Guangdong University of Technology
Video-MTR presents a reinforced multi-turn reasoning framework that enables Multimodal Large Language Models to iteratively process and understand long-form videos. This approach achieves state-of-the-art or competitive performance on benchmarks such as VideoMME, MLVU, and EgoSchema while using significantly fewer input frames and requiring only 8K supervision-rich training examples.
SAGE proposes a framework for self-evolving Large Language Model agents by integrating iterative feedback, reflection, and a novel memory optimization system inspired by the Ebbinghaus forgetting curve. This approach improves performance for both proprietary and open-source models, notably enabling Qwen-1.8B to achieve results comparable to GPT-3.5 and reducing memory consumption by nearly 50% in RAG tasks.
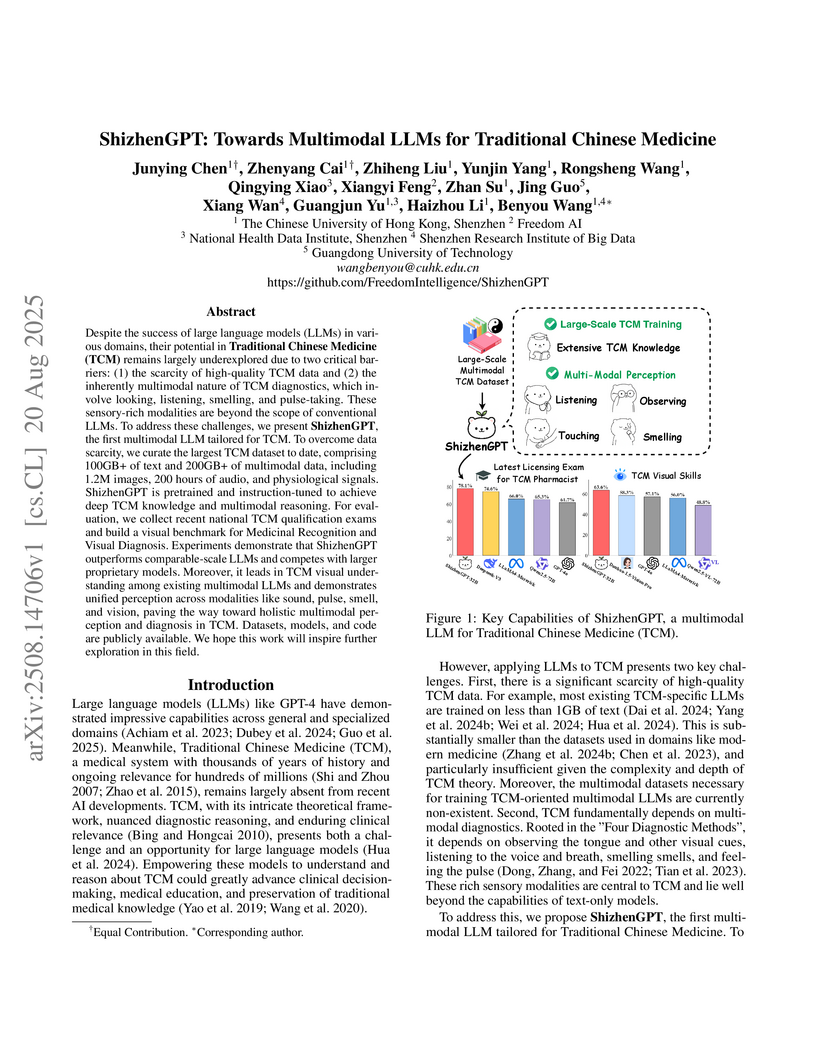
ShizhenGPT is introduced as the first multimodal Large Language Model (LLM) tailored for Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), integrating textual, visual, audio, smell, and pulse signals to support diagnosis. It establishes new benchmarks, achieving state-of-the-art results on TCM national qualification exams and specialized multimodal diagnostic tasks, built upon the largest curated TCM dataset to date.
26 Nov 2025
E₀ introduces a continuized discrete diffusion framework for Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models, reformulating action generation as iterative denoising of Gaussian-noised one-hot action vectors. This approach achieves state-of-the-art performance with an average 10.7% improvement across 14 diverse simulation environments and demonstrates robust real-world generalization on a robotic arm.
