Ericsson ResearchEricsson
Researchers from Lund University and Ericsson developed a Predictability-Aware Error-State Kalman Filter (PsudoESKF) for head motion prediction in remote XR. The framework achieved lower position and orientation errors, and improved robustness to packet loss (e.g., 49.6% reduction in orientation error for hard motions at 50% loss) compared to existing filter-based methods, while maintaining computational efficiency suitable for edge deployment.
Northwestern Polytechnical University Northeastern University
Northeastern University Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University
Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute
University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra
Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra NVIDIA
NVIDIA Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology
Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design
King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design Aalto University
Aalto University Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University
Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécom
KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécom
 Northeastern University
Northeastern University Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University
Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute
University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra
Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra NVIDIA
NVIDIA Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology
Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design
King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design Aalto University
Aalto University Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University
Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécom
KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécomA comprehensive white paper from the GenAINet Initiative introduces Large Telecom Models (LTMs) as a novel framework for integrating AI into telecommunications infrastructure, providing a detailed roadmap for innovation while addressing critical challenges in scalability, hardware requirements, and regulatory compliance through insights from a diverse coalition of academic, industry and regulatory experts.
The emergence of 5G technology marks a significant milestone in developing telecommunication networks, enabling exciting new applications such as augmented reality and self-driving vehicles. However, these improvements bring an increased management complexity and a special concern in dealing with failures, as the applications 5G intends to support heavily rely on high network performance and low latency. Thus, automatic self-healing solutions have become effective in dealing with this requirement, allowing a learning-based system to automatically detect anomalies and perform Root Cause Analysis (RCA). However, there are inherent challenges to the implementation of such intelligent systems. First, there is a lack of suitable data for anomaly detection and RCA, as labelled data for failure scenarios is uncommon. Secondly, current intelligent solutions are tailored to LTE networks and do not fully capture the spatio-temporal characteristics present in the data. Considering this, we utilize a calibrated simulator, Simu5G, and generate open-source data for normal and failure scenarios. Using this data, we propose Simba, a state-of-the-art approach for anomaly detection and root cause analysis in 5G Radio Access Networks (RANs). We leverage Graph Neural Networks to capture spatial relationships while a Transformer model is used to learn the temporal dependencies of the data. We implement a prototype of Simba and evaluate it over multiple failures. The outcomes are compared against existing solutions to confirm the superiority of Simba.
Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have recently enabled considerable advances in the realm of image and video quality assessment, but this progress has yet to be fully explored in the domain of 3D assets. We are interested in using these models to conduct No-Reference Point Cloud Quality Assessment (NR-PCQA), where the aim is to automatically evaluate the perceptual quality of a point cloud in absence of a reference. We begin with the observation that different modalities of data - text descriptions, 2D projections, and 3D point cloud views - provide complementary information about point cloud quality. We then construct PIT-QMM, a novel LMM for NR-PCQA that is capable of consuming text, images and point clouds end-to-end to predict quality scores. Extensive experimentation shows that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art by significant margins on popular benchmarks with fewer training iterations. We also demonstrate that our framework enables distortion localization and identification, which paves a new way forward for model explainability and interactivity. Code and datasets are available at this https URL.
In distributed multiple-input multiple-output (D-MIMO) networks, power
control is crucial to optimize the spectral efficiencies of users and max-min
fairness (MMF) power control is a commonly used strategy as it satisfies
uniform quality-of-service to all users. The optimal solution of MMF power
control requires high complexity operations and hence deep neural network based
artificial intelligence (AI) solutions are proposed to decrease the complexity.
Although quite accurate models can be achieved by using AI, these models have
some intrinsic vulnerabilities against adversarial attacks where carefully
crafted perturbations are applied to the input of the AI model. In this work,
we show that threats against the target AI model which might be originated from
malicious users or radio units can substantially decrease the network
performance by applying a successful adversarial sample, even in the most
constrained circumstances. We also demonstrate that the risk associated with
these kinds of adversarial attacks is higher than the conventional attack
threats. Detailed simulations reveal the effectiveness of adversarial attacks
and the necessity of smart defense techniques.
