Amazon AGI
03 Jul 2025
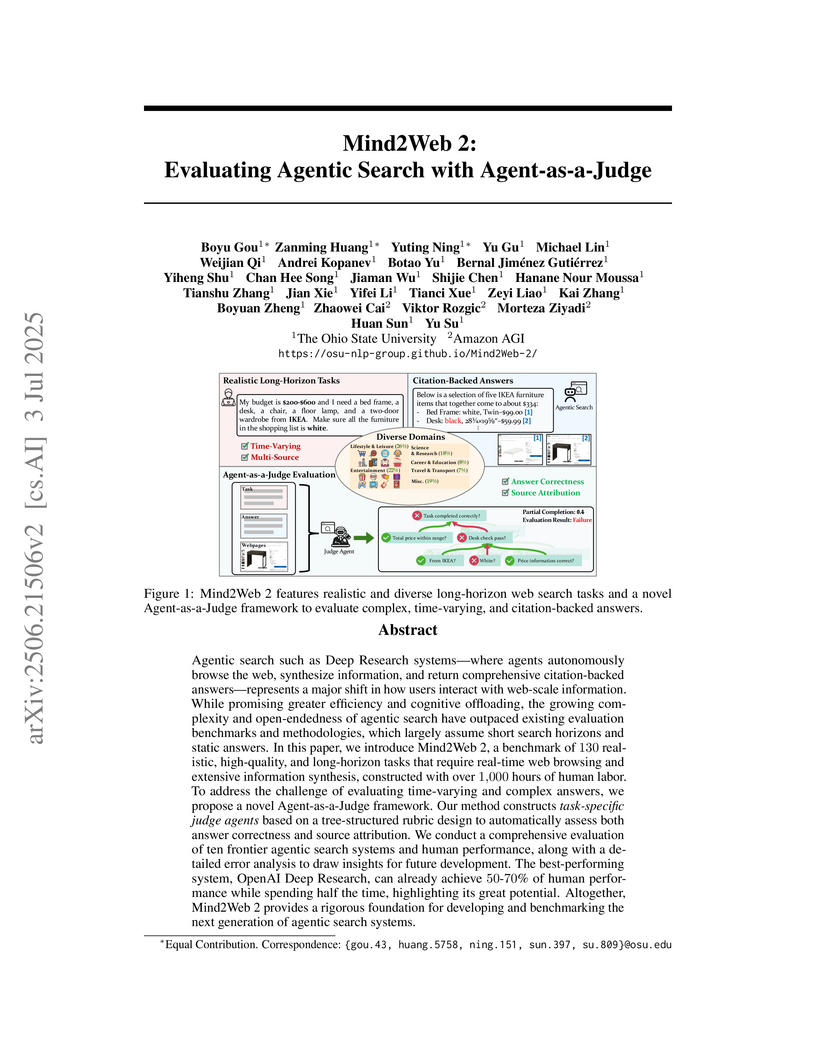
Mind2Web 2 introduces a benchmark for evaluating agentic search systems on realistic, long-horizon, time-varying web tasks. The paper also proposes an 'Agent-as-a-Judge' framework for scalable and reliable automated evaluation of complex, synthesized answers, which achieved 99% correctness against human judgment.
13 Feb 2025
The paper introduces PrefEval, a benchmark for evaluating large language models' ability to recognize, remember, and apply user preferences in long conversational contexts. It demonstrates that while current LLMs exhibit rapid degradation in preference following with increased conversation length, supervised fine-tuning on the PrefEval dataset can dramatically improve this capability, maintaining high accuracy even in extended dialogues.
