The University of Texas at San Antonio
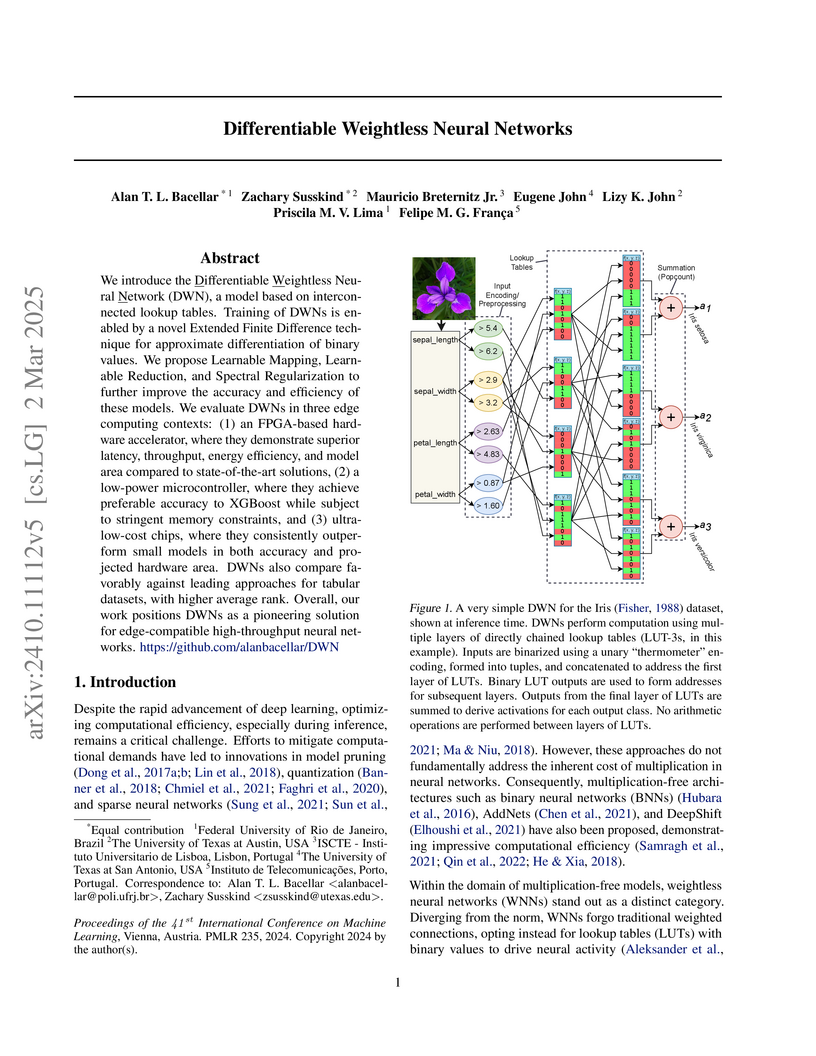
We introduce the Differentiable Weightless Neural Network (DWN), a model
based on interconnected lookup tables. Training of DWNs is enabled by a novel
Extended Finite Difference technique for approximate differentiation of binary
values. We propose Learnable Mapping, Learnable Reduction, and Spectral
Regularization to further improve the accuracy and efficiency of these models.
We evaluate DWNs in three edge computing contexts: (1) an FPGA-based hardware
accelerator, where they demonstrate superior latency, throughput, energy
efficiency, and model area compared to state-of-the-art solutions, (2) a
low-power microcontroller, where they achieve preferable accuracy to XGBoost
while subject to stringent memory constraints, and (3) ultra-low-cost chips,
where they consistently outperform small models in both accuracy and projected
hardware area. DWNs also compare favorably against leading approaches for
tabular datasets, with higher average rank. Overall, our work positions DWNs as
a pioneering solution for edge-compatible high-throughput neural networks.