While diffusion models excel at generating continuous data such as images, adapting them to discrete tasks has relied on indirect approaches that either operate in continuous embedding spaces or use token masking mechanisms, both of which deviate from modeling the true discrete data distribution that can be theoretically guaranteed by Tweedie's formula. We propose in-situ Tweedie Discrete Diffusion (TDD), a framework that performs diffusion guaranteed by Tweedie's formula directly within the discrete one-hot space, hence "in-situ." Unlike prior methods that diffuse continuous embeddings or mask tokens, TDD directly corrupts one-hot vectors with Gaussian noise and performs iterative denoising through a timestep-conditioned cross-entropy objective rather than mean-squared-error reconstruction. At each denoising step, the model predicts class probabilities, applies argmax to obtain discrete predictions, converts them to one-hot vectors, and feeds them into the next iteration with progressively reduced noise. This process naturally unifies discriminative classification and generative modeling under a single framework. Experiments demonstrate that TDD achieves strong performance on both image classification and text generation tasks, with extensive ablation studies confirming the effectiveness of each design component. Our work establishes a principled approach to discrete diffusion that preserves the core characteristics of diffusion models while operating natively in discrete space.
Open large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced the field of
natural language processing, showcasing impressive performance across various
tasks.Despite the significant advancements in LLMs, their effective operation
still relies heavily on human input to accurately guide the dialogue flow, with
agent tuning being a crucial optimization technique that involves human
adjustments to the model for better response to such guidance.Addressing this
dependency, our work introduces the TinyAgent model, trained on a meticulously
curated high-quality dataset. We also present the Collaborative Multi-Agent
Tuning (CMAT) framework, an innovative system designed to augment language
agent capabilities through adaptive weight updates based on environmental
feedback. This framework fosters collaborative learning and real-time
adaptation among multiple intelligent agents, enhancing their context-awareness
and long-term memory. In this research, we propose a new communication agent
framework that integrates multi-agent systems with environmental feedback
mechanisms, offering a scalable method to explore cooperative behaviors.
Notably, our TinyAgent-7B model exhibits performance on par with GPT-3.5,
despite having fewer parameters, signifying a substantial improvement in the
efficiency and effectiveness of LLMs.
MotionCtrl introduces a framework that achieves unified and flexible control over video generation by independently managing camera and object motion. The system integrates specialized modules into latent video diffusion models, yielding more natural videos with precise motion control and enhanced text-to-video alignment.
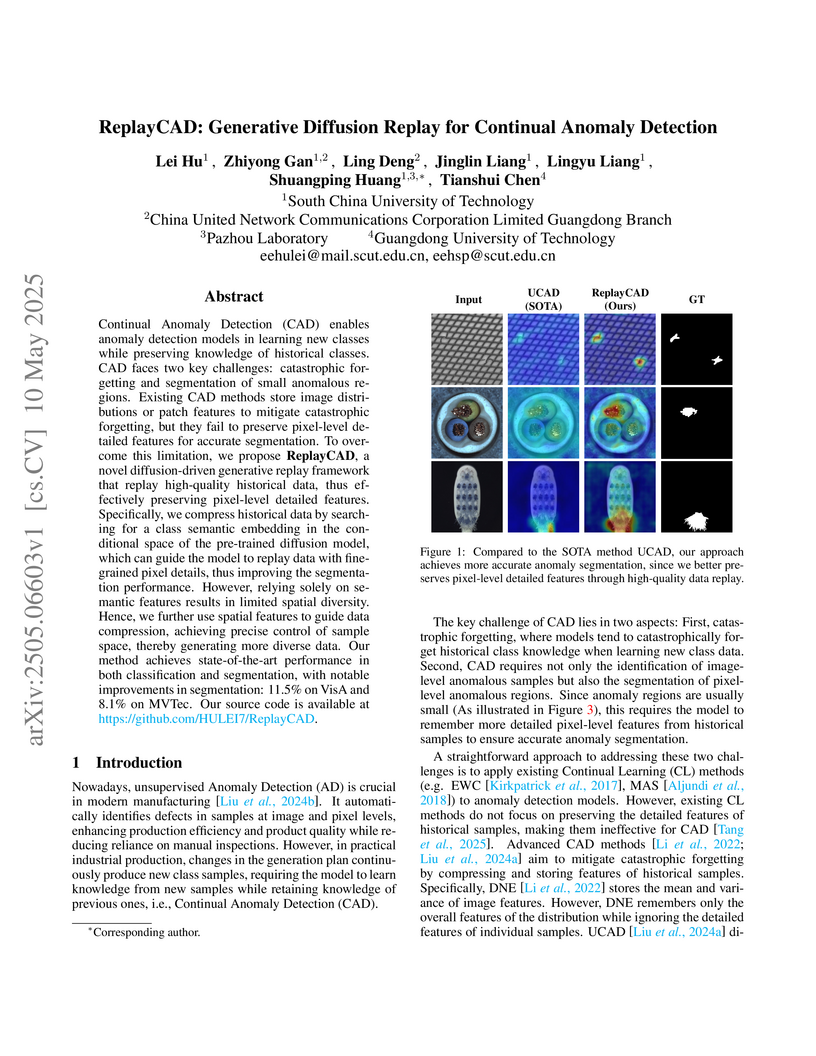
Continual Anomaly Detection (CAD) enables anomaly detection models in
learning new classes while preserving knowledge of historical classes. CAD
faces two key challenges: catastrophic forgetting and segmentation of small
anomalous regions. Existing CAD methods store image distributions or patch
features to mitigate catastrophic forgetting, but they fail to preserve
pixel-level detailed features for accurate segmentation. To overcome this
limitation, we propose ReplayCAD, a novel diffusion-driven generative replay
framework that replay high-quality historical data, thus effectively preserving
pixel-level detailed features. Specifically, we compress historical data by
searching for a class semantic embedding in the conditional space of the
pre-trained diffusion model, which can guide the model to replay data with
fine-grained pixel details, thus improving the segmentation performance.
