Ask or search anything...
 KAUST
KAUSTResearchers from KAUST and RWTH Aachen University investigated the impact of training algorithms on neural network properties, demonstrating that Adaptive Random Fourier Features (ARFF) enables two-layer networks to achieve spectral unbiasedness and enhanced robustness against adversarial noise compared to Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD). ARFF-trained networks showed spectral bias approaching zero and improved resilience, especially when using noisy validation data during training.
View blogCausalTAD presents a temporal action detection model that explicitly leverages temporal causality through a Hybrid Causal Block, which integrates causal Mamba and causal attention mechanisms. This approach achieved state-of-the-art performance, including first-place rankings in the Ego4D Moment Query and EPIC-Kitchens Challenges 2024.
View blogTuna, a native unified multimodal model developed by Meta BizAI, introduces a novel cascaded VAE and representation encoder to construct a single, continuous visual representation for both understanding and generation. This architecture achieves state-of-the-art performance across diverse image and video understanding, generation, and editing benchmarks, often outperforming larger, specialized models while utilizing smaller LLM decoders.
View blogNVIDIA researchers and collaborators developed SANA-Video, an efficient video generation model that uses a Block Linear Diffusion Transformer to enable high-resolution, long-duration video synthesis with significantly reduced computational costs. The model reduces training cost to 1% of MovieGen and achieves 16x faster inference than existing small diffusion models, generating a 5-second 720p video in 36 seconds on an H100 GPU.
View blogOpenHands is an open-source platform facilitating the development, evaluation, and deployment of generalist AI agents that interact with digital environments by writing code, using command lines, and browsing the web. Its CodeAct agent achieved competitive performance across 15 diverse benchmarks, including software engineering, web browsing, and general assistance tasks, without task-specific modifications.
