manually annotated datasets which is both expensive and time-consuming. Furthermore, the available annotated datasets are tailored to a specific domain, language, and text type. In this work, we address this notable challenge in current state-of-the-art ABSA research. We propose a hybrid approach for Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis using transfer learning. The approach focuses on generating weakly-supervised annotations by exploiting the strengths of both large language models (LLM) and traditional syntactic dependencies. We utilise syntactic dependency structures of sentences to complement the annotations generated by LLMs, as they may overlook domain-specific aspect terms. Extensive experimentation on multiple datasets is performed to demonstrate the efficacy of our hybrid method for the tasks of aspect term extraction and aspect sentiment classification.
Keywords: Aspect Based Sentiment Analysis, Syntactic Parsing, large language model (LLM)
With the recent surge of social networks like Facebook, new forms of
recommendations have become possible - personalized recommendations of ads,
content, and even new friend and product connections based on one's social
interactions. Since recommendations may use sensitive social information, it is
speculated that these recommendations are associated with privacy risks. The
main contribution of this work is in formalizing these expected trade-offs
between the accuracy and privacy of personalized social recommendations.
In this paper, we study whether "social recommendations", or recommendations
that are solely based on a user's social network, can be made without
disclosing sensitive links in the social graph. More precisely, we quantify the
loss in utility when existing recommendation algorithms are modified to satisfy
a strong notion of privacy, called differential privacy. We prove lower bounds
on the minimum loss in utility for any recommendation algorithm that is
differentially private. We adapt two privacy preserving algorithms from the
differential privacy literature to the problem of social recommendations, and
analyze their performance in comparison to the lower bounds, both analytically
and experimentally. We show that good private social recommendations are
feasible only for a small subset of the users in the social network or for a
lenient setting of privacy parameters.
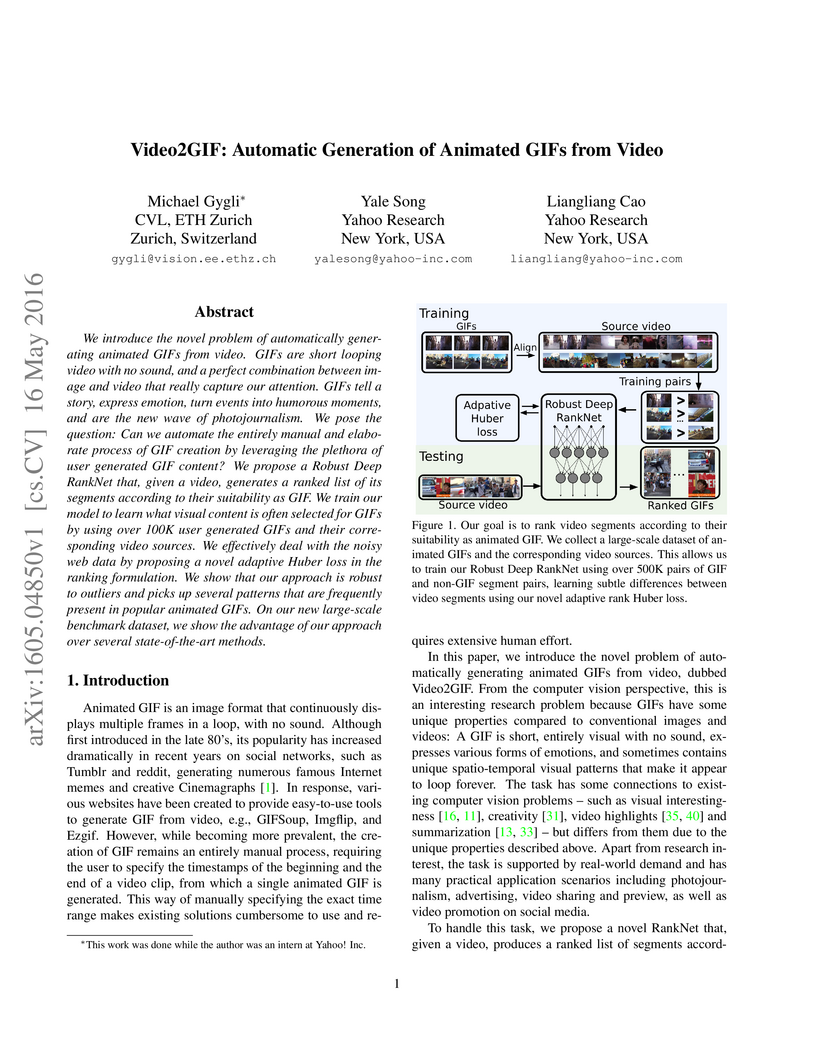
We introduce the novel problem of automatically generating animated GIFs from video. GIFs are short looping video with no sound, and a perfect combination between image and video that really capture our attention. GIFs tell a story, express emotion, turn events into humorous moments, and are the new wave of photojournalism. We pose the question: Can we automate the entirely manual and elaborate process of GIF creation by leveraging the plethora of user generated GIF content? We propose a Robust Deep RankNet that, given a video, generates a ranked list of its segments according to their suitability as GIF. We train our model to learn what visual content is often selected for GIFs by using over 100K user generated GIFs and their corresponding video sources. We effectively deal with the noisy web data by proposing a novel adaptive Huber loss in the ranking formulation. We show that our approach is robust to outliers and picks up several patterns that are frequently present in popular animated GIFs. On our new large-scale benchmark dataset, we show the advantage of our approach over several state-of-the-art methods.
