Ask or search anything...
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of SciencesA comprehensive survey formally defines Agentic Reinforcement Learning (RL) for Large Language Models (LLMs) as a Partially Observable Markov Decision Process (POMDP), distinct from conventional LLM-RL, and provides a two-tiered taxonomy of capabilities and task domains. The work consolidates open-source resources and outlines critical open challenges for the field.
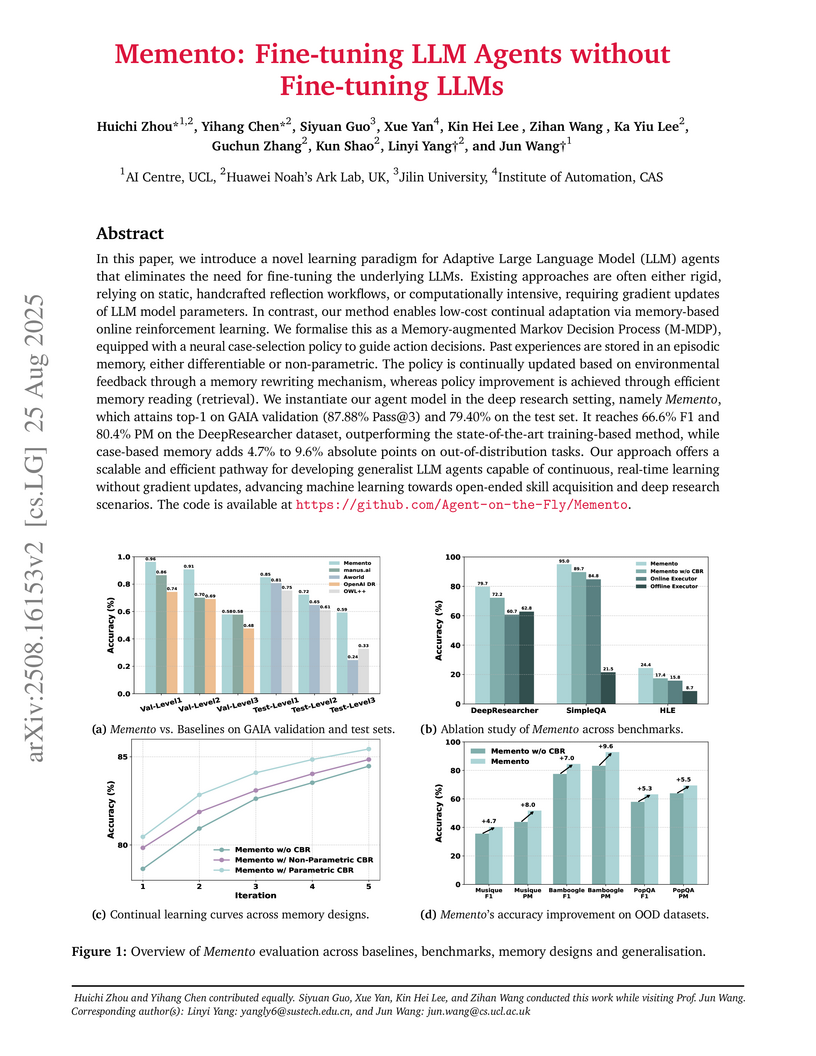
View blogResearchers from UCL AI Centre and Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab developed Memento, a memory-based learning framework enabling LLM agents to continually adapt and improve without fine-tuning their underlying large language models. The framework achieved top performance on complex benchmarks, including 87.88% Pass@3 on GAIA and 95.0% accuracy on SimpleQA, demonstrating efficient, robust adaptation and generalization.
View blogMei et al. formalize "Context Engineering" as a systematic discipline for optimizing information supplied to Large Language Models, proposing a comprehensive taxonomy that unifies fragmented research domains. Their analysis identifies a critical "comprehension-generation asymmetry," where LLMs demonstrate strong understanding but limitations in generating equally sophisticated long-form outputs.
View blogResearchers from the University of Science and Technology of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a framework utilizing conditional deep generative models (cDGMs) to learn demand distributions influenced by price and contextual features. This approach enables robust, data-driven optimization of inventory and pricing decisions, demonstrating superior profitability and asymptotic optimality compared to traditional methods in both simulations and a real-world case study.
View blogResearchers at the Institute of Information Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed an automatic framework to infer Protocol State Machines (PSMs) for unknown network protocols directly from mixed traffic environments. This framework accurately clusters protocol formats and sessions, then reconstructs PSMs for both binary and text-based protocols like TLSv1.2 and SMTP, achieving high matching coefficients of 1.0 and 0.91/0.86 respectively.
View blogResearchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences provide a systematic analysis differentiating image-to-image translation (I2I) and style transfer (ST), two foundational generative AI techniques. The analysis clarifies their distinct concepts, forms, training modes, and evaluation processes, offering a framework to address existing confusion in the research community.
View blogResearchers developed and experimentally validated a reinforcement learning-based quantum compiler on a 9-qubit superconducting processor, demonstrating its ability to find shorter, hardware-optimized quantum circuits. This approach achieved superior experimental fidelities on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices compared to conventional compilation methods, notably reducing the 3-qubit Quantum Fourier Transform to just seven CZ gates.