View blogThe Agent-as-a-Judge framework and the DevAI benchmark provide a scalable and reliable method for evaluating AI agents, demonstrating a superior alignment with human judgment compared to LLM-as-a-Judge. This approach achieves substantial cost and time reductions in evaluating complex, real-world AI application development tasks.
View blogOASIS presents an open agent social interaction simulator capable of scaling to one million LLM-based agents, designed to mimic real-world social media platforms. The platform successfully replicates and investigates complex social phenomena like information propagation, group polarization, and herd effects, providing a testbed for understanding emergent behaviors at unprecedented scales.
View blogThis research introduces WORKFORCE, a modular multi-agent inference architecture that decouples planning from execution, and OPTIMIZED WORKFORCE LEARNING (OWL), a training paradigm focused on a domain-agnostic planner. The system achieved 69.70% accuracy on the GAIA benchmark, setting a new open-source state-of-the-art and outperforming commercial baselines like OpenAI's Deep Research.
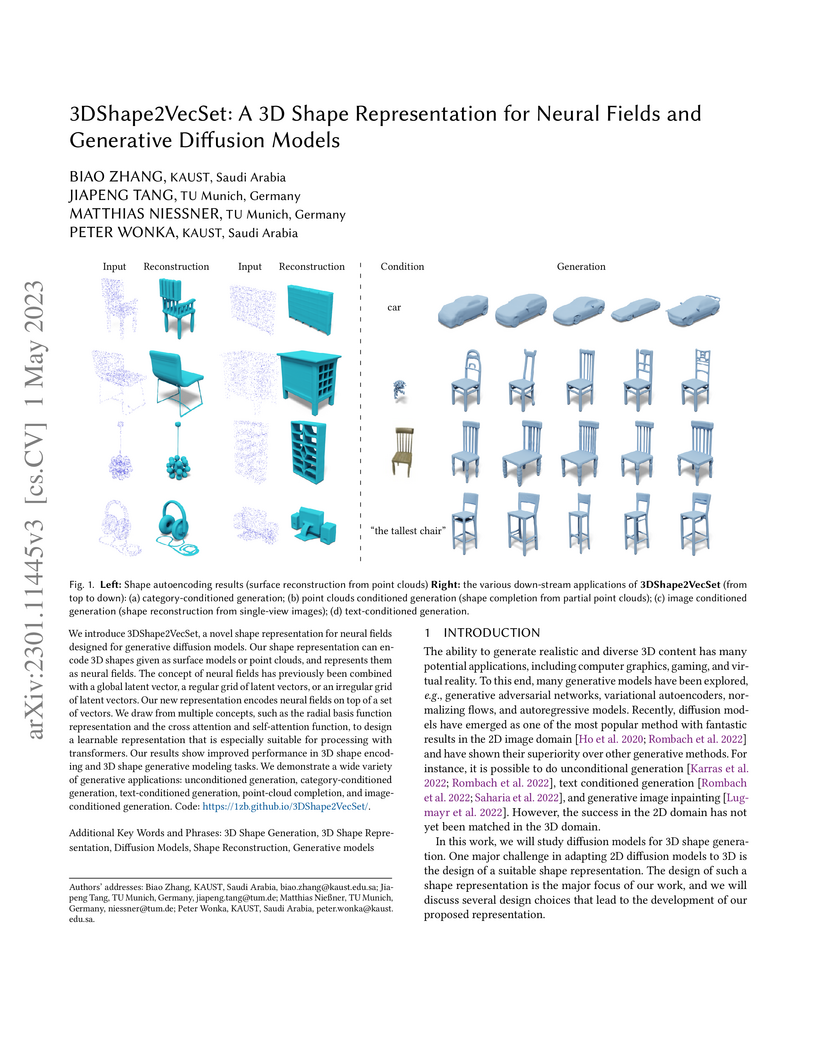
View blogResearchers from KAUST and TU Munich introduce 3DShape2VecSet, a 3D shape representation that uses a fixed-size set of latent vectors for neural fields, enabling high-fidelity 3D shape generation with diffusion models. This approach achieves superior reconstruction quality, with a mean IoU of 0.965, and generates shapes with lower Surface-FPD (0.76) compared to previous methods, also demonstrating the first text-conditioned 3D shape generation using diffusion models.
View blogReflectionFlow introduces an inference-time framework for text-to-image diffusion models, employing iterative self-reflection and textual feedback to refine generated images. This approach improves image generation quality, particularly for complex prompts, and provides interpretable visual reasoning through reflection chains.
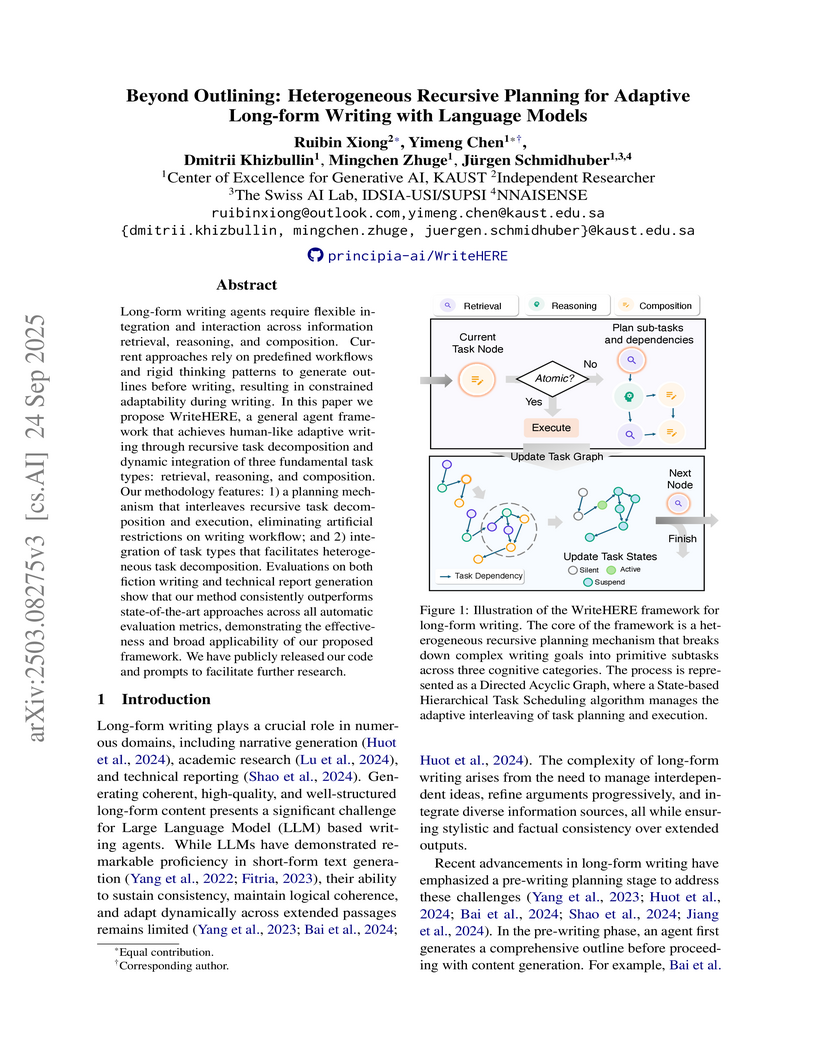
View blogThe WriteHERE framework introduces a heterogeneous recursive planning approach that enables large language models to generate adaptive, high-quality long-form text by dynamically interleaving retrieval, reasoning, and composition tasks. This method consistently outperforms existing baselines in narrative and technical report generation, showing improved performance in content quality and length scalability, including reports exceeding 10,000 words.