07 Oct 2025
The COVID-19 pandemic has permanently altered workplace structures, normalizing remote work. However, critical evidence highlights challenges with fully remote arrangements, particularly for software teams. This study investigates employee resignation patterns at Ericsson, a global developer of software-intensive systems, before, during, and after the pandemic. Using HR data from 2016-2025 in Ericsson Sweden, we analyze how different work modalities (onsite, remote, and hybrid) influence employee retention. Our findings show a marked increase in resignations from summer 2021 to summer 2023, especially among employees with less than five years of tenure. Employees onboarded remotely during the pandemic were significantly more likely to resign within their first three years, even after returning to the office. Exit surveys suggest that remote onboarding may fail to establish the necessary organizational attachment, the feeling of belonging and long-term retention. By contrast, the company's eventual successful return to pre-pandemic retention rates illustrates the value of differentiated work policies and supports reconsidering selective return-to-office (RTO) mandates. Our study demonstrates the importance of employee integration practices in hybrid environments where the requirement for in-office presence for recent hires shall be accompanied by in-office presence from their team members and more senior staff whose mentoring and social interactions contribute to integration into the corporate work environment. We hope these actionable insights will inform HR leaders and policymakers in shaping post-pandemic work practices, demonstrating that carefully crafted hybrid models anchored in organizational attachment and mentorship can sustain retention in knowledge-intensive companies.
Network capacity expansion is a critical challenge for telecom operators, requiring strategic placement of new cell sites to ensure optimal coverage and performance. Traditional approaches, such as manual drive tests and static optimization, often fail to consider key real-world factors including user density, terrain features, and financial constraints. In this paper, we propose a machine learning-based framework that combines deep neural networks for signal coverage prediction with spatial clustering to recommend new tower locations in underserved areas. The system integrates geospatial, demographic, and infrastructural data, and incorporates budget-aware constraints to prioritize deployments. Operating within an iterative planning loop, the framework refines coverage estimates after each proposed installation, enabling adaptive and cost-effective expansion. While full-scale simulation was limited by data availability, the architecture is modular, robust to missing inputs, and generalizable across diverse deployment scenarios. This approach advances radio network planning by offering a scalable, data-driven alternative to manual methods.
Network Slices (NSs) are virtual networks operating over a shared physical infrastructure, each designed to meet specific application requirements while maintaining consistent Quality of Service (QoS). In Fifth Generation (5G) networks, User Equipment (UE) can connect to and seamlessly switch between multiple NSs to access diverse services. However, this flexibility, known as Inter-Slice Switching (ISS), introduces a potential vulnerability that can be exploited to launch Distributed Slice Mobility (DSM) attacks, a form of Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack. To secure 5G networks and their NSs against DSM attacks, we present in this work, PUL-Inter-Slice Defender; an anomaly detection solution that leverages Positive Unlabeled Learning (PUL) and incorporates a combination of Long Short-Term Memory Autoencoders and K-Means clustering. PUL-Inter-Slice Defender leverages the Third Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) key performance indicators and performance measurement counters as features for its machine learning models to detect DSM attack variants while maintaining robustness in the presence of contaminated training data. When evaluated on data collected from our 5G testbed based on the open-source free5GC and UERANSIM, a UE/ Radio Access Network (RAN) simulator; PUL-Inter-Slice Defender achieved F1-scores exceeding 98.50% on training datasets with 10% to 40% attack contamination, consistently outperforming its counterpart Inter-Slice Defender and other PUL based solutions combining One-Class Support Vector Machine (OCSVM) with Random Forest and XGBoost.
02 Dec 2024
As mission- and safety-critical wireless applications grow in complexity and diversity, next-generation wireless systems must meet increasingly stringent and multifaceted requirements. These systems demand resilience along with enhanced intelligence and adaptability to ensure reliable communication under diverse conditions. This paper proposes an event-based multi-stage resilience framework, offering a guideline for efficiently integrating a combination of error mitigation techniques. The framework is applied to a case study focusing on uplink transmission of mixed-criticality data in the presence of random link blockages. The proposed scheme combines multiple blockage mitigation strategies - rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA), one-sided access point cooperation, and central decoding - within an event-driven algorithm. Each method, increasing in effectiveness and complexity, is activated sequentially to systematically overcome blockages. We model a mixed-criticality queuing system and formulate two transmit power allocation problems, one for separate decoding and one for central decoding, to ensure queue stability and fairness. Simulations evaluate the delay performance under varying blockage durations and examine the cost tradeoffs among resilience mechanisms within the proposed framework. The results suggest that passive robustness strategies effectively handle frequent short-term fluctuations, while more complex adaptation becomes germane for rare and prolonged blockages. Additionally, the results emphasize the importance of criticality-awareness for resilient communication design.
