Yanshan University
The C2P-CLIP method enhances deepfake detection by injecting category-common prompts into a fine-tuned CLIP model, achieving a mean accuracy of 93.79% and mAP of 98.66% on the UniversalFakeDetect dataset, a substantial 12.41% and 8.52% improvement over baseline UniFd, respectively, without adding inference parameters. This approach leverages an understanding that CLIP detects forgeries by matching similar concepts rather than semantic content.
GuideFlow is an end-to-end autonomous driving planner that employs a constrained flow matching architecture to generate diverse and inherently safe trajectories. It achieves state-of-the-art performance with an EPDMS of 43.0 on NavSim, significantly lower collision rates (0.07% on NuScenes), and strong closed-loop driving scores on Bench2Drive.
A new framework for end-to-end autonomous driving, CATG, leverages Flow Matching to generate diverse, inherently constrained trajectories, overcoming the limitations of imitation learning. It demonstrated robust performance in the ICCV NAVSIM V2 End-to-End Driving Challenge, securing 2nd place and an Innovation Award while achieving 100% Drivable Area Compliance in initial tests.
03 Oct 2025
KGCompass, a framework developed by researchers across four universities, enhances repository-level software repair by integrating repository-aware knowledge graphs (KGs) with Large Language Models. It achieves 58.3% repair accuracy and 56.0% function-level fault localization on SWE-bench Lite with Claude-4 Sonnet, notably outperforming pure LLM baselines at an average cost of $0.2 per repair.
Recently, the proliferation of highly realistic synthetic images, facilitated through a variety of GANs and Diffusions, has significantly heightened the susceptibility to misuse. While the primary focus of deepfake detection has traditionally centered on the design of detection algorithms, an investigative inquiry into the generator architectures has remained conspicuously absent in recent years. This paper contributes to this lacuna by rethinking the architectures of CNN-based generators, thereby establishing a generalized representation of synthetic artifacts. Our findings illuminate that the up-sampling operator can, beyond frequency-based artifacts, produce generalized forgery artifacts. In particular, the local interdependence among image pixels caused by upsampling operators is significantly demonstrated in synthetic images generated by GAN or diffusion. Building upon this observation, we introduce the concept of Neighboring Pixel Relationships(NPR) as a means to capture and characterize the generalized structural artifacts stemming from up-sampling operations. A comprehensive analysis is conducted on an open-world dataset, comprising samples generated by \tft{28 distinct generative models}. This analysis culminates in the establishment of a novel state-of-the-art performance, showcasing a remarkable \tft{11.6\%} improvement over existing methods. The code is available at this https URL.
FreqNet is a deepfake detection framework that enhances generalizability by learning directly within the frequency domain, rather than merely analyzing frequency features. The method integrates high-frequency representations and frequency convolutional layers, achieving state-of-the-art accuracy across diverse, unseen GAN models with significantly fewer parameters than previous approaches.
04 Dec 2025
Large language models (LLMs) are reshaping automated program repair. We present a unified taxonomy that groups 62 recent LLM-based repair systems into four paradigms defined by parameter adaptation and control authority over the repair loop, and overlays two cross-cutting layers for retrieval and analysis augmentation. Prior surveys have either focused on classical software repair techniques, on LLMs in software engineering more broadly, or on subsets of LLM-based software repair, such as fine-tuning strategies or vulnerability repair. We complement these works by treating fine-tuning, prompting, procedural pipelines, and agentic frameworks as first-class paradigms and systematically mapping representative systems to each of these paradigms. We also consolidate evaluation practice on common benchmarks by recording benchmark scope, pass@k, and fault-localization assumptions to support a more meaningful comparison of reported success rates. We clarify trade-offs among paradigms in task alignment, deployment cost, controllability, and ability to repair multi-hunk or cross-file bugs. We discuss challenges in current LLM-based software repair and outline research directions. Our artifacts, including the representation papers and scripted survey pipeline, are publicly available at this https URL.