View blogZoeDepth, developed by researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology and Intel, is a framework for single-image depth estimation that combines relative and metric depth estimation to achieve both strong generalization across diverse environments and accurate absolute depth measurements. It demonstrates a 21% improvement in relative absolute error on the NYU Depth v2 benchmark and unprecedented zero-shot generalization, with some metrics improving by up to 976% on unseen datasets.
View blogThis work introduces Triangle Splatting, a differentiable rendering approach that optimizes unstructured 3D triangles to reconstruct photorealistic scenes from images. The method achieves state-of-the-art visual fidelity, notably improving perceptual quality over prior splatting techniques, and renders at thousands of frames per second, outperforming implicit methods by orders of magnitude.
View blogA comprehensive framework called General-Level introduces a 5-level taxonomy for evaluating multimodal large language models (MLLMs), accompanied by General-Bench - a large-scale benchmark testing diverse modalities and tasks, revealing that even leading models like GPT-4V achieve only Level-3 capabilities while demonstrating limited cross-modal synergy.
View blogSHAPEGEN4D directly synthesizes high-quality dynamic 3D meshes and their textures from monocular video, leveraging adapted 3D generative models to achieve superior geometric accuracy (e.g., Chamfer distance of 0.1220) and robust temporal consistency over prior methods.
View blogResearchers at KAUST developed PHYSGYM, an interactive benchmark to evaluate large language models' physics discovery capabilities under controlled prior knowledge. Experiments revealed that while prior information generally improves performance, abundant context can sometimes impede discovery, highlighting a conflict between pattern-matching and mechanistic inference.
View blogMoEUT enables Universal Transformers to scale efficiently to large language models by integrating Mixture-of-Experts with novel architectural components like layer grouping and peri-layernorm. The architecture slightly outperforms parameter-matched standard Transformers on language modeling tasks while demonstrating improved compute and memory efficiency.
