Ask or search anything...
pi3 presents a permutation-equivariant architecture for visual geometry learning that completely removes the reliance on a fixed reference view. The model achieves state-of-the-art performance across camera pose, depth, and point map estimation, demonstrating superior robustness to input image order and efficiency.
View blogP³-SAM, developed by Tencent Hunyuan and academic collaborators, introduces a native 3D point-promptable part segmentation model trained on a new 3.7 million model dataset, achieving fully automatic and precise segmentation of complex 3D objects. This approach bypasses limitations of 2D-dependent methods, leading to superior quantitative performance and robust generalization.
View blogG G ²VLM integrates 3D reconstruction and spatial reasoning within a single Vision-Language Model, addressing the spatial intelligence limitations of current VLMs. It learns explicit visual geometry from 2D data using a Mixture-of-Transformer-Experts architecture, leading to robust spatial understanding and strong performance on both 3D reconstruction and complex spatial reasoning benchmarks.
View blogHoloCine, developed by Ant Group and HKUST, generates coherent, cinematic multi-shot long video narratives from hierarchical text prompts. The framework introduces architectural innovations to maintain global consistency and directorial control while achieving computational efficiency, outperforming prior text-to-video approaches in narrative fidelity and consistency for minute-scale videos.
View blogReward Forcing introduces EMA-Sink and Rewarded Distribution Matching Distillation (Re-DMD) to enable efficient, real-time streaming video generation. This framework achieves an overall VBench score of 84.13 and a generation speed of 23.1 FPS, while significantly enhancing motion dynamics and maintaining long-horizon consistency.
View blogResearchers from HKUST(GZ), Kuaishou, and Ant Group introduced Minimal Test-Time Intervention (MTI), a training-free framework that enhances large language model reasoning accuracy and stability. MTI achieves this by selectively applying Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) only at highly uncertain tokens, utilizing a lightweight negative-prompt mechanism for efficiency.
View blogSJTU, USTC, Tsinghua, and Shanghai AI Lab researchers develop DeepVerse, a 4D autoregressive world model that generates video sequences by explicitly incorporating depth maps and camera poses alongside visual observations through a composite state representation and geometry-aware memory mechanism, addressing core limitations of visual-only approaches including scale ambiguity and temporal drift by training on 10 million synthetic game frames with precise geometric annotations and achieving superior performance in VBench consistency metrics while enabling long-horizon predictions through a sliding window approach that maintains global coordinate alignment across extended sequences.
View blogA comprehensive framework called General-Level introduces a 5-level taxonomy for evaluating multimodal large language models (MLLMs), accompanied by General-Bench - a large-scale benchmark testing diverse modalities and tasks, revealing that even leading models like GPT-4V achieve only Level-3 capabilities while demonstrating limited cross-modal synergy.
View blogResearchers from Australian National University, University of Sydney, Tencent, and other institutions developed "Motion Anything," a framework for human motion generation that adaptively integrates multimodal conditions like text and music. It employs an attention-based masking strategy to dynamically prioritize motion segments, outperforming prior models in text-to-motion (e.g., 15% lower FID on HumanML3D) and music-to-dance tasks, and introduces a new Text-Music-Dance dataset.
View blogThe paper "Keeping Yourself is Important in Downstream Tuning Multimodal Large Language Model" provides a systematic review and unified benchmark for tuning MLLMs, classifying methods into Selective, Additive, and Reparameterization paradigms. It empirically analyzes the trade-offs between task-expert specialization and open-world stabilization, offering practical guidelines for MLLM deployment.
View blogMagicQuill V2 introduces a layered composition paradigm for precise, interactive image editing, integrating state-of-the-art diffusion transformers with granular control mechanisms. This system, developed by researchers at HKUST and Ant Group, integrates user-provided foreground pieces with context awareness, precisely adheres to visual cues (edges, colors), and achieves superior local editing and object removal, demonstrating a 68.5% user preference rate over baselines.
View blogBlendedMVS introduces a large-scale dataset for Multi-view Stereo (MVS) that leverages real-world 3D meshes and a novel frequency-domain image blending technique to provide geometrically consistent and visually realistic training data. Training MVS networks on BlendedMVS significantly improves their generalization ability to diverse, real-world scenes like Tanks and Temples, outperforming models trained on existing datasets.
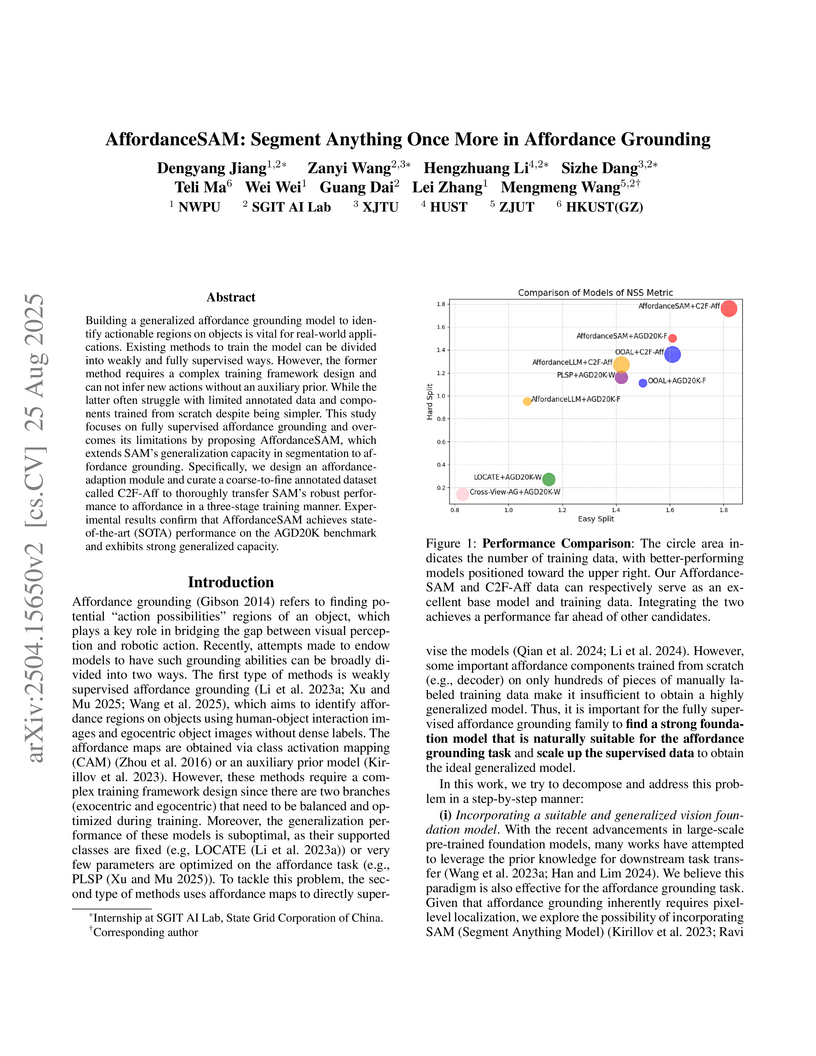
View blogAffordanceSAM adapts the Segment Anything Model (SAM) for affordance grounding, integrating a specialized adaptation module and a coarse-to-fine training scheme. The framework achieves state-of-the-art performance on the AGD20K benchmark and demonstrates robust generalization to novel objects and actions.
View blogResearchers at Shanghai AI Lab developed SPA, a framework that imbues 2D Vision Transformers with 3D spatial awareness using differentiable neural rendering from multi-view images. It achieves superior performance across 268 embodied AI tasks and generalizes to real-world robot manipulation by effectively capturing 3D spatial relationships.
View blog

