Oregon State University
01 Aug 2025
Princeton AI Lab University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Fudan University
Fudan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University University of Michigan
University of Michigan The Chinese University of Hong KongThe Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
The Chinese University of Hong KongThe Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou) University of California, San DiegoPennsylvania State University
University of California, San DiegoPennsylvania State University The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong Princeton University
Princeton University University of SydneyOregon State University
University of SydneyOregon State University
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign University of California, Santa Barbara
University of California, Santa Barbara Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Fudan University
Fudan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University University of Michigan
University of Michigan The Chinese University of Hong KongThe Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)
The Chinese University of Hong KongThe Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou) University of California, San DiegoPennsylvania State University
University of California, San DiegoPennsylvania State University The University of Hong Kong
The University of Hong Kong Princeton University
Princeton University University of SydneyOregon State University
University of SydneyOregon State UniversityAn extensive international collaboration offers the first systematic review of self-evolving agents, establishing a unified theoretical framework categorized by 'what to evolve,' 'when to evolve,' and 'how to evolve'. The work consolidates diverse research, highlights key challenges, and maps applications, aiming to guide the development of AI systems capable of continuous autonomous improvement.
10 Aug 2024
Undesignable RNA Structure Identification via Rival Structure Generation and Structure Decomposition
Undesignable RNA Structure Identification via Rival Structure Generation and Structure Decomposition
RNA design is the search for a sequence or set of sequences that will fold into predefined structures, also known as the inverse problem of RNA folding. While numerous RNA design methods have been invented to find sequences capable of folding into a target structure, little attention has been given to the identification of undesignable structures according to the minimum free energy (MFE) criterion under the Turner model. In this paper, we address this gap by first introducing mathematical theorems outlining sufficient conditions for recognizing undesignable structures, then proposing efficient algorithms, guided by these theorems, to verify the undesignability of RNA structures. Through the application of these theorems and algorithms to the Eterna100 puzzles, we demonstrate the ability to efficiently establish that 15 of the puzzles indeed fall within the category of undesignable structures. In addition, we provide specific insights from the study of undesignability, in the hope that it will enable more understanding of RNA folding and RNA design.
02 Jun 2025
This research introduces and defines automated failure attribution for Large Language Model (LLM) multi-agent systems, providing a method to automatically identify which agent and at what step a task failure occurred. The study evaluates three LLM-based attribution methods on a newly created, human-annotated dataset called "Who&When," finding that different methods excel at agent-level versus step-level accuracy and that performance degrades with longer conversation logs.
 ETH Zurich
ETH Zurich University of Toronto
University of Toronto University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal New York University
New York University University of Oxford
University of Oxford Stanford University
Stanford University Mila - Quebec AI Institute
Mila - Quebec AI Institute Seoul National University
Seoul National University Princeton University
Princeton University HKUSTIndian Institute of Technology MadrasThe University of New South WalesOregon State UniversityConcordia AIUniversity of São PauloGerman Research Center for Artificial IntelligenceSony Group CorporationUniversity of LoughboroughBrookings InstitutionLobsterTelELLIS AlicanteInfocomm Media Development AuthorityUniversidad Técnica Federico Santa Maria
HKUSTIndian Institute of Technology MadrasThe University of New South WalesOregon State UniversityConcordia AIUniversity of São PauloGerman Research Center for Artificial IntelligenceSony Group CorporationUniversity of LoughboroughBrookings InstitutionLobsterTelELLIS AlicanteInfocomm Media Development AuthorityUniversidad Técnica Federico Santa MariaA landmark international scientific assessment, led by Prof. Yoshua Bengio and 96 global AI experts, provides the first comprehensive evidence-based framework for understanding advanced AI safety risks and mitigation strategies, establishing crucial scientific foundations for international policy while highlighting urgent challenges requiring proactive governance.
Researchers from Bytedance and partner universities develop a visualization framework for analyzing where Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) focus their attention when answering questions about images, revealing that different vision architectures lead to distinct attention patterns and that model performance doesn't always align with visual understanding behavior.
A new framework called Heima allows Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) to perform complex reasoning efficiently by compressing verbose Chain-of-Thought (CoT) steps into single "thinking tokens." This approach reduces token generation to as low as 6% of original counts while maintaining or improving zero-shot accuracy on diverse benchmarks and enabling interpretation of the hidden reasoning process through a dedicated decoder.