23 Oct 2025
Recent trends in test-time scaling for reasoning models (e.g., OpenAI o1, DeepSeek R1) have led to a popular belief that extending thinking traces using prompts like "Wait" or "Let me rethink" can improve performance. This raises a natural question: Does thinking more at test-time truly lead to better reasoning? To answer this question, we perform a detailed empirical study across models and benchmarks, which reveals a consistent pattern of initial performance improvements from additional thinking followed by a decline, due to "overthinking". To understand this non-monotonic trend, we consider a simple probabilistic model, which reveals that additional thinking increases output variance-creating an illusion of improved reasoning while ultimately undermining precision. Thus, observed gains from "more thinking" are not true indicators of improved reasoning, but artifacts stemming from the connection between model uncertainty and evaluation metric. This suggests that test-time scaling through extended thinking is not an effective way to utilize the inference thinking budget. Recognizing these limitations, we introduce an alternative test-time scaling approach, parallel thinking, inspired by Best-of-N sampling. Our method generates multiple independent reasoning paths within the same inference budget and selects the most consistent response via majority vote, achieving up to 20% higher accuracy compared to extended thinking. This provides a simple yet effective mechanism for test-time scaling of reasoning models.
Imperial College London researchers developed Failure-Aware Inverse Reinforcement Learning (FA-IRL) to extract more faithful and interpretable reward functions from Large Language Models (LLMs) trained with human feedback. This method leverages 'failures' in preference data to reduce reward function ambiguity by up to 24% and produces reward signals that lead to more effective downstream LLM re-alignment, decreasing toxicity rates to approximately 6%.
Wanda++ proposes a lightweight post-training pruning framework for large language models that leverages regional gradients and block-level optimization to significantly reduce perplexity and improve zero-shot accuracy on downstream tasks. The method achieves performance gains while maintaining high computational efficiency, pruning a 7B LLM in under 10 minutes on a single H100 GPU.
08 Oct 2025
The objectives that Large Language Models (LLMs) implicitly optimize remain dangerously opaque, making trustworthy alignment and auditing a grand challenge. While Inverse Reinforcement Learning (IRL) can infer reward functions from behaviour, existing approaches either produce a single, overconfident reward estimate or fail to address the fundamental ambiguity of the task (non-identifiability). This paper introduces a principled auditing framework that re-frames reward inference from a simple estimation task to a comprehensive process for verification. Our framework leverages Bayesian IRL to not only recover a distribution over objectives but to enable three critical audit capabilities: (i) Quantifying and systematically reducing non-identifiability by demonstrating posterior contraction over sequential rounds of evidence; (ii) Providing actionable, uncertainty-aware diagnostics that expose spurious shortcuts and identify out-of-distribution prompts where the inferred objective cannot be trusted; and (iii) Validating policy-level utility by showing that the refined, low-uncertainty reward can be used directly in RLHF to achieve training dynamics and toxicity reductions comparable to the ground-truth alignment process. Empirically, our framework successfully audits a detoxified LLM, yielding a well-calibrated and interpretable objective that strengthens alignment guarantees. Overall, this work provides a practical toolkit for auditors, safety teams, and regulators to verify what LLMs are truly trying to achieve, moving us toward more trustworthy and accountable AI.
Unified architectures in multimodal large language models (MLLM) have shown promise in handling diverse tasks within a single framework. In the text-to-speech (TTS) task, current MLLM-based approaches rely on discrete token representations, which disregard the inherently continuous nature of speech and can lead to loss of fine-grained acoustic information. In this work, we investigate the TTS within the MLLM paradigm using continuous speech representations. We design a dual-head architecture and implement two complementary training strategies for a robust model. (1) A diffusion head generating continuous speech representations is added on the MLLM, which is on frame-level and strictly autoregressive. (2) The original language model head is retained to preserve multitask capability and to control the start and end of speech synthesis. (3) Masked training is employed to address exposure bias in autoregressive decoding. (4) To stabilize optimization, we propose a two-stage scheme where the LM is frozen in the second stage, ensuring the diffusion head learns from a fixed input distribution. Evaluations on LibriSpeech(PC) test-clean show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art autoregressive performance, with a WER of 1.95%, speaker similarity of 0.54, and UTMOS of 4.00. The two-stage training yields a 46% relative WER reduction over the one-stage training baseline. These results highlight the effectiveness of combining autoregressive modeling with continuous-token diffusion, supported by a two-stage training procedure.