 UCLA
UCLA CUHK
CUHK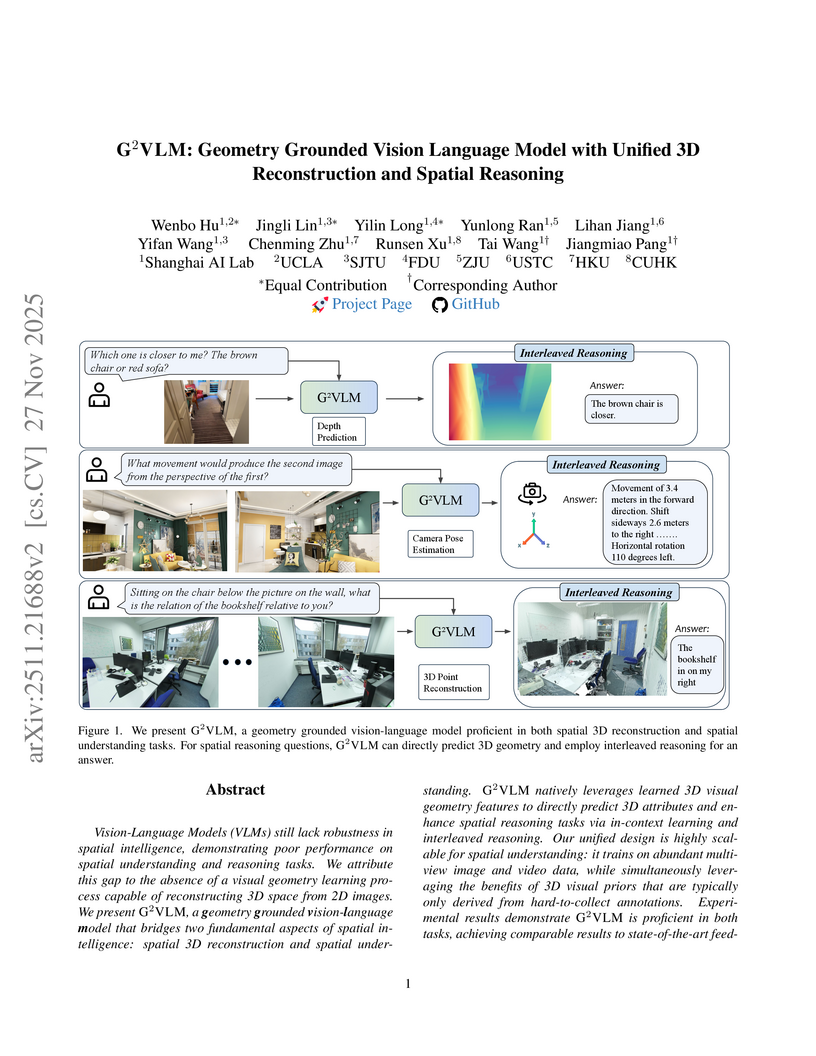


 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University



 HKUST
HKUST


 Google
Google
 Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University