However, relying solely on semantic features results in limited spatial
diversity. Hence, we further use spatial features to guide data compression,
achieving precise control of sample space, thereby generating more diverse
data. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance in both classification
and segmentation, with notable improvements in segmentation: 11.5% on VisA and
8.1% on MVTec. Our source code is available at
this https URL
This research introduces life-long personalization for Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling them to continuously adapt to individual user profiles. The AI PERSONA framework, coupled with the new PERSONABENCH dataset, allows LLMs to dynamically learn user preferences and habits without requiring costly model retraining, achieving personalized helpfulness and personalization scores (e.g., 8.29 and 7.63) that approach an empirical upper bound.
The Physical Autoregressive Model (PAR) enables high-performance robotic manipulation by transferring world knowledge from pretrained autoregressive video generation models, eliminating the need for action-specific pretraining. It achieves an average success rate of 74% across manipulation tasks on ManiSkill, including 100% on PushCube, showing competitive results against methods with extensive action pretraining.
We report a local minimum in thermal conductivity in twisted bilayer graphene (TBG) at the angle of 1.08∘, which corresponds to the 'magic angle' in the transition of several other reported properties. Within the supercell of a moiré lattice, different stacking modes generate phonon scattering sites which reduce the thermal conductivity of TBG. The thermal magic angle arises from the competition between the delocalization of atomic vibrational amplitudes and stresses on one hand, and the increased AA stacking density on the other hand. The former effect weakens the scattering strength of a single scatterer while the latter one increases the density of scatterers. The combination of these two effects eventually leads to the apparition of the highlighted irregularity in heat conduction. The manifestation of a magic angle, disclosing new thermal mechanisms at nanoscale, further uncovers the unique physics of two-dimensional materials.
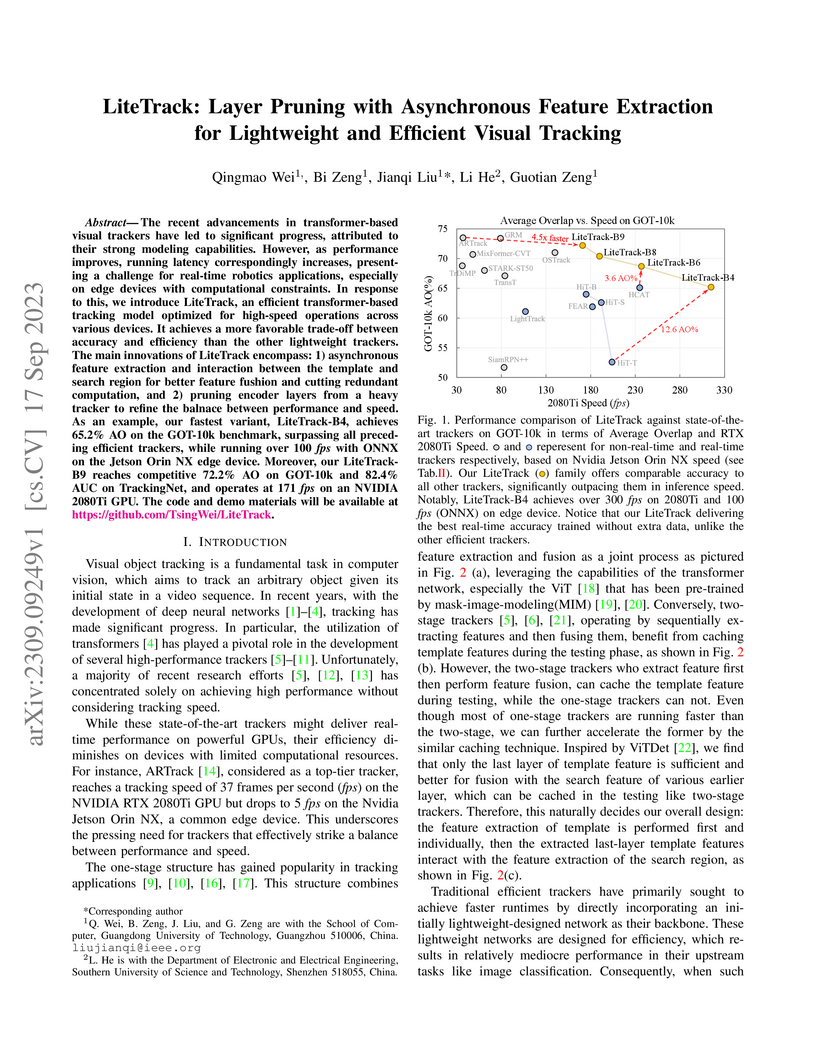
LiteTrack introduces a lightweight and efficient visual tracker that combines systematic layer pruning with asynchronous feature extraction for transformer models. This approach enables real-time operation on edge devices, achieving 64 FPS on a Jetson Orin NX while maintaining competitive accuracy with non-real-time state-of-the-art trackers.