Most existing bundle generation approaches fall short in generating
fixed-size bundles. Furthermore, they often neglect the underlying user intents
reflected by the bundles in the generation process, resulting in less
intelligible bundles. This paper addresses these limitations through the
exploration of two interrelated tasks, i.e., personalized bundle generation and
the underlying intent inference, based on different user sessions. Inspired by
the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs), we propose an
adaptive in-context learning paradigm, which allows LLMs to draw tailored
lessons from related sessions as demonstrations, enhancing the performance on
target sessions. Specifically, we first employ retrieval augmented generation
to identify nearest neighbor sessions, and then carefully design prompts to
guide LLMs in executing both tasks on these neighbor sessions. To tackle
reliability and hallucination challenges, we further introduce (1) a
self-correction strategy promoting mutual improvements of the two tasks without
supervision signals and (2) an auto-feedback mechanism for adaptive supervision
based on the distinct mistakes made by LLMs on different neighbor sessions.
Thereby, the target session can gain customized lessons for improved
performance by observing the demonstrations of its neighbor sessions.
Experiments on three real-world datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our
proposed method.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are emerging as promising approaches to enhance session-based recommendation (SBR), where both prompt-based and fine-tuning-based methods have been widely investigated to align LLMs with SBR. However, the former methods struggle with optimal prompts to elicit the correct reasoning of LLMs due to the lack of task-specific feedback, leading to unsatisfactory recommendations. Although the latter methods attempt to fine-tune LLMs with domain-specific knowledge, they face limitations such as high computational costs and reliance on open-source backbones. To address such issues, we propose a Reflective Reinforcement Large Language Model (Re2LLM) for SBR, guiding LLMs to focus on specialized knowledge essential for more accurate recommendations effectively and efficiently. In particular, we first design the Reflective Exploration Module to effectively extract knowledge that is readily understandable and digestible by LLMs. To be specific, we direct LLMs to examine recommendation errors through self-reflection and construct a knowledge base (KB) comprising hints capable of rectifying these errors. To efficiently elicit the correct reasoning of LLMs, we further devise the Reinforcement Utilization Module to train a lightweight retrieval agent. It learns to select hints from the constructed KB based on the task-specific feedback, where the hints can serve as guidance to help correct LLMs reasoning for better recommendations. Extensive experiments on multiple real-world datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
27 Oct 2025
With the rapid advancement of large language models (LLMs) and robotics, service robots are increasingly becoming an integral part of daily life, offering a wide range of services in complex environments. To deliver these services intelligently and efficiently, robust and accurate task planning capabilities are essential. This paper presents a comprehensive overview of the integration of LLMs into service robotics, with a particular focus on their role in enhancing robotic task planning. First, the development and foundational techniques of LLMs, including pre-training, fine-tuning, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and prompt engineering, are reviewed. We then explore the application of LLMs as the cognitive core-`brain'-of service robots, discussing how LLMs contribute to improved autonomy and decision-making. Furthermore, recent advancements in LLM-driven task planning across various input modalities are analyzed, including text, visual, audio, and multimodal inputs. Finally, we summarize key challenges and limitations in current research and propose future directions to advance the task planning capabilities of service robots in complex, unstructured domestic environments. This review aims to serve as a valuable reference for researchers and practitioners in the fields of artificial intelligence and robotics.
21 Sep 2025
Within the realm of software engineering, specialized tasks on code, such as program repair, present unique challenges, necessitating fine-tuning Large language models~(LLMs) to unlock state-of-the-art performance. Fine-tuning approaches proposed in the literature for LLMs on program repair tasks generally overlook the need to reason about the logic behind code changes, beyond syntactic patterns in the data. High-performing fine-tuning experiments also usually come at very high computational costs. With MORepair, we propose a novel perspective on the learning focus of LLM fine-tuning for program repair: we not only adapt the LLM parameters to the syntactic nuances of the task of code transformation (objective 1), but we also specifically fine-tune the LLM with respect to the logical reason behind the code change in the training data (objective 2). Such a multi-objective fine-tuning will instruct LLMs to generate high-quality patches. We apply MORepair to fine-tune four open-source LLMs with different sizes and architectures. Experimental results on function-level and repository-level repair benchmarks show that the implemented fine-tuning effectively boosts LLM repair performance by 11.4% to 56.0%. We further show that our fine-tuning strategy yields superior performance compared to the state-of-the-art approaches, including standard fine-tuning, Fine-tune-CoT, and RepairLLaMA.