Virtual Reality (VR) is quickly establishing itself in various industries, including training, education, medicine, and entertainment, in which users are frequently required to carry out multiple complex cognitive and physical activities. However, the relationship between cognitive activities, physical activities, and familiar feelings of cybersickness is not well understood and thus can be unpredictable for developers. Researchers have previously provided labeled datasets for predicting cybersickness while users are stationary, but there have been few labeled datasets on cybersickness while users are physically walking. Thus, from 39 participants, we collected head orientation, head position, eye tracking, images, physiological readings from external sensors, and the self-reported cybersickness severity, physical load, and mental load in VR. Throughout the data collection, participants navigated mazes via real walking and performed tasks challenging their attention and working memory. To demonstrate the dataset's utility, we conducted a case study of training classifiers in which we achieved 95% accuracy for cybersickness severity classification. The noteworthy performance of the straightforward classifiers makes this dataset ideal for future researchers to develop cybersickness detection and reduction models. To better understand the features that helped with classification, we performed SHAP(SHapley Additive exPlanations) analysis, highlighting the importance of eye tracking and physiological measures for cybersickness prediction while walking. This open dataset can allow future researchers to study the connection between cybersickness and cognitive loads and develop prediction models. This dataset will empower future VR developers to design efficient and effective Virtual Environments by improving cognitive load management and minimizing cybersickness.
23 May 2025
InfantAgent-Next introduces a multimodal generalist agent framework for automated computer interaction, integrating tool-based and pure vision-based approaches through a modular architecture. The framework achieves competitive performance on OSWorld, SWE-Bench, and GAIA benchmarks, demonstrating enhanced accuracy in precise execution tasks.
24 Sep 2025
Conventional multi-agent reinforcement learning (MARL) methods rely on time-triggered execution, where agents sample and communicate actions at fixed intervals. This approach is often computationally expensive and communication-intensive. To address this limitation, we propose ET-MAPG (Event-Triggered Multi-Agent Policy Gradient reinforcement learning), a framework that jointly learns an agent's control policy and its event-triggering policy. Unlike prior work that decouples these mechanisms, ET-MAPG integrates them into a unified learning process, enabling agents to learn not only what action to take but also when to execute it. For scenarios with inter-agent communication, we introduce AET-MAPG, an attention-based variant that leverages a self-attention mechanism to learn selective communication patterns. AET-MAPG empowers agents to determine not only when to trigger an action but also with whom to communicate and what information to exchange, thereby optimizing coordination. Both methods can be integrated with any policy gradient MARL algorithm. Extensive experiments across diverse MARL benchmarks demonstrate that our approaches achieve performance comparable to state-of-the-art, time-triggered baselines while significantly reducing both computational load and communication overhead.
A Lyapunov-based Resource Optimization Algorithm (LROA) jointly optimizes client scheduling and resource allocation in federated edge learning, achieving up to 50.1% reduction in training latency and improved convergence speed on non-IID data while managing energy consumption.
With the advantage of high mobility, Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are used to fuel numerous important applications in computer vision, delivering more efficiency and convenience than surveillance cameras with fixed camera angle, scale and view. However, very limited UAV datasets are proposed, and they focus only on a specific task such as visual tracking or object detection in relatively constrained scenarios. Consequently, it is of great importance to develop an unconstrained UAV benchmark to boost related researches. In this paper, we construct a new UAV benchmark focusing on complex scenarios with new level challenges. Selected from 10 hours raw videos, about 80,000 representative frames are fully annotated with bounding boxes as well as up to 14 kinds of attributes (e.g., weather condition, flying altitude, camera view, vehicle category, and occlusion) for three fundamental computer vision tasks: object detection, single object tracking, and multiple object tracking. Then, a detailed quantitative study is performed using most recent state-of-the-art algorithms for each task. Experimental results show that the current state-of-the-art methods perform relative worse on our dataset, due to the new challenges appeared in UAV based real scenes, e.g., high density, small object, and camera motion. To our knowledge, our work is the first time to explore such issues in unconstrained scenes comprehensively.