ICM-Fusion offers an in-context meta-optimized framework for fusing multiple LoRA models, enhancing multi-task adaptation and generalization. This method effectively mitigates inter-weight conflicts, achieving improved performance on vision and language tasks and demonstrating robust adaptability in few-shot learning scenarios.
13 Aug 2025
Edge General Intelligence (EGI) represents a transformative evolution of edge computing, where distributed agents possess the capability to perceive, reason, and act autonomously across diverse, dynamic environments. Central to this vision are world models, which act as proactive internal simulators that not only predict but also actively imagine future trajectories, reason under uncertainty, and plan multi-step actions with foresight. This proactive nature allows agents to anticipate potential outcomes and optimize decisions ahead of real-world interactions. While prior works in robotics and gaming have showcased the potential of world models, their integration into the wireless edge for EGI remains underexplored. This survey bridges this gap by offering a comprehensive analysis of how world models can empower agentic artificial intelligence (AI) systems at the edge. We first examine the architectural foundations of world models, including latent representation learning, dynamics modeling, and imagination-based planning. Building on these core capabilities, we illustrate their proactive applications across EGI scenarios such as vehicular networks, unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) networks, the Internet of Things (IoT) systems, and network functions virtualization, thereby highlighting how they can enhance optimization under latency, energy, and privacy constraints. We then explore their synergy with foundation models and digital twins, positioning world models as the cognitive backbone of EGI. Finally, we highlight open challenges, such as safety guarantees, efficient training, and constrained deployment, and outline future research directions. This survey provides both a conceptual foundation and a practical roadmap for realizing the next generation of intelligent, autonomous edge systems.
The rapid expansion of sixth-generation (6G) wireless networks and the Internet of Things (IoT) has catalyzed the evolution from centralized cloud intelligence towards decentralized edge general intelligence. However, traditional edge intelligence methods, characterized by static models and limited cognitive autonomy, fail to address the dynamic, heterogeneous, and resource-constrained scenarios inherent to emerging edge networks. Agentic artificial intelligence (Agentic AI) emerges as a transformative solution, enabling edge systems to autonomously perceive multimodal environments, reason contextually, and adapt proactively through continuous perception-reasoning-action loops. In this context, the agentification of edge intelligence serves as a key paradigm shift, where distributed entities evolve into autonomous agents capable of collaboration and continual adaptation. This paper presents a comprehensive survey dedicated to Agentic AI and agentification frameworks tailored explicitly for edge general intelligence. First, we systematically introduce foundational concepts and clarify distinctions from traditional edge intelligence paradigms. Second, we analyze important enabling technologies, including compact model compression, energy-aware computing strategies, robust connectivity frameworks, and advanced knowledge representation and reasoning mechanisms. Third, we provide representative case studies demonstrating Agentic AI's capabilities in low-altitude economy networks, intent-driven networking, vehicular networks, and human-centric service provisioning, supported by numerical evaluations. Furthermore, we identify current research challenges, review emerging open-source platforms, and highlight promising future research directions to guide robust, scalable, and trustworthy Agentic AI deployments for next-generation edge environments.