View blog
 NVIDIA
NVIDIA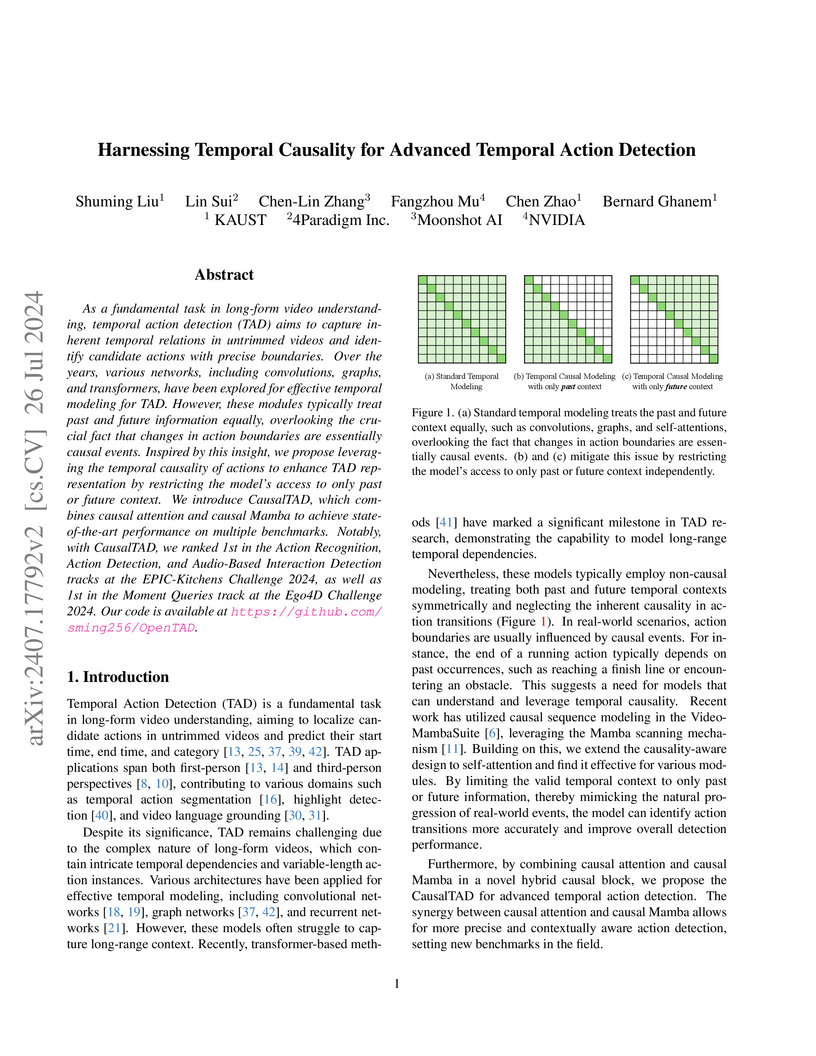
 University of Waterloo
University of Waterloo Meta
Meta
 Tsinghua University
Tsinghua University Peking University
Peking University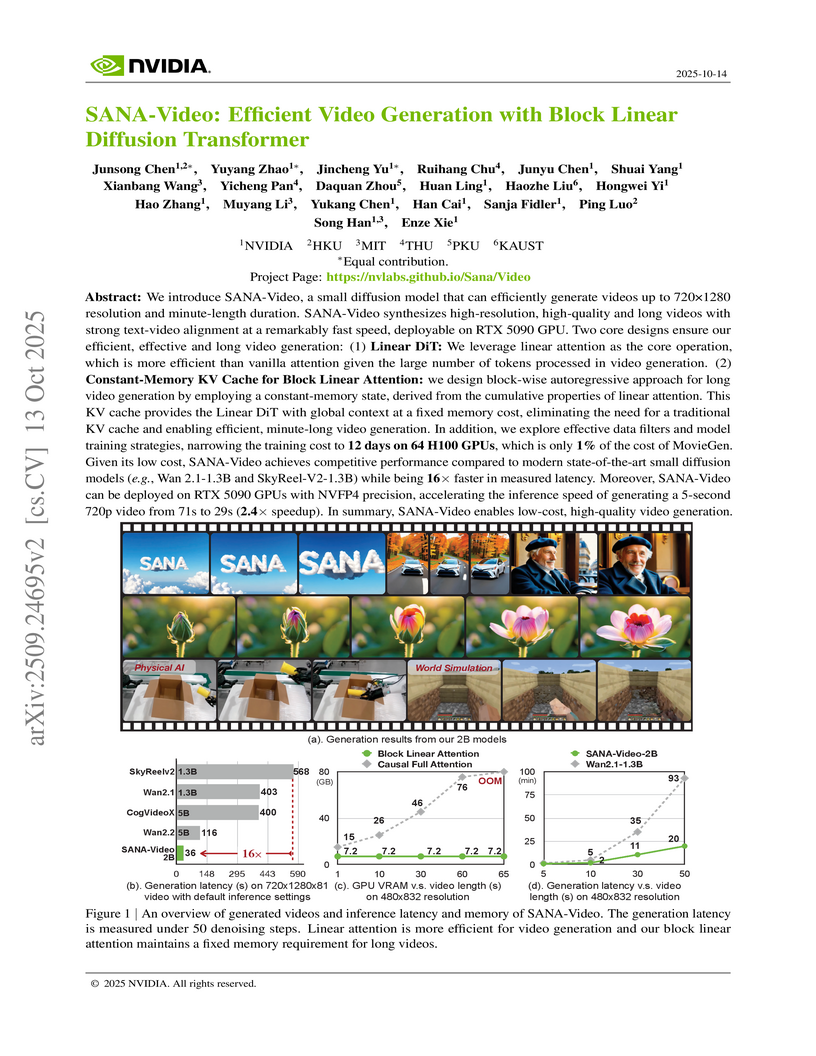
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley

 Imperial College London
Imperial College London