CausalMed introduces a patient health state-centric framework for personalized medication recommendation, which employs causal inference to establish direct, point-to-point relationships between diseases/procedures and medications. The system achieves superior accuracy and safety compared to existing methods on MIMIC-III and MIMIC-IV datasets, providing more interpretable recommendations.
Visible and infrared image fusion (VIF) is an important multimedia task in computer vision. Most VIF methods focus primarily on optimizing fused image quality. Recent studies have begun incorporating downstream tasks, such as semantic segmentation and object detection, to provide semantic guidance for VIF. However, semantic segmentation requires extensive annotations, while object detection, despite reducing annotation efforts compared with segmentation, faces challenges in highly crowded scenes due to overlapping bounding boxes and occlusion. Moreover, although RGB-T crowd counting has gained increasing attention in recent years, no studies have integrated VIF and crowd counting into a unified framework. To address these challenges, we propose FusionCounting, a novel multi-task learning framework that integrates crowd counting into the VIF process. Crowd counting provides a direct quantitative measure of population density with minimal annotation, making it particularly suitable for dense scenes. Our framework leverages both input images and population density information in a mutually beneficial multi-task design. To accelerate convergence and balance tasks contributions, we introduce a dynamic loss function weighting strategy. Furthermore, we incorporate adversarial training to enhance the robustness of both VIF and crowd counting, improving the model's stability and resilience to adversarial attacks. Experimental results on public datasets demonstrate that FusionCounting not only enhances image fusion quality but also achieves superior crowd counting performance.
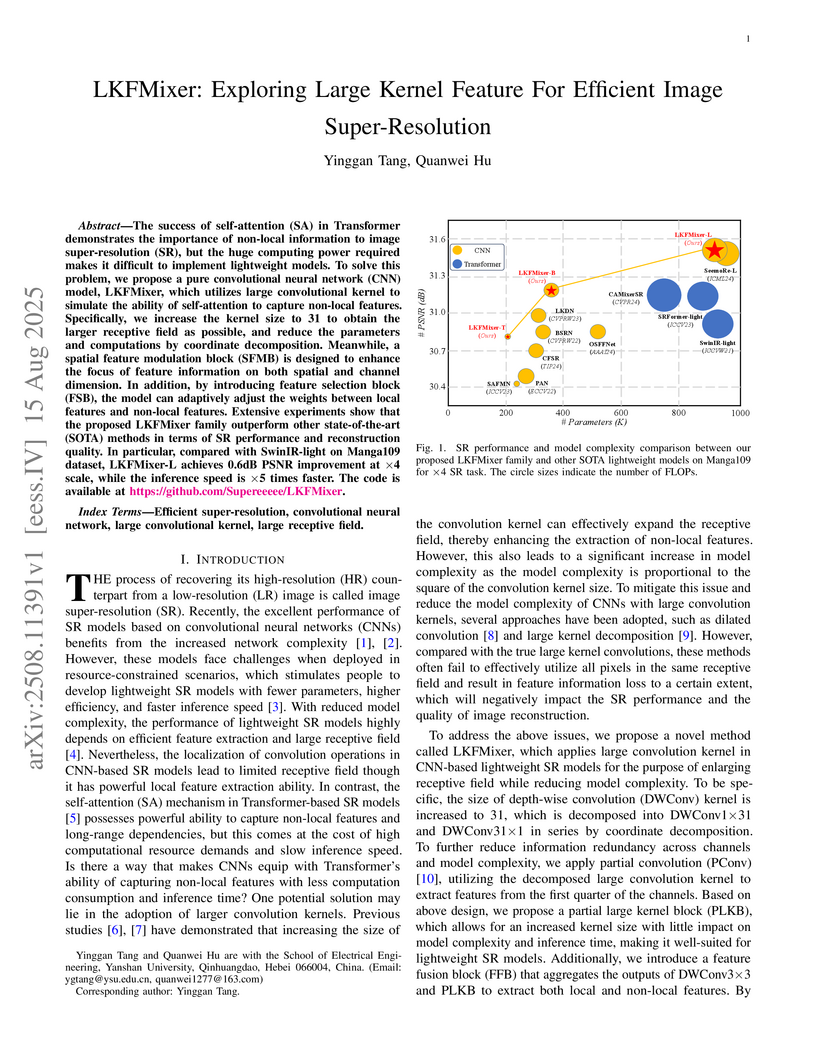
The success of self-attention (SA) in Transformer demonstrates the importance of non-local information to image super-resolution (SR), but the huge computing power required makes it difficult to implement lightweight models. To solve this problem, we propose a pure convolutional neural network (CNN) model, LKFMixer, which utilizes large convolutional kernel to simulate the ability of self-attention to capture non-local features. Specifically, we increase the kernel size to 31 to obtain the larger receptive field as possible, and reduce the parameters and computations by coordinate decomposition. Meanwhile, a spatial feature modulation block (SFMB) is designed to enhance the focus of feature information on both spatial and channel dimension. In addition, by introducing feature selection block (FSB), the model can adaptively adjust the weights between local features and non-local features. Extensive experiments show that the proposed LKFMixer family outperform other state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods in terms of SR performance and reconstruction quality. In particular, compared with SwinIR-light on Manga109 dataset, LKFMixer-L achieves 0.6dB PSNR improvement at ×4 scale, while the inference speed is ×5 times faster. The code is available at this https URL.