Click-through rate (CTR) prediction plays a critical role in recommender systems and online advertising. The data used in these applications are multi-field categorical data, where each feature belongs to one field. Field information is proved to be important and there are several works considering fields in their models. In this paper, we proposed a novel approach to model the field information effectively and efficiently. The proposed approach is a direct improvement of FwFM, and is named as Field-matrixed Factorization Machines (FmFM, or FM2). We also proposed a new explanation of FM and FwFM within the FmFM framework, and compared it with the FFM. Besides pruning the cross terms, our model supports field-specific variable dimensions of embedding vectors, which acts as soft pruning. We also proposed an efficient way to minimize the dimension while keeping the model performance. The FmFM model can also be optimized further by caching the intermediate vectors, and it only takes thousands of floating-point operations (FLOPs) to make a prediction. Our experiment results show that it can out-perform the FFM, which is more complex. The FmFM model's performance is also comparable to DNN models which require much more FLOPs in runtime.
BlockLLM, developed by researchers at the University of British Columbia, Yahoo! Research, and ServiceNow Research, offers a memory-efficient approach for adapting large language models by dynamically selecting and optimizing only critical coordinate blocks of parameters. This method significantly reduces memory consumption during finetuning and pretraining, achieving competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art memory-efficient techniques without altering the model's architecture.
Dimension reduction is a key algorithmic tool with many applications
including nearest-neighbor search, compressed sensing and linear algebra in the
streaming model. In this work we obtain a {\em sparse} version of the
fundamental tool in dimension reduction --- the Johnson--Lindenstrauss
transform. Using hashing and local densification, we construct a sparse
projection matrix with just O~(ϵ1) non-zero entries
per column. We also show a matching lower bound on the sparsity for a large
class of projection matrices. Our bounds are somewhat surprising, given the
known lower bounds of Ω(ϵ21) both on the number of rows
of any projection matrix and on the sparsity of projection matrices generated
by natural constructions.
Using this, we achieve an O~(ϵ1) update time per
non-zero element for a (1±ϵ)-approximate projection, thereby
substantially outperforming the O~(ϵ21) update time
required by prior approaches. A variant of our method offers the same
guarantees for sparse vectors, yet its O~(d) worst case running time
matches the best approach of Ailon and Liberty.
Learning a good representation of text is key to many recommendation applications. Examples include news recommendation where texts to be recommended are constantly published everyday. However, most existing recommendation techniques, such as matrix factorization based methods, mainly rely on interaction histories to learn representations of items. While latent factors of items can be learned effectively from user interaction data, in many cases, such data is not available, especially for newly emerged items.
In this work, we aim to address the problem of personalized recommendation for completely new items with text information available. We cast the problem as a personalized text ranking problem and propose a general framework that combines text embedding with personalized recommendation. Users and textual content are embedded into latent feature space. The text embedding function can be learned end-to-end by predicting user interactions with items. To alleviate sparsity in interaction data, and leverage large amount of text data with little or no user interactions, we further propose a joint text embedding model that incorporates unsupervised text embedding with a combination module. Experimental results show that our model can significantly improve the effectiveness of recommendation systems on real-world datasets.