Federated learning (FL) is a distributed machine learning approach that allows multiple clients to collaboratively train a model without sharing their raw data. To prevent sensitive information from being inferred through the model updates shared in FL, differentially private federated learning (DPFL) has been proposed. DPFL ensures formal and rigorous privacy protection in FL by clipping and adding random noise to the shared model updates. However, the existing DPFL methods often result in severe model utility degradation, especially in settings with data heterogeneity. To enhance model utility, we propose a novel DPFL method named DP2-FedSAM: Differentially Private and Personalized Federated Learning with Sharpness-Aware Minimization. DP2-FedSAM leverages personalized partial model-sharing and sharpness-aware minimization optimizer to mitigate the adverse impact of noise addition and clipping, thereby significantly improving model utility without sacrificing privacy. From a theoretical perspective, we provide a rigorous theoretical analysis of the privacy and convergence guarantees of our proposed method. To evaluate the effectiveness of DP2-FedSAM, we conduct extensive evaluations based on common benchmark datasets. Our results verify that our method improves the privacy-utility trade-off compared to the existing DPFL methods, particularly in heterogeneous data settings.
12 Oct 2024
Accurate flood modeling is crucial for effective analysis and forecasting.
Full momentum hydrodynamic models often require extensive computational time,
sometimes exceeding the forecast horizon. In contrast, low-complexity models,
like local-inertial approximations, provide accurate results in subcritical
flows but may have limited skillfulness in supercritical conditions. This paper
explores two main aspects: (i) the impact of urban infrastructure on 2D
hydrodynamic modeling without detailed sewer and drainage data, and (ii) the
accuracy of 2D local-inertial modeling using three numerical schemes (original
formulation, s-centered, and s-upwind) in a dam-break scenario on complex, flat
terrain. The HydroPol2D model is benchmarked against HEC-RAS 2D full momentum
solver. We present one numerical case study and three real-world scenarios in
S\~ao Paulo, Brazil: a detention pond with a 1 in 100-year inflow, a highly
urbanized catchment with a 1 in 50-year hyetograph, and a dam-break
scenario threatening a coastal city of nearly 200,000 residents. Results show
that the model accurately simulates internal boundary conditions, achieving
peak errors under 5\% compared to HEC-RAS 2D. However, neglecting urban
infrastructure can lead to a 17.5\% difference in peak discharges at the outlet
and significant mismatches in hydrographs, with computational times nearly
doubling. The dam-break scenario demonstrates good predictive performance for
maximum flood depths (CSI = 0.95 for the original model, 0.92 for
s-centered, and 0.89 for s-upwind), though the model's lack of convective
inertia results in faster flood wave propagation than the full momentum solver.
Notably, HydroPol2D is 23 times faster than HEC-RAS 2D, making it well-suited
for simulating dam collapses in forecasting systems and capable of modeling
urban drainage infrastructure such as orifices, weirs, and pumps.
A hybrid attention-based deep learning architecture, SETransformer, is developed for robust Human Activity Recognition (HAR) using wearable sensor data. The model achieves 84.68% accuracy and 84.64% macro F1-score on the WISDM dataset, improving upon existing CNN and RNN baselines by over 13 percentage points.
Text-to-SQL systems empower users to interact with databases using natural language, automatically translating queries into executable SQL code. However, their reliance on database schema information for SQL generation exposes them to significant security vulnerabilities, particularly schema inference attacks that can lead to unauthorized data access or manipulation. In this paper, we introduce a novel zero-knowledge framework for reconstructing the underlying database schema of text-to-SQL models without any prior knowledge of the database. Our approach systematically probes text-to-SQL models with specially crafted questions and leverages a surrogate GPT-4 model to interpret the outputs, effectively uncovering hidden schema elements -- including tables, columns, and data types. We demonstrate that our method achieves high accuracy in reconstructing table names, with F1 scores of up to .99 for generative models and .78 for fine-tuned models, underscoring the severity of schema leakage risks. We also show that our attack can steal prompt information in non-text-to-SQL models. Furthermore, we propose a simple protection mechanism for generative models and empirically show its limitations in mitigating these attacks.