24 Feb 2025
Air-ground collaborative robots have shown great potential in the field of
fire and rescue, which can quickly respond to rescue needs and improve the
efficiency of task execution. Mapping and navigation, as the key foundation for
air-ground collaborative robots to achieve efficient task execution, have
attracted a great deal of attention. This growing interest in collaborative
robot mapping and navigation is conducive to improving the intelligence of fire
and rescue task execution, but there has been no comprehensive investigation of
this field to highlight their strengths. In this paper, we present a systematic
review of the ground-to-ground cooperative robots for fire and rescue from a
new perspective of mapping and navigation. First, an air-ground collaborative
robots framework for fire and rescue missions based on unmanned aerial vehicle
(UAV) mapping and unmanned ground vehicle (UGV) navigation is introduced. Then,
the research progress of mapping and navigation under this framework is
systematically summarized, including UAV mapping, UAV/UGV co-localization, and
UGV navigation, with their main achievements and limitations. Based on the
needs of fire and rescue missions, the collaborative robots with different
numbers of UAVs and UGVs are classified, and their practicality in fire and
rescue tasks is elaborated, with a focus on the discussion of their merits and
demerits. In addition, the application examples of air-ground collaborative
robots in various firefighting and rescue scenarios are given. Finally, this
paper emphasizes the current challenges and potential research opportunities,
rounding up references for practitioners and researchers willing to engage in
this vibrant area of air-ground collaborative robots.
29 Jul 2025
Conformance testing is essential for ensuring that protocol implementations comply with their specifications. However, traditional testing approaches involve manually creating numerous test cases and scripts, making the process labor-intensive and inefficient. Recently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive text comprehension and code generation abilities, providing promising opportunities for automation. In this paper, we propose iPanda, the first framework that leverages LLMs to automate protocol conformance testing. Given a protocol specification document and its implementation, iPanda first employs a keyword-based method to automatically generate comprehensive test cases. Then, it utilizes retrieval-augmented generation and customized CoT strategy to effectively interpret the implementation and produce executable test programs. To further enhance programs' quality, iPanda incorporates an iterative optimization mechanism to refine generated test scripts interactively. Finally, by executing and analyzing the generated tests, iPanda systematically verifies compliance between implementations and protocol specifications. Comprehensive experiments on various protocols show that iPanda significantly outperforms pure LLM-based approaches, improving the success rate (Pass@1) of test-program generation by factors ranging from 4.675 times to 10.751 times.