Researchers at UC Berkeley and Oregon State University introduced ImageNet-C and ImageNet-P, comprehensive benchmarks for evaluating neural network robustness to common image corruptions and perturbations. Their evaluations demonstrated that modern deep learning models, despite high clean accuracy, often exhibit similar or worse relative robustness to these natural degradations compared to older architectures, alongside significant prediction instability.
The paper introduces Vision-and-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments (VLN-CE), a more realistic benchmark where agents execute low-level actions in 3D environments, moving beyond prior "nav-graph" assumptions. This setting significantly challenges existing models, with the best cross-modal attention agent achieving a 0.30 SPL (32% SR) on val-unseen, revealing a substantial performance gap compared to nav-graph-based methods.
19 Sep 2025
Researchers at Oregon State University developed `decPLM`, a hierarchical reinforcement learning framework enabling teams of quadrupedal robots to cooperatively transport ungraspable objects through physical contact, without communication or rigid coupling. The approach, leveraging a novel constellation reward, demonstrates effective generalization from two-robot training to teams of up to ten robots, reducing velocity errors by 80% and achieving drop rates below 1% for diverse payloads.
Natural Gradient Descent, a second-degree optimization method motivated by the information geometry, makes use of the Fisher Information Matrix instead of the Hessian which is typically used. However, in many cases, the Fisher Information Matrix is equivalent to the Generalized Gauss-Newton Method, that both approximate the Hessian. It is an appealing method to be used as an alternative to stochastic gradient descent, potentially leading to faster convergence. However, being a second-order method makes it infeasible to be used directly in problems with a huge number of parameters and data. This is evident from the community of deep learning sticking with the stochastic gradient descent method since the beginning. In this paper, we look at the different perspectives on the natural gradient method, study the current developments on its efficient-scalable empirical approximations, and finally examine their performance with extensive experiments.
This technical report presents Prithvi-EO-2.0, a new geospatial foundation
model that offers significant improvements over its predecessor,
Prithvi-EO-1.0. Trained on 4.2M global time series samples from NASA's
Harmonized Landsat and Sentinel-2 data archive at 30m resolution, the new 300M
and 600M parameter models incorporate temporal and location embeddings for
enhanced performance across various geospatial tasks. Through extensive
benchmarking with GEO-Bench, the 600M version outperforms the previous
Prithvi-EO model by 8\% across a range of tasks. It also outperforms six other
geospatial foundation models when benchmarked on remote sensing tasks from
different domains and resolutions (i.e. from 0.1m to 15m). The results
demonstrate the versatility of the model in both classical earth observation
and high-resolution applications. Early involvement of end-users and subject
matter experts (SMEs) are among the key factors that contributed to the
project's success. In particular, SME involvement allowed for constant feedback
on model and dataset design, as well as successful customization for diverse
SME-led applications in disaster response, land use and crop mapping, and
ecosystem dynamics monitoring. Prithvi-EO-2.0 is available on Hugging Face and
IBM terratorch, with additional resources on GitHub. The project exemplifies
the Trusted Open Science approach embraced by all involved organizations.
A comprehensive review surveys machine learning methods for generating synthetic data, exploring diverse applications, the capabilities of deep generative models, and critical ethical considerations. The paper outlines current challenges and future opportunities in creating high-quality, privacy-preserving synthetic datasets across various fields.
4D-LRM introduces a Transformer-based Large Reconstruction Model that leverages 4D Gaussian Splatting to reconstruct dynamic objects from sparse, unconstrained input views and timestamps into full space-time representations. The model reconstructs a 24-frame dynamic object in under 1.5 seconds on an A100 GPU, achieving high fidelity and generalizing to novel view-time combinations.
We propose Long-LRM, a feed-forward 3D Gaussian reconstruction model for instant, high-resolution, 360° wide-coverage, scene-level reconstruction. Specifically, it takes in 32 input images at a resolution of 960x540 and produces the Gaussian reconstruction in just 1 second on a single A100 GPU. To handle the long sequence of 250K tokens brought by the large input size, Long-LRM features a mixture of the recent Mamba2 blocks and the classical transformer blocks, enhanced by a light-weight token merging module and Gaussian pruning steps that balance between quality and efficiency. We evaluate Long-LRM on the large-scale DL3DV benchmark and Tanks&Temples, demonstrating reconstruction quality comparable to the optimization-based methods while achieving an 800x speedup w.r.t. the optimization-based approaches and an input size at least 60x larger than the previous feed-forward approaches. We conduct extensive ablation studies on our model design choices for both rendering quality and computation efficiency. We also explore Long-LRM's compatibility with other Gaussian variants such as 2D GS, which enhances Long-LRM's ability in geometry reconstruction. Project page: this https URL
This Systematization of Knowledge (SoK) comprehensively surveys watermarking techniques for AI-generated content, formalizing key properties, analyzing trade-offs, and reviewing state-of-the-art methods across modalities. It aims to guide future research and inform policy development for AI safety and transparency.