The construction industry increasingly relies on visual data to support Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) applications for site monitoring. High-quality, domain-specific datasets, comprising images, videos, and point clouds, capture site geometry and spatiotemporal dynamics, including the location and interaction of objects, workers, and materials. However, despite growing interest in leveraging visual datasets, existing resources vary widely in sizes, data modalities, annotation quality, and representativeness of real-world construction conditions. A systematic review to categorize their data characteristics and application contexts is still lacking, limiting the community's ability to fully understand the dataset landscape, identify critical gaps, and guide future directions toward more effective, reliable, and scalable AI applications in construction. To address this gap, this study conducts an extensive search of academic databases and open-data platforms, yielding 51 publicly available visual datasets that span the 2005-2024 period. These datasets are categorized using a structured data schema covering (i) data fundamentals (e.g., size and license), (ii) data modalities (e.g., RGB and point cloud), (iii) annotation frameworks (e.g., bounding boxes), and (iv) downstream application domains (e.g., progress tracking). This study synthesizes these findings into an open-source catalog, OpenConstruction, supporting data-driven method development. Furthermore, the study discusses several critical limitations in the existing construction dataset landscape and presents a roadmap for future data infrastructure anchored in the Findability, Accessibility, Interoperability, and Reusability (FAIR) principles. By reviewing the current landscape and outlining strategic priorities, this study supports the advancement of data-centric solutions in the construction sector.
Browser fingerprinting defenses have historically focused on detecting JavaScript(JS)-based tracking techniques. However, the widespread adoption of WebAssembly (WASM) introduces a potential blind spot, as adversaries can convert JS to WASM's low-level binary format to obfuscate malicious logic. This paper presents the first systematic evaluation of how such WASM-based obfuscation impacts the robustness of modern fingerprinting defenses. We develop an automated pipeline that translates real-world JS fingerprinting scripts into functional WASM-obfuscated variants and test them against two classes of defenses: state-of-the-art detectors in research literature and commercial, in-browser tools. Our findings reveal a notable divergence: detectors proposed in the research literature that rely on feature-based analysis of source code show moderate vulnerability, stemming from outdated datasets or a lack of WASM compatibility. In contrast, defenses such as browser extensions and native browser features remained completely effective, as their API-level interception is agnostic to the script's underlying implementation. These results highlight a gap between academic and practical defense strategies and offer insights into strengthening detection approaches against WASM-based obfuscation, while also revealing opportunities for more evasive techniques in future attacks.
Despite demonstrating superior performance across a variety of linguistic tasks, pre-trained large language models (LMs) often require fine-tuning on specific datasets to effectively address different downstream tasks. However, fine-tuning these LMs for downstream tasks necessitates collecting data from individuals, which raises significant privacy concerns. Federated learning (FL) has emerged as the de facto solution, enabling collaborative model training without sharing raw data. While promising, federated fine-tuning of large LMs faces significant challenges, including restricted access to model parameters and high computation, communication, and memory overhead. To address these challenges, this paper introduces \textbf{Fed}erated \textbf{P}roxy-\textbf{T}uning (FedPT), a novel framework for federated fine-tuning of black-box large LMs, requiring access only to their predictions over the output vocabulary instead of their parameters. Specifically, devices in FedPT first collaboratively tune a smaller LM, and then the server combines the knowledge learned by the tuned small LM with the knowledge learned by the larger pre-trained LM to construct a large proxy-tuned LM that can reach the performance of directly tuned large LMs. The experimental results demonstrate that FedPT can significantly reduce computation, communication, and memory overhead while maintaining competitive performance compared to directly federated fine-tuning of large LMs. FedPT offers a promising solution for efficient, privacy-preserving fine-tuning of large LMs on resource-constrained devices, broadening the accessibility and applicability of state-of-the-art large LMs.
10 May 2019
The power grid is rapidly transforming, and while recent grid innovations
increased the utilization of advanced control methods, the next-generation grid
demands technologies that enable the integration of distributed energy
resources (DERs)---and consumers that both seamlessly buy and sell electricity.