Empirical evidence suggests that hashing is an effective strategy for dimensionality reduction and practical nonparametric estimation. In this paper we provide exponential tail bounds for feature hashing and show that the interaction between random subspaces is negligible with high probability. We demonstrate the feasibility of this approach with experimental results for a new use case -- multitask learning with hundreds of thousands of tasks.
We consider the online sparse linear regression problem, which is the problem of sequentially making predictions observing only a limited number of features in each round, to minimize regret with respect to the best sparse linear regressor, where prediction accuracy is measured by square loss. We give an inefficient algorithm that obtains regret bounded by O~(T) after T prediction rounds. We complement this result by showing that no algorithm running in polynomial time per iteration can achieve regret bounded by O(T1−δ) for any constant δ>0 unless NP⊆BPP. This computational hardness result resolves an open problem presented in COLT 2014 (Kale, 2014) and also posed by Zolghadr et al. (2013). This hardness result holds even if the algorithm is allowed to access more features than the best sparse linear regressor up to a logarithmic factor in the dimension.
DocTag2Vec introduces an embedding-based multi-label learning approach for document tagging that jointly learns vector representations for words, documents, and tags directly from raw text. This method demonstrates competitive precision against state-of-the-art baselines on larger datasets and offers practical advantages such as incremental learning for dynamic content streams.
20 Jun 2017
Machine-learned models are often described as "black boxes". In many
real-world applications however, models may have to sacrifice predictive power
in favour of human-interpretability. When this is the case, feature engineering
becomes a crucial task, which requires significant and time-consuming human
effort. Whilst some features are inherently static, representing properties
that cannot be influenced (e.g., the age of an individual), others capture
characteristics that could be adjusted (e.g., the daily amount of carbohydrates
taken). Nonetheless, once a model is learned from the data, each prediction it
makes on new instances is irreversible - assuming every instance to be a static
point located in the chosen feature space. There are many circumstances however
where it is important to understand (i) why a model outputs a certain
prediction on a given instance, (ii) which adjustable features of that instance
should be modified, and finally (iii) how to alter such a prediction when the
mutated instance is input back to the model. In this paper, we present a
technique that exploits the internals of a tree-based ensemble classifier to
offer recommendations for transforming true negative instances into positively
predicted ones. We demonstrate the validity of our approach using an online
advertising application. First, we design a Random Forest classifier that
effectively separates between two types of ads: low (negative) and high
(positive) quality ads (instances). Then, we introduce an algorithm that
provides recommendations that aim to transform a low quality ad (negative
instance) into a high quality one (positive instance). Finally, we evaluate our
approach on a subset of the active inventory of a large ad network, Yahoo
Gemini.
Model training algorithms which observe a small portion of the training set
in each computational step are ubiquitous in practical machine learning, and
include both stochastic and online optimization methods. In the vast majority
of cases, such algorithms typically observe the training samples via the
gradients of the cost functions the samples incur. Thus, these methods exploit
are the slope of the cost functions via their first-order approximations. To
address limitations of gradient-based methods, such as sensitivity to step-size
choice in the stochastic setting, or inability to use small function
variability in the online setting, several streams of research attempt to
exploit more information about the cost functions than just their gradients via
the well-known proximal operators. However, implementing such methods in
practice poses a challenge, since each iteration step boils down to computing
the proximal operator, which may not be easy. In this work we devise a novel
algorithmic framework, which exploits convex duality theory to achieve both
algorithmic efficiency and software modularity of proximal operator
implementations, in order to make experimentation with incremental proximal
optimization algorithms accessible to a larger audience of researchers and
practitioners, by reducing the gap between their theoretical description in
research papers and their use in practice. We provide a reference Python
implementation for the framework developed in this paper as an open source
library at on
https://github.com/alexshtf/inc_prox_pt/releases/tag/prox_pt_paper, along with
examples which demonstrate our implementation on a variety of problems, and
reproduce the numerical experiments in this paper. The pure Python reference
implementation is not necessarily the most efficient, but is a basis for
creating efficient implementations by combining Python with a native backend.
Researchers from Yahoo Research and the University at Buffalo, SUNY, developed SCOT, a self-supervised pretraining strategy for zero-shot compositional image retrieval (CIR). This method utilizes large language models (LLMs) to synthesize text-based supervision and pre-trained vision-language models (VLMs) to train a composition network, demonstrating state-of-the-art performance on zero-shot CIR datasets like FashionIQ and CIRR without requiring human-annotated triplets.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.