This research introduces AutoDefense, a multi-agent system designed to defend Large Language Models against jailbreak attacks by filtering harmful content from generated responses. The framework achieved a reduction in Attack Success Rate on GPT-3.5 from 55.74% to 7.95% while maintaining a low false positive rate on legitimate requests.
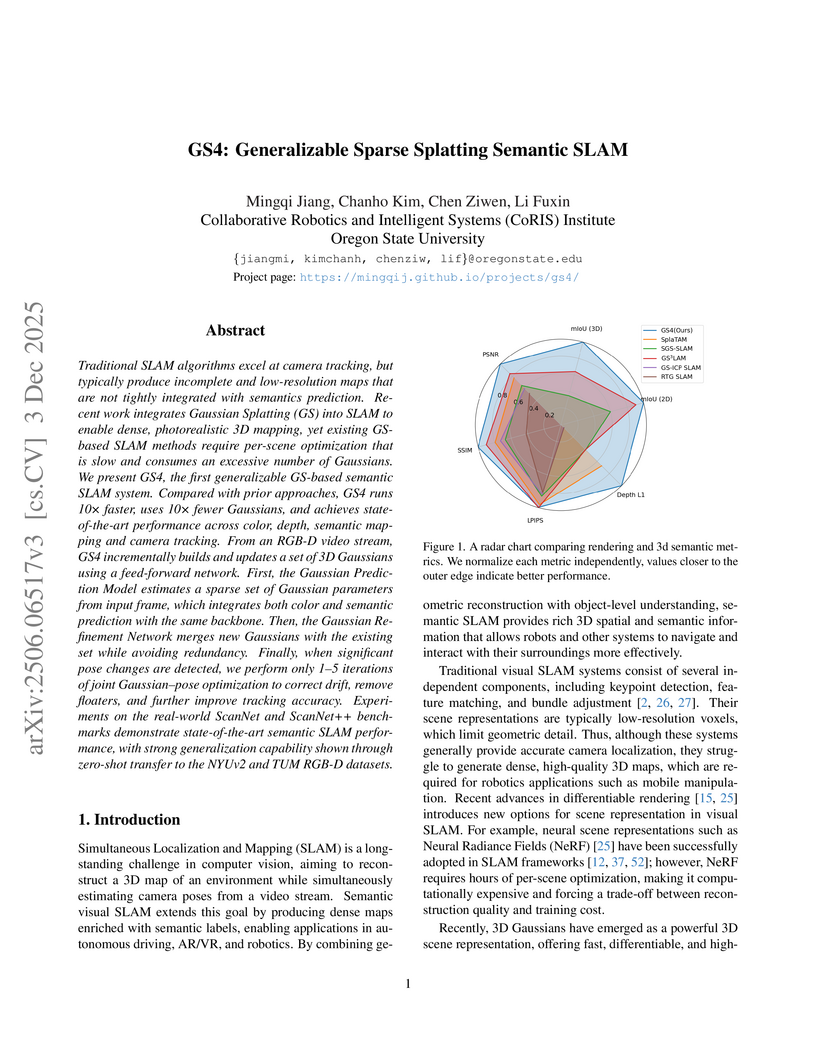
Traditional SLAM algorithms excel at camera tracking, but typically produce incomplete and low-resolution maps that are not tightly integrated with semantics prediction. Recent work integrates Gaussian Splatting (GS) into SLAM to enable dense, photorealistic 3D mapping, yet existing GS-based SLAM methods require per-scene optimization that is slow and consumes an excessive number of Gaussians. We present GS4, the first generalizable GS-based semantic SLAM system. Compared with prior approaches, GS4 runs 10x faster, uses 10x fewer Gaussians, and achieves state-of-the-art performance across color, depth, semantic mapping and camera tracking. From an RGB-D video stream, GS4 incrementally builds and updates a set of 3D Gaussians using a feed-forward network. First, the Gaussian Prediction Model estimates a sparse set of Gaussian parameters from input frame, which integrates both color and semantic prediction with the same backbone. Then, the Gaussian Refinement Network merges new Gaussians with the existing set while avoiding redundancy. Finally, when significant pose changes are detected, we perform only 1-5 iterations of joint Gaussian-pose optimization to correct drift, remove floaters, and further improve tracking accuracy. Experiments on the real-world ScanNet and ScanNet++ benchmarks demonstrate state-of-the-art semantic SLAM performance, with strong generalization capability shown through zero-shot transfer to the NYUv2 and TUM RGB-D datasets.