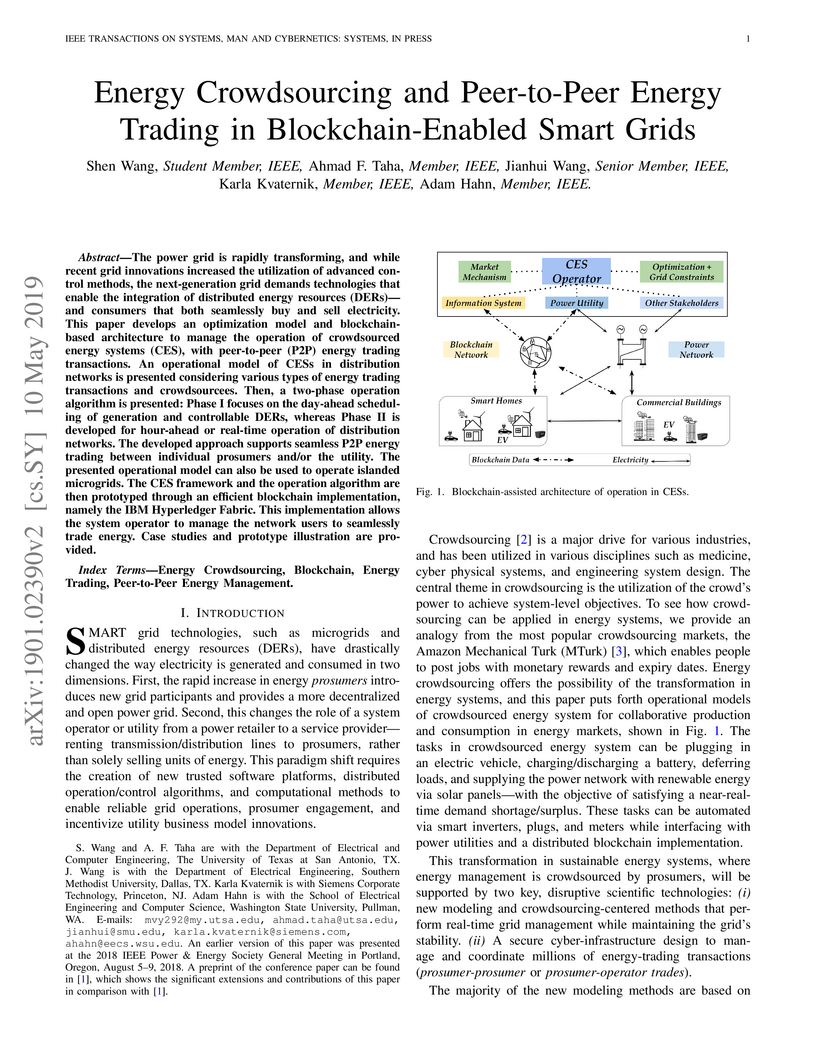
This paper develops an optimization model and blockchain-based architecture to
manage the operation of crowdsourced energy systems (CES), with peer-to-peer
(P2P) energy trading transactions. An operational model of CESs in distribution
networks is presented considering various types of energy trading transactions
and crowdsourcees. Then, a two-phase operation algorithm is presented: Phase I
focuses on the day-ahead scheduling of generation and controllable DERs,
whereas Phase II is developed for hour-ahead or real-time operation of
distribution networks. The developed approach supports seamless P2P energy
trading between individual prosumers and/or the utility. The presented
operational model can also be used to operate islanded microgrids. The CES
framework and the operation algorithm are then prototyped through an efficient
blockchain implementation, namely the IBM Hyperledger Fabric. This
implementation allows the system operator to manage the network users to
seamlessly trade energy. Case studies and prototype illustration are provided.
Recent advances in foundation models, such as LLMs, have revolutionized conversational AI. Chatbots are increasingly being developed by customizing LLMs on specific conversational datasets. However, mitigating toxicity during this customization, especially when dealing with untrusted training data, remains a significant challenge. To address this, we introduce TuneShield, a defense framework designed to mitigate toxicity during chatbot fine-tuning while preserving conversational quality. TuneShield leverages LLM-based toxicity classification, utilizing the instruction-following capabilities and safety alignment of LLMs to effectively identify toxic samples, outperforming industry API services. TuneShield generates synthetic conversation samples, termed 'healing data', based on the identified toxic samples, using them to mitigate toxicity while reinforcing desirable behavior during fine-tuning. It performs an alignment process to further nudge the chatbot towards producing desired responses. Our findings show that TuneShield effectively mitigates toxicity injection attacks while preserving conversational quality, even when the toxicity classifiers are imperfect or biased. TuneShield proves to be resilient against adaptive adversarial and jailbreak attacks. Additionally, TuneShield demonstrates effectiveness in mitigating adaptive toxicity injection attacks during dialog-based learning (DBL).