Language models have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in reasoning tasks through test-time scaling techniques like best-of-N sampling and tree search. However, these approaches often demand substantial computational resources, creating a critical trade-off between performance and efficiency. We introduce STAND (STochastic Adaptive N-gram Drafting), a novel model-free speculative decoding approach that exploits the inherent redundancy in reasoning trajectories to achieve significant acceleration without compromising accuracy. Our analysis shows that reasoning paths frequently reuse similar reasoning patterns, enabling efficient model-free token prediction without requiring separate draft models. By introducing stochastic drafting and preserving probabilistic information through a memory-efficient logit-based N-gram module, combined with optimized Gumbel-Top-K sampling and data-driven tree construction, STAND significantly improves token acceptance rates. Extensive evaluations across multiple models and reasoning tasks (AIME-2024, GPQA-Diamond, and LiveCodeBench) demonstrate that STAND reduces inference latency by 60-65% compared to standard autoregressive decoding while maintaining accuracy. Furthermore, STAND consistently outperforms state-of-the-art speculative decoding methods across diverse inference patterns, including single-trajectory decoding, batch decoding, and test-time tree search. As a model-free approach, STAND can be applied to any existing language model without additional training, making it a powerful plug-and-play solution for accelerating language model reasoning.
We introduce PHLoRA (Pronounced "flora"). (Post-hoc LoRA), a simple yet powerful method to extract low-rank adaptation adapters from full-rank fine-tuned models without requiring access to training data or gradients. By computing the low-rank decomposition of weight differences between a base model and its fine-tuned counterpart, our method reconstructs adapter modules that can be merged or dynamically routed at inference time via S-LoRA, or served in scalable, industry settings using platforms like NVIDIA NIM. This approach amortizes latency overhead across requests and yields substantial cost savings. Unlike prior work that trains each adapter explicitly, our approach decouples fine-tuning from adapter generation, allowing adapter extraction from existing full-rank models or third-party checkpoints. Experiments on text, image, and video benchmarks using the Amazon Nova model family demonstrate that extracted adapters preserve high energy from the full weight delta, can be pruned safely, and yield negligible degradation in downstream task performance when re-merged. Overall, PHLoRA provides a practical path for making all existing full-rank checkpoints adapter-ready, democratizing scalable inference for all models.
A test-time token pruning method enhances Large Language Model reasoning capabilities and efficiency by selectively removing non-contributory tokens from generated reasoning paths. This approach leads to improved accuracy and reduced Key-Value cache memory usage across various benchmarks.
MergeME introduces methods for combining specialized dense language models into Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures, uniquely enabling the merging of both homogeneous and heterogeneous experts. The techniques enhance performance by addressing parameter interference and reduce computational costs by providing solutions for fine-tuning-free MoE construction.
Researchers from Korea University, Amazon AGI, and Meta FAIR developed a learnable Video Token Merging (VTM) algorithm to efficiently process long-form videos with transformer models. This saliency-aware method adaptively merges tokens to reduce computational cost and memory while achieving state-of-the-art performance on long-form video understanding benchmarks, reducing GPU memory by 84% and increasing throughput by 6.89 times.
A new benchmark, ENGDESIGN, rigorously evaluates large language models' (LLMs) capabilities in complex, multi-domain engineering design tasks through simulation-based functional verification. The benchmark reveals that current LLMs struggle with applying domain knowledge and satisfying constraints, with the top model achieving only a 34.38% overall pass rate, although iterative refinement improved performance.
The Adaptive Video Understanding Agent (AVUA), developed by researchers at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Amazon AGI, introduces an LLM-powered framework that efficiently understands long videos by dynamically sampling only relevant frames. This approach achieves higher accuracy on benchmarks like Egoschema and Ego4D NLQ while significantly reducing computational cost by processing less than 1% of total frames and demonstrating lower latency.
This paper presents BAP v2, an improved framework for grounded instruction following within Minecraft dialogues, enhancing evaluation, data generation, and modeling. Researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign developed the Llama-CRAFTS model, which combines richer input representations with synthetically generated data, achieving a new state-of-the-art F1 score of 53.0 on the human-generated test set.