The paper demonstrates that imposing prompt-based organizational structures significantly improves the cooperative efficiency and communication of multi-LLM-agent teams in embodied tasks. It also introduces a "Criticize-Reflect" framework, enabling LLM agents to autonomously optimize these structures, leading to reduced task completion times and communication overhead.
We present Decentralized Distributed Proximal Policy Optimization (DD-PPO), a method for distributed reinforcement learning in resource-intensive simulated environments. DD-PPO is distributed (uses multiple machines), decentralized (lacks a centralized server), and synchronous (no computation is ever stale), making it conceptually simple and easy to implement. In our experiments on training virtual robots to navigate in Habitat-Sim, DD-PPO exhibits near-linear scaling -- achieving a speedup of 107x on 128 GPUs over a serial implementation. We leverage this scaling to train an agent for 2.5 Billion steps of experience (the equivalent of 80 years of human experience) -- over 6 months of GPU-time training in under 3 days of wall-clock time with 64 GPUs.
This massive-scale training not only sets the state of art on Habitat Autonomous Navigation Challenge 2019, but essentially solves the task --near-perfect autonomous navigation in an unseen environment without access to a map, directly from an RGB-D camera and a GPS+Compass sensor. Fortuitously, error vs computation exhibits a power-law-like distribution; thus, 90% of peak performance is obtained relatively early (at 100 million steps) and relatively cheaply (under 1 day with 8 GPUs). Finally, we show that the scene understanding and navigation policies learned can be transferred to other navigation tasks -- the analog of ImageNet pre-training + task-specific fine-tuning for embodied AI. Our model outperforms ImageNet pre-trained CNNs on these transfer tasks and can serve as a universal resource (all models and code are publicly available).
15 Oct 2025
 University of Toronto
University of Toronto University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge Harvard University
Harvard University Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of Oxford
University of Oxford Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Stanford University
Stanford University Mila - Quebec AI InstituteIEEE
Mila - Quebec AI InstituteIEEE University of MarylandThe Alan Turing Institute
University of MarylandThe Alan Turing Institute Stony Brook UniversityInstitute for Advanced Study
Stony Brook UniversityInstitute for Advanced Study Inria
Inria MIT
MIT Princeton UniversityMaastricht UniversityUniversity College DublinOregon State UniversityLinköping UniversityPontificia Universidad Católica de ChileUniversity of YorkELLIS Institute TübingenLoughborough UniversityCentre for the Governance of AIApollo ResearchSaferAIUK AI Security InstituteFederal University of PernambucoDukeCarnegie Endowment for International PeaceLawZeroKIRA CenterAdvanced Research and Invention Agency (ARIA)AI CollaborativeResponsible AI UK
Princeton UniversityMaastricht UniversityUniversity College DublinOregon State UniversityLinköping UniversityPontificia Universidad Católica de ChileUniversity of YorkELLIS Institute TübingenLoughborough UniversityCentre for the Governance of AIApollo ResearchSaferAIUK AI Security InstituteFederal University of PernambucoDukeCarnegie Endowment for International PeaceLawZeroKIRA CenterAdvanced Research and Invention Agency (ARIA)AI CollaborativeResponsible AI UKSince the publication of the first International AI Safety Report, AI capabilities have continued to improve across key domains. New training techniques that teach AI systems to reason step-by-step and inference-time enhancements have primarily driven these advances, rather than simply training larger models. As a result, general-purpose AI systems can solve more complex problems in a range of domains, from scientific research to software development. Their performance on benchmarks that measure performance in coding, mathematics, and answering expert-level science questions has continued to improve, though reliability challenges persist, with systems excelling on some tasks while failing completely on others. These capability improvements also have implications for multiple risks, including risks from biological weapons and cyber attacks. Finally, they pose new challenges for monitoring and controllability. This update examines how AI capabilities have improved since the first Report, then focuses on key risk areas where substantial new evidence warrants updated assessments.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.