12 Jun 2025
Next Point-of-Interest (POI) recommendation is a critical task in
location-based services, aiming to predict users' next visits based on their
check-in histories. While many existing methods leverage Graph Neural Networks
(GNNs) to incorporate collaborative information and improve recommendation
accuracy, most of them model each type of context using separate graphs,
treating different factors in isolation. This limits their ability to model the
co-influence of multiple contextual factors on user transitions during message
propagation, resulting in suboptimal attention weights and recommendation
performance. Furthermore, they often prioritize sequential components as the
primary predictor, potentially undermining the semantic and structural
information encoded in the POI embeddings learned by GNNs. To address these
limitations, we propose a Context-Adaptive Graph Neural Networks (CAGNN) for
next POI recommendation, which dynamically adjusts attention weights using
edge-specific contextual factors and enables mutual enhancement between
graph-based and sequential components. Specifically, CAGNN introduces (1) a
context-adaptive attention mechanism that jointly incorporates different types
of contextual factors into the attention computation during graph propagation,
enabling the model to dynamically capture collaborative and context-dependent
transition patterns; (2) a graph-sequential mutual enhancement module, which
aligns the outputs of the graph- and sequential-based modules via the KL
divergence, enabling mutual enhancement of both components. Experimental
results on three real-world datasets demonstrate that CAGNN consistently
outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Meanwhile, theoretical guarantees are
provided that our context-adaptive attention mechanism improves the
expressiveness of POI representations.
15 Oct 2025
Inspired by the recent experimental progress in pyrochlore derivative \ce{RE3Sb3A2O14 (A=Mg, Zn)}, we investigate the Hubbard model on the kagome lattice with an additional hopping t′/t, which enables continuous interpolation between the kagome and triangular lattices by using determinant quantum Monte Carlo simulations. We analyze the evolution of magnetic correlations and thermodynamic responses across different values of t′/t and on-site interaction U. It is found that increasing t′/t suppresses short-range antiferromagnetic correlations, while the next-nearest-neighbor correlations exhibit a sign change near t′/t≈0.3–0.4. Within this regime, the specific heat shows a pronounced low-temperature peak, indicating an emergent spin-related energy scale. Increasing U enhances magnetic correlations and shifts the associated t′/t crossover points to larger values. We also discuss the sign problem to clarify which parameter region of our numerical simulations is accessible and reliable. Our results uncover the competition between frustration and correlations and the interplay of magnetic and thermodynamic responses in the kagome lattice, providing insights into correlated states in frustrated materials.
08 Nov 2024
During the process of driving, humans usually rely on multiple senses to gather information and make decisions. Analogously, in order to achieve embodied intelligence in autonomous driving, it is essential to integrate multidimensional sensory information in order to facilitate interaction with the environment. However, the current multi-modal fusion sensing schemes often neglect these additional sensory inputs, hindering the realization of fully autonomous driving. This paper considers multi-sensory information and proposes a multi-modal interactive perception dataset named MIPD, enabling expanding the current autonomous driving algorithm framework, for supporting the research on embodied intelligent driving. In addition to the conventional camera, lidar, and 4D radar data, our dataset incorporates multiple sensor inputs including sound, light intensity, vibration intensity and vehicle speed to enrich the dataset comprehensiveness. Comprising 126 consecutive sequences, many exceeding twenty seconds, MIPD features over 8,500 meticulously synchronized and annotated frames. Moreover, it encompasses many challenging scenarios, covering various road and lighting conditions. The dataset has undergone thorough experimental validation, producing valuable insights for the exploration of next-generation autonomous driving frameworks.
Membership inference (MI) attacks threaten user privacy through determining if a given data example has been used to train a target model. However, it has been increasingly recognized that the "comparing different MI attacks" methodology used in the existing works has serious limitations. Due to these limitations, we found (through the experiments in this work) that some comparison results reported in the literature are quite misleading. In this paper, we seek to develop a comprehensive benchmark for comparing different MI attacks, called MIBench, which consists not only the evaluation metrics, but also the evaluation scenarios. And we design the evaluation scenarios from four perspectives: the distance distribution of data samples in the target dataset, the distance between data samples of the target dataset, the differential distance between two datasets (i.e., the target dataset and a generated dataset with only nonmembers), and the ratio of the samples that are made no inferences by an MI attack. The evaluation metrics consist of ten typical evaluation metrics. We have identified three principles for the proposed "comparing different MI attacks" methodology, and we have designed and implemented the MIBench benchmark with 84 evaluation scenarios for each dataset. In total, we have used our benchmark to fairly and systematically compare 15 state-of-the-art MI attack algorithms across 588 evaluation scenarios, and these evaluation scenarios cover 7 widely used datasets and 7 representative types of models. All codes and evaluations of MIBench are publicly available at this https URL.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.