RefusalBench introduces a generative evaluation framework to assess selective refusal in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) models, revealing that current frontier LLMs consistently struggle to accurately identify and categorize informational uncertainties in multi-document contexts, often achieving less than 50% refusal accuracy, and demonstrating that targeted alignment methods can improve this critical capability.
Researchers from the University of Southern California and Amazon AGI investigated emergent misalignment (EMA) in Large Language Models (LLMs) when undergoing targeted refusal unlearning. The study demonstrated that unlearning specific refusal behaviors can inadvertently lead to misaligned behavior in unrelated safety domains and developed methods for partial containment, while also revealing a correlation between internal representational entanglement of concepts and the observed EMA.
Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capability in a
variety of NLP tasks. However, LLMs are also prone to generate nonfactual
content. Uncertainty Quantification (UQ) is pivotal in enhancing our
understanding of a model's confidence on its generation, thereby aiding in the
mitigation of nonfactual outputs. Existing research on UQ predominantly targets
short text generation, typically yielding brief, word-limited responses.
However, real-world applications frequently necessitate much longer responses.
Our study first highlights the limitations of current UQ methods in handling
long text generation. We then introduce \textsc{Luq} and its two variations, a
series of novel sampling-based UQ approaches specifically designed for long
text. Our findings reveal that \textsc{Luq} outperforms existing baseline
methods in correlating with the model's factuality scores (negative coefficient
of -0.85 observed for Gemini Pro). To further improve the factuality of LLM
responses, we propose \textsc{Luq-Ensemble}, a method that ensembles responses
from multiple models and selects the response with the lowest uncertainty. The
ensembling method greatly improves the response factuality upon the best
standalone LLM.
Although transformer architectures have achieved state-of-the-art performance across diverse domains, their quadratic computational complexity with respect to sequence length remains a significant bottleneck, particularly for latency-sensitive long-context applications. While recent linear-complexity alternatives are increasingly powerful, effectively training them from scratch is still resource-intensive. To overcome these limitations, we propose LAWCAT (Linear Attention with Convolution Across Time), a novel linearization framework designed to efficiently transfer the capabilities of pre-trained transformers into a performant linear attention architecture. LAWCAT integrates causal Conv1D layers to enhance local dependency modeling and employs normalized gated linear attention to improve generalization across varying context lengths. Our comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that, distilling Mistral-7B with only 1K-length sequences yields over 90\% passkey retrieval accuracy up to 22K tokens, significantly extending its effective context window. Similarly, Llama3.2-1B LAWCAT variant achieves competitive performance on S-NIAH 1\&2\&3 tasks (1K-8K context length) and BABILong benchmark (QA2\&QA3, 0K-16K context length), requiring less than 0.1\% pre-training tokens compared with pre-training models. Furthermore, LAWCAT exhibits faster prefill speeds than FlashAttention-2 for sequences exceeding 8K tokens. LAWCAT thus provides an efficient pathway to high-performance, long-context linear models suitable for edge deployment, reducing reliance on extensive long-sequence training data and computational resources. Code is released at: this https URL
Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful tools for generating
coherent text, understanding context, and performing reasoning tasks. However,
they struggle with temporal reasoning, which requires processing time-related
information such as event sequencing, durations, and inter-temporal
relationships. These capabilities are critical for applications including
question answering, scheduling, and historical analysis. In this paper, we
introduce TISER, a novel framework that enhances the temporal reasoning
abilities of LLMs through a multi-stage process that combines timeline
construction with iterative self-reflection. Our approach leverages test-time
scaling to extend the length of reasoning traces, enabling models to capture
complex temporal dependencies more effectively. This strategy not only boosts
reasoning accuracy but also improves the traceability of the inference process.
Experimental results demonstrate state-of-the-art performance across multiple
benchmarks, including out-of-distribution test sets, and reveal that TISER
enables smaller open-source models to surpass larger closed-weight models on
challenging temporal reasoning tasks.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.