 University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge CUHK
CUHK
 Hugging Face
Hugging Face
 UCLA
UCLA

 University of Toronto
University of Toronto Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind



 Purdue University
Purdue University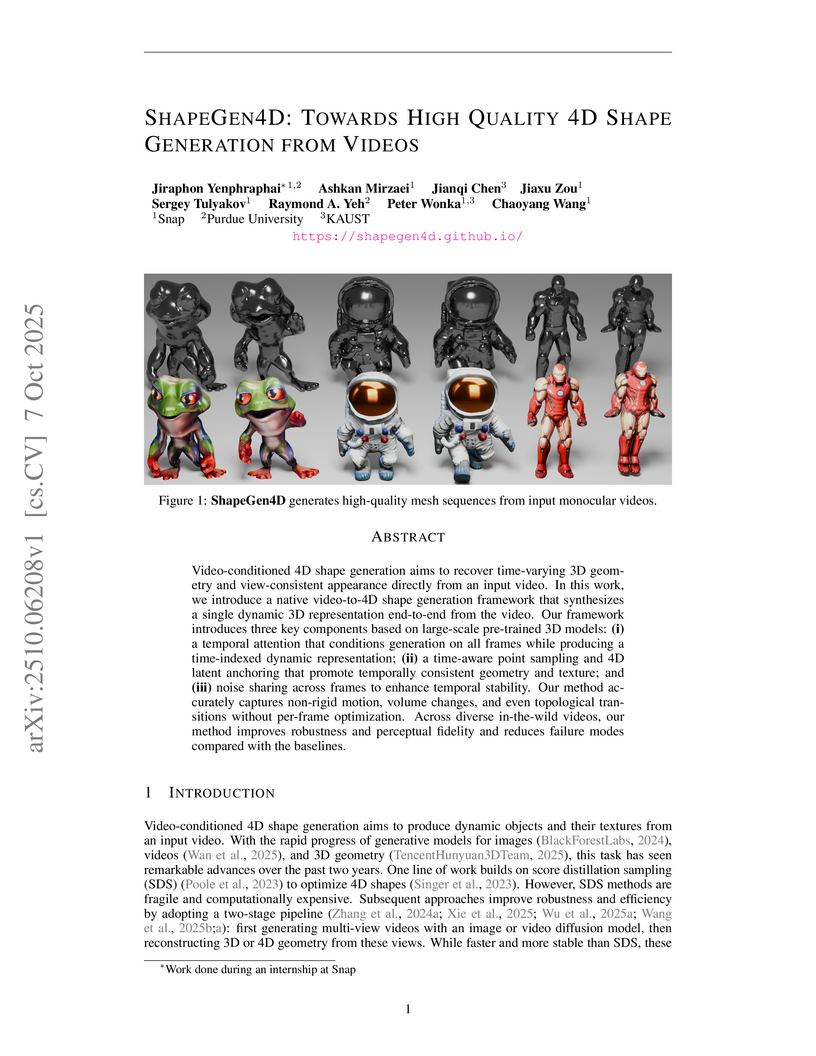

 Harvard University
Harvard University Stanford University
Stanford University