LRQ-Solver: A Transformer-Based Neural Operator for Fast and Accurate Solving of Large-scale 3D PDEs
LRQ-Solver: A Transformer-Based Neural Operator for Fast and Accurate Solving of Large-scale 3D PDEs
Solving large-scale Partial Differential Equations (PDEs) on complex three-dimensional geometries represents a central challenge in scientific and engineering computing, often impeded by expensive pre-processing stages and substantial computational overhead. We introduce Low-Rank Query-based PDE Solver (LRQ-Solver), a physics-integrated framework engineered for rapid, accurate, and highly scalable simulations of industrial-grade models. This framework is built upon two primary technical innovations. First, our Parameter Conditioned Lagrangian Modeling (PCLM) approach explicitly couples local physical states with global design parameters, enabling robust predictions across varied simulation configurations. By embedding physical consistency directly into the learning architecture, PCLM ensures that predictions remain physically meaningful even under unseen design conditions, significantly enhancing generalization and reliability. Second, the Low-Rank Query Attention (LR-QA) module leverages the second-order statistics of physical fields to construct a global coherence kernel, reducing the computational complexity of attention from O(N2) to O(NC2 + C3). By replacing point-wise clustering with covariance decomposition, LRQ-Solver achieves exceptional scalability efficiently processing up to 2 million points on a single GPU. Validated on standard benchmarks, LRQ-Solver achieves a 38.9% error reduction on the DrivAerNet++ dataset and 28.76% on the 3D Beam dataset, alongside a training speedup of up to 50 times. Our results establish that LRQ-Solver offers a powerful paradigm for multi-configuration physics simulations, delivering a SOTA combination of accuracy, scalability, and efficiency. Code to reproduce the experiments is available at this https URL.
02 Sep 2025
Integrating the AVS PCRM standard for geometry compression into the i3DV 3D Gaussian Splatting framework achieves substantial bitrate savings of over 50% for geometry data and 10-25% overall, while maintaining identical objective and subjective rendering quality. This enables more efficient storage and transmission of volumetric video for real-time immersive applications.
In the multimedia domain, Infrared Small Target Detection (ISTD) plays a important role in drone-based multi-modality sensing. To address the dual challenges of cross-domain shift and heteroscedastic noise perturbations in ISTD, we propose a doubly wavelet-guided Invariance learning framework(Ivan-ISTD). In the first stage, we generate training samples aligned with the target domain using Wavelet-guided Cross-domain Synthesis. This wavelet-guided alignment machine accurately separates the target background through multi-frequency wavelet filtering. In the second stage, we introduce Real-domain Noise Invariance Learning, which extracts real noise characteristics from the target domain to build a dynamic noise library. The model learns noise invariance through self-supervised loss, thereby overcoming the limitations of distribution bias in traditional artificial noise modeling. Finally, we create the Dynamic-ISTD Benchmark, a cross-domain dynamic degradation dataset that simulates the distribution shifts encountered in real-world applications. Additionally, we validate the versatility of our method using other real-world datasets. Experimental results demonstrate that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of many quantitative metrics. In particular, Ivan-ISTD demonstrates excellent robustness in cross-domain scenarios. The code for this work can be found at: this https URL.
Creating recipe images is a key challenge in food computing, with applications in culinary education and multimodal recipe assistants. However, existing datasets lack fine-grained alignment between recipe goals, step-wise instructions, and visual content. We present RecipeGen, the first large-scale, real-world benchmark for recipe-based Text-to-Image (T2I), Image-to-Video (I2V), and Text-to-Video (T2V) generation. RecipeGen contains 26,453 recipes, 196,724 images, and 4,491 videos, covering diverse ingredients, cooking procedures, styles, and dish types. We further propose domain-specific evaluation metrics to assess ingredient fidelity and interaction modeling, benchmark representative T2I, I2V, and T2V models, and provide insights for future recipe generation models. Project page is available now.
Breast cancer lesion segmentation in DCE-MRI remains challenging due to
heterogeneous tumor morphology and indistinct boundaries. To address these
challenges, this study proposes a novel hybrid segmentation network, HCMA-UNet,
for lesion segmentation of breast cancer. Our network consists of a lightweight
CNN backbone and a Multi-view Axial Self-Attention Mamba (MISM) module. The
MISM module integrates Visual State Space Block (VSSB) and Axial Self-Attention
(ASA) mechanism, effectively reducing parameters through Asymmetric Split
Channel (ASC) strategy to achieve efficient tri-directional feature extraction.
Our lightweight model achieves superior performance with 2.87M parameters and
126.44 GFLOPs. A Feature-guided Region-aware loss function (FRLoss) is proposed
to enhance segmentation accuracy. Extensive experiments on one private and two
public DCE-MRI breast cancer datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves
state-of-the-art performance while maintaining computational efficiency. FRLoss
also exhibits good cross-architecture generalization capabilities. The source
code is available at this https URL
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.