View blogA systematic analysis from researchers at Chinese Academy of Sciences and Tsinghua University investigates why Multimodal Large Language Models struggle with spatial understanding, introducing a novel multi-view spatial understanding benchmark (MulSeT). The study reveals that architectural design limitations, particularly in visual encoder positional encodings, are more constraining than insufficient training data for complex spatial reasoning.
View blogA comprehensive survey from an international research consortium led by Peking University examines Large Language Model (LLM) agents through a methodology-centered taxonomy, analyzing their construction, collaboration mechanisms, and evolution while providing a unified architectural framework for understanding agent systems across different application domains.
View blogResearchers present a comprehensive survey of the "LLM-as-a-Judge" paradigm, providing formal definitions, a unified framework, and an empirical meta-evaluation to assess the reliability of large language models in evaluative roles. The work identifies effective strategies and highlights persistent biases and the need for advanced benchmarks.
View blogResearchers from ICT, CAS and collaborating institutions present the first comprehensive survey of Vibe Coding, a novel LLM-powered software development methodology, formalizing its processes and outlining five distinct development models. The work thoroughly analyzes the ecosystem's infrastructure, revealing critical challenges in human-AI collaboration and a shift in developer roles.
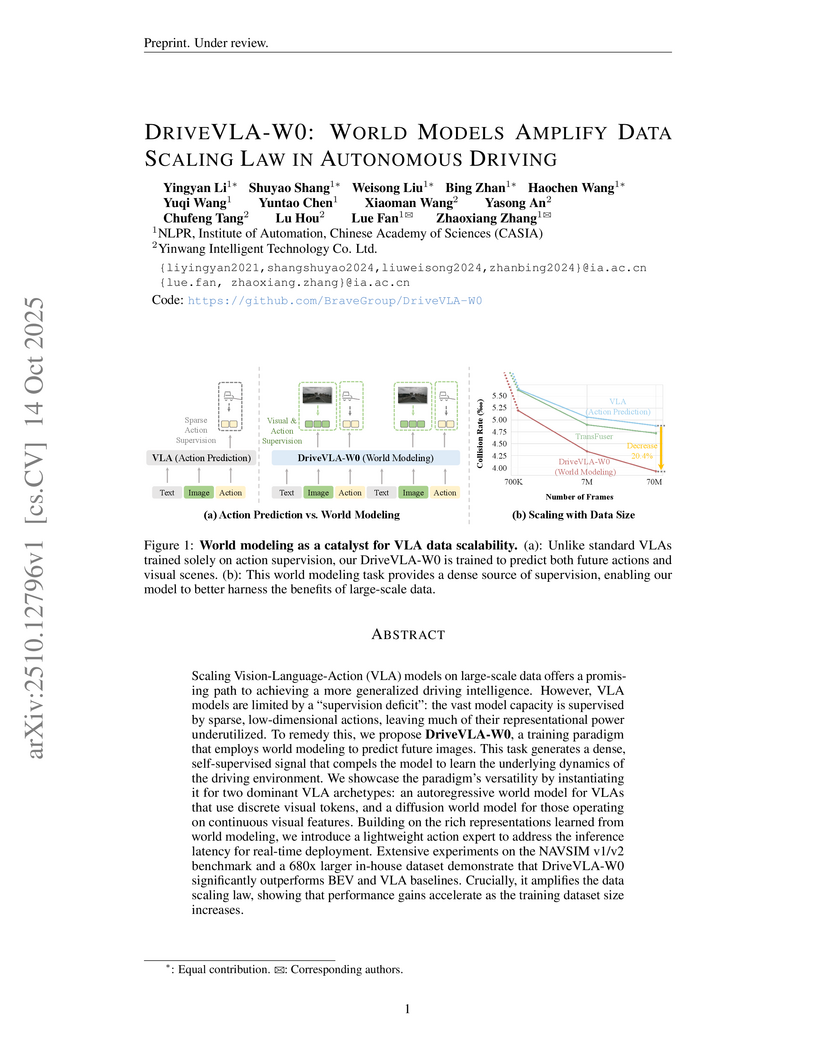
View blogDriveVLA-W0 integrates world modeling into Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models for autonomous driving, utilizing future image prediction as a dense self-supervision signal. This framework amplifies data scaling laws, enabling VLAs to achieve state-of-the-art performance and enhanced generalization by learning robust environmental representations.
View blogA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
View blog University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara
 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University

 University of Toronto
University of Toronto
 University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China
 Peking University
Peking University

 Beijing Normal University
Beijing Normal University

 Tohoku University
Tohoku University California Institute of Technology
California Institute of Technology



 University of Washington
University of Washington Harvard University
Harvard University
 Imperial College London
Imperial College London

 Beihang University
Beihang University
 Monash University
Monash University