13 May 2025
Heart rate (HR) and heart rate variability (HRV) are important vital signs
for human physical and mental health. Recent research has demonstrated that
photoplethysmography (PPG) sensors can infer HR and HRV. However, it is
difficult to find a comprehensive PPG-based dataset for HR/HRV studies,
especially for various study needs: multiple scenes, long-term monitoring, and
multimodality (multiple PPG channels and extra acceleration data). In this
study, we collected a comprehensive multimodal long-term dataset to address the
gap of missing an all-in-one HR/HRV dataset (denoted as UTSA-PPG). We began by
reviewing state-of-the-art datasets, emphasizing their strengths and
limitations. Following this, we developed a custom data acquisition system and
then collected the UTSA-PPG dataset and compared its key features with those of
existing datasets. Additionally, five case studies were conducted, including
comparisons with state-of-the-art datasets. The outcomes highlight the value of
our dataset, demonstrating its utility for HR/HRV estimation exploration and
its potential to aid researchers in creating generalized models for targeted
research challenges.
This paper explores multiple optimization methods to improve the performance of rating-based reinforcement learning (RbRL). RbRL, a method based on the idea of human ratings, has been developed to infer reward functions in reward-free environments for the subsequent policy learning via standard reinforcement learning, which requires the availability of reward functions. Specifically, RbRL minimizes the cross entropy loss that quantifies the differences between human ratings and estimated ratings derived from the inferred reward. Hence, a low loss means a high degree of consistency between human ratings and estimated ratings. Despite its simple form, RbRL has various hyperparameters and can be sensitive to various factors. Therefore, it is critical to provide comprehensive experiments to understand the impact of various hyperparameters on the performance of RbRL. This paper is a work in progress, providing users some general guidelines on how to select hyperparameters in RbRL.
Recommender systems have been successfully applied in many applications. Nonetheless, recent studies demonstrate that recommender systems are vulnerable to membership inference attacks (MIAs), leading to the leakage of users' membership privacy. However, existing MIAs relying on shadow training suffer a large performance drop when the attacker lacks knowledge of the training data distribution and the model architecture of the target recommender system. To better understand the privacy risks of recommender systems, we propose shadow-free MIAs that directly leverage a user's recommendations for membership inference. Without shadow training, the proposed attack can conduct MIAs efficiently and effectively under a practice scenario where the attacker is given only black-box access to the target recommender system. The proposed attack leverages an intuition that the recommender system personalizes a user's recommendations if his historical interactions are used by it. Thus, an attacker can infer membership privacy by determining whether the recommendations are more similar to the interactions or the general popular items. We conduct extensive experiments on benchmark datasets across various recommender systems. Remarkably, our attack achieves far better attack accuracy with low false positive rates than baselines while with a much lower computational cost.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming healthcare, enabling fast development of tools like stress monitors, wellness trackers, and mental health chatbots. However, rapid and low-barrier development can introduce risks of bias, privacy violations, and unequal access, especially when systems ignore real-world contexts and diverse user needs. Many recent methods use AI to detect risks automatically, but this can reduce human engagement in understanding how harms arise and who they affect. We present a human-centered framework that generates user stories and supports multi-agent discussions to help people think creatively about potential benefits and harms before deployment. In a user study, participants who read stories recognized a broader range of harms, distributing their responses more evenly across all 13 harm types. In contrast, those who did not read stories focused primarily on privacy and well-being (58.3%). Our findings show that storytelling helped participants speculate about a broader range of harms and benefits and think more creatively about AI's impact on users.
Digital Surface Models (DSM) offer a wealth of height information for understanding the Earth's surface as well as monitoring the existence or change in natural and man-made structures. Classical height estimation requires multi-view geospatial imagery or LiDAR point clouds which can be expensive to acquire. Single-view height estimation using neural network based models shows promise however it can struggle with reconstructing high resolution features. The latest advancements in diffusion models for high resolution image synthesis and editing have yet to be utilized for remote sensing imagery, particularly height estimation. Our approach involves training a generative diffusion model to learn the joint distribution of optical and DSM images across both domains as a Markov chain. This is accomplished by minimizing a denoising score matching objective while being conditioned on the source image to generate realistic high resolution 3D surfaces. In this paper we experiment with conditional denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPM) for height estimation from a single remotely sensed image and show promising results on the Vaihingen benchmark dataset.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.