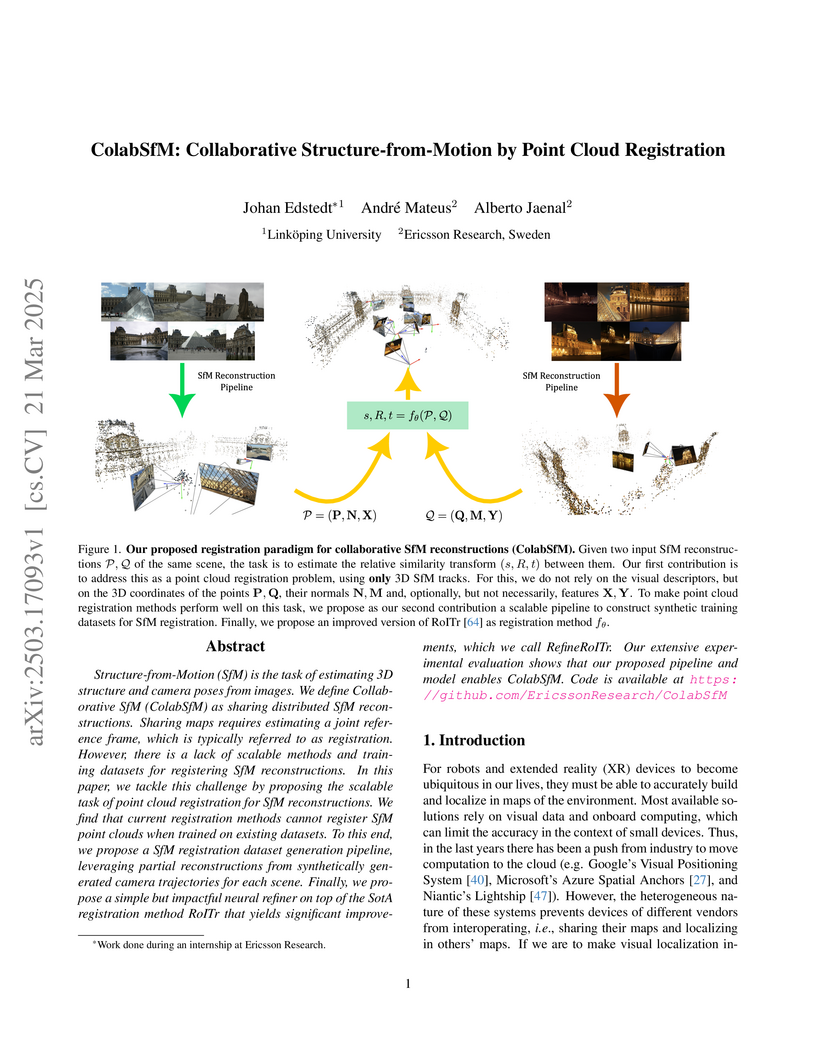
Structure-from-Motion (SfM) is the task of estimating 3D structure and camera
poses from images. We define Collaborative SfM (ColabSfM) as sharing
distributed SfM reconstructions. Sharing maps requires estimating a joint
reference frame, which is typically referred to as registration. However, there
is a lack of scalable methods and training datasets for registering SfM
reconstructions. In this paper, we tackle this challenge by proposing the
scalable task of point cloud registration for SfM reconstructions. We find that
current registration methods cannot register SfM point clouds when trained on
existing datasets. To this end, we propose a SfM registration dataset
generation pipeline, leveraging partial reconstructions from synthetically
generated camera trajectories for each scene. Finally, we propose a simple but
impactful neural refiner on top of the SotA registration method RoITr that
yields significant improvements, which we call RefineRoITr. Our extensive
experimental evaluation shows that our proposed pipeline and model enables
ColabSfM. Code is available at this https URL
A plethora of outlier detectors have been explored in the time series domain,
however, in a business sense, not all outliers are anomalies of interest.
Existing anomaly detection solutions are confined to certain outlier detectors
limiting their applicability to broader anomaly detection use cases. Network
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) tend to exhibit stochastic behaviour
producing statistical outliers, most of which do not adversely affect business
operations. Thus, a heuristic is required to capture the business definition of
an anomaly for time series KPI. This article proposes an Adaptive Thresholding
Heuristic (ATH) to dynamically adjust the detection threshold based on the
local properties of the data distribution and adapt to changes in time series
patterns. The heuristic derives the threshold based on the expected periodicity
and the observed proportion of anomalies minimizing false positives and
addressing concept drift. ATH can be used in conjunction with any underlying
seasonality decomposition method and an outlier detector that yields an outlier
score. This method has been tested on EON1-Cell-U, a labeled KPI anomaly
dataset produced by Ericsson, to validate our hypothesis. Experimental results
show that ATH is computationally efficient making it scalable for near real
time anomaly detection and flexible with multiple forecasters and outlier
detectors.
Homographies are among the most prevalent transformations occurring in geometric computer vision and projective geometry, and homography estimation is consequently a crucial step in a wide assortment of computer vision tasks. When working with real images, which are often afflicted with geometric distortions caused by the camera lens, it may be necessary to determine both the homography and the lens distortion-particularly the radial component, called radial distortion-simultaneously to obtain anything resembling useful estimates. When considering a homography with radial distortion between two images, there are three conceptually distinct configurations for the radial distortion; (i) distortion in only one image, (ii) identical distortion in the two images, and (iii) independent distortion in the two images. While these cases have been addressed separately in the past, the present paper provides a novel and unified approach to solve all three cases. We demonstrate how the proposed approach can be used to construct new fast, stable, and accurate minimal solvers for radially distorted homographies. In all three cases, our proposed solvers are faster than the existing state-of-the-art solvers while maintaining similar accuracy. The solvers are tested on well-established benchmarks including images taken with fisheye cameras. The source code for our solvers will be made available in the event our paper is accepted for publication.
MatChA introduces a two-stage pipeline for robust visual feature matching across heterogeneous detection and description algorithms, a previously unaddressed challenge in visual localization. This approach significantly boosts image matching accuracy and visual localization rates in cross-algorithm settings, achieving improvements like a 10-12 percentage point increase in day query localization on Aachen Day and Night v1.1.
Code review is one of the primary means of assuring the quality of released software along with testing and static analysis. However, code review requires experienced developers who may not always have the time to perform an in-depth review of code. Thus, automating code review can help alleviate the cognitive burden on experienced software developers allowing them to focus on their primary activities of writing code to add new features and fix bugs. In this paper, we describe our experience in using Large Language Models towards automating the code review process in Ericsson. We describe the development of a lightweight tool using LLMs and static program analysis. We then describe our preliminary experiments with experienced developers in evaluating our code review tool and the encouraging results.
Adapting visual object detectors to operational target domains is a
challenging task, commonly achieved using unsupervised domain adaptation (UDA)
methods. Recent studies have shown that when the labeled dataset comes from
multiple source domains, treating them as separate domains and performing a
multi-source domain adaptation (MSDA) improves the accuracy and robustness over
blending these source domains and performing a UDA. For adaptation, existing
MSDA methods learn domain-invariant and domain-specific parameters (for each
source domain). However, unlike single-source UDA methods, learning
domain-specific parameters makes them grow significantly in proportion to the
number of source domains. This paper proposes a novel MSDA method called
Prototype-based Mean Teacher (PMT), which uses class prototypes instead of
domain-specific subnets to encode domain-specific information. These prototypes
are learned using a contrastive loss, aligning the same categories across
domains and separating different categories far apart. Given the use of
prototypes, the number of parameters required for our PMT method does not
increase significantly with the number of source domains, thus reducing memory
issues and possible overfitting. Empirical studies indicate that PMT
outperforms state-of-the-art MSDA methods on several challenging object
detection datasets. Our code is available at
this https URL
22 Sep 2025
This paper proposes a joint optimization of pilot subcarrier allocation and non-orthogonal sequence for multiple-input-multiple-output (MIMO)-orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) systems under compressed sensing (CS)-based channel estimation exploiting delay and angle sparsity. Since the performance of CS-based approaches depends on a coherence metric of the sensing matrix in the measurement process, we formulate a joint optimization problem to minimize this coherence. Due to the discrete nature of subcarrier allocation, a straightforward formulation of the joint optimization results in a mixed-integer nonlinear program (MINLP), which is computationally intractable due to the combinatorial explosion of allocation candidates. To overcome the intractability of discrete variables, we introduce a block sparse penalty for pilots across all subcarriers, which ensures that the power of some unnecessary pilots approaches zero. This framework enables joint optimization using only continuous variables. In addition, we propose an efficient computation method for the coherence metric by exploiting the structure of the sensing matrix, which allows its gradient to be derived in closed form, making the joint optimization problem solvable in an efficient way via a gradient descent approach. Numerical results confirm that the proposed pilot sequence exhibits superior coherence properties and enhances the CS-based channel estimation performance.
Channel state information (CSI)-based user equipment (UE) positioning with neural networks -- referred to as neural positioning -- is a promising approach for accurate off-device UE localization. Most existing methods train their neural networks with ground-truth position labels obtained from external reference positioning systems, which requires costly hardware and renders label acquisition difficult in large areas. In this work, we propose a novel neural positioning pipeline that avoids the need for any external reference positioning system. Our approach trains the positioning network only using CSI acquired off-device and relative displacement commands executed on commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) robot platforms, such as robotic vacuum cleaners -- such an approach enables inexpensive training of accurate neural positioning functions over large areas. We evaluate our method in three real-world scenarios, ranging from small line-of-sight (LoS) areas to larger non-line-of-sight (NLoS) environments, using CSI measurements acquired in IEEE 802.11 Wi-Fi and 5G New Radio (NR) systems. Our experiments demonstrate that the proposed neural positioning pipeline achieves UE localization accuracies close to state-of-the-art methods that require externally acquired high-precision ground-truth position labels for training.
Retrieval augmented generation (RAG) for technical documents creates
challenges as embeddings do not often capture domain information. We review
prior art for important factors affecting RAG and perform experiments to
highlight best practices and potential challenges to build RAG systems for
technical documents.
For the energy-efficient deployment of cell-free massive MIMO functionality in a practical wireless network, the end-to-end (from radio site to the cloud) energy-aware operation is essential. In line with the cloudification and virtualization in the open radio access networks (O-RAN), it is indisputable to envision prospective cell-free infrastructure on top of the O-RAN architecture. In this paper, we explore the performance and power consumption of cell-free massive MIMO technology in comparison with traditional small-cell systems, in the virtualized O-RAN architecture. We compare two different functional split options and different resource orchestration mechanisms. In the end-to-end orchestration scheme, we aim to minimize the end-to-end power consumption by jointly allocating the radio, optical fronthaul, and virtualized cloud processing resources. We compare end-to-end orchestration with two other schemes: i) "radio-only" where radio resources are optimized independently from the cloud and ii) "local cloud coordination" where orchestration is only allowed among a local cluster of radio units. We develop several algorithms to solve the end-to-end power minimization and sum spectral efficiency maximization problems. The numerical results demonstrate that end-to-end resource allocation with fully virtualized fronthaul and cloud resources provides a substantial additional power saving than the other resource orchestration schemes.
Business models of network service providers are undergoing an evolving transformation fueled by vertical customer demands and technological advances such as 5G, Software Defined Networking~(SDN), and Network Function Virtualization~(NFV). Emerging scenarios call for agile network services consuming network, storage, and compute resources across heterogeneous infrastructures and administrative domains. Coordinating resource control and service creation across interconnected domains and diverse technologies becomes a grand challenge. Research and development efforts are being devoted to enabling orchestration processes to automate, coordinate, and manage the deployment and operation of network services. In this survey, we delve into the topic of Network Service Orchestration~(NSO) by reviewing the historical background, relevant research projects, enabling technologies, and standardization activities. We define key concepts and propose a taxonomy of NSO approaches and solutions to pave the way towards a common understanding of the various ongoing efforts around the realization of diverse NSO application scenarios. Based on the analysis of the state of affairs, we present a series of open challenges and research opportunities, altogether contributing to a timely and comprehensive survey on the vibrant and strategic topic of network service orchestration.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.