Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology
Fish-Speech introduces a multilingual text-to-speech framework that bypasses traditional grapheme-to-phoneme conversion by leveraging large language models for direct linguistic feature extraction. It achieves high-fidelity and efficient speech synthesis through a Dual Autoregressive architecture and the Firefly-GAN vocoder, demonstrating strong performance in intelligibility, speaker similarity, and perceptual quality while enabling real-time inference on consumer hardware.
The paper presents AIGIBench, a comprehensive benchmark designed to rigorously evaluate the robustness and generalization capabilities of state-of-the-art Artificial Intelligence Generated Image (AIGI) detectors. It demonstrates that current methods suffer significant performance limitations across diverse generative models, real-world image degradations, and data processing variations, confirming that AIGI detection remains an unsolved challenge.
Agent-Pro introduces a framework that enables Large Language Model (LLM) agents to learn and evolve their strategic policies through interactive experience, utilizing policy-level reflection and prompt optimization. It achieved superior performance against various LLM baselines and certain reinforcement learning agents in imperfect-information games like Blackjack and Limit Texas Hold'em, demonstrating the ability to acquire complex, human-like game strategies.
RemoteSAM introduces a unified visual foundation model for Earth observation that leverages a referring expression segmentation framework to achieve robust pixel-level to image-level perception, alongside a new large-scale, automatically curated RemoteSAM-270K dataset. The model demonstrates superior parameter efficiency and state-of-the-art performance across various remote sensing tasks, including segmentation, visual grounding, and multi-label classification.
Researchers open-sourced a comprehensive dataset for end-to-end autonomous parking, the E2E Parking Dataset, generated through an iterative process in the CARLA simulator. Training an existing E2E model on this dataset yielded an 85.156% target success rate with an average position error of 0.237 meters and an average orientation error of 0.335 degrees, demonstrating enhanced precision and robustness.
Researchers from Shanghai AI Lab and collaborating institutions developed FengWu, an AI model that extends skillful global medium-range weather forecasts to 10.75 days for z500 and 11.5 days for t2m, outperforming the state-of-the-art GraphCast on 80% of predictands. The model achieves this with high computational efficiency, generating a 10-day forecast in under 30 seconds on a single A100 GPU, consuming approximately 2000 times less energy than traditional numerical weather prediction systems.
03 Nov 2025
Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory Fudan University
Fudan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of SydneyEast China Normal UniversityNanjing University of Information Science and TechnologyChinese Academy of Meteorological SciencesInstitute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of SydneyEast China Normal UniversityNanjing University of Information Science and TechnologyChinese Academy of Meteorological SciencesInstitute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
 Fudan University
Fudan University Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of SydneyEast China Normal UniversityNanjing University of Information Science and TechnologyChinese Academy of Meteorological SciencesInstitute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
The Chinese University of Hong KongThe University of SydneyEast China Normal UniversityNanjing University of Information Science and TechnologyChinese Academy of Meteorological SciencesInstitute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesScientific progress in Earth science depends on integrating data across the planet's interconnected spheres. However, the accelerating volume and fragmentation of multi-sphere knowledge and data have surpassed human analytical capacity. This creates a major bottleneck for discovery, especially in climate science. To address this challenge, we introduce EarthLink, the first self-evolving AI agent system designed as an interactive "copilot" for Earth scientists. Through natural language interaction, EarthLink automates the entire research workflow by integrating planning, code execution, data analysis, and physical reasoning into a unified process that directly addresses this limitation. Beyond efficiency, it exhibits human-like cross-disciplinary analytical ability and achieves proficiency comparable to a junior researcher in expert evaluations on core large-scale climate tasks, including model-observation comparison and climate change understanding. When tasked with an open scientific problem, specifically the discovery of precursors of the Atlantic Niño, EarthLink autonomously developed a research strategy, identified sources of predictability, verified its hypotheses with available data, and proposed a physically consistent mechanism. These emerging capabilities enable a new human-AI research paradigm. Scientists can focus on value and result judgments, while AI systems handle complex data analysis and knowledge integration. This accelerates the pace and breadth of discovery in Earth sciences. The system is accessible at our website this https URL.
Moment-GPT introduces a tuning-free zero-shot video moment retrieval framework that uses off-the-shelf multimodal large language models. The framework enhances VMR accuracy by correcting language biases in queries and decomposing the retrieval task into sub-tasks aligned with MLLM strengths, achieving state-of-the-art zero-shot performance on QVHighlights, Charades-STA, and ActivityNet-Captions datasets.
Transcending Forgery Specificity with Latent Space Augmentation for Generalizable Deepfake Detection
Transcending Forgery Specificity with Latent Space Augmentation for Generalizable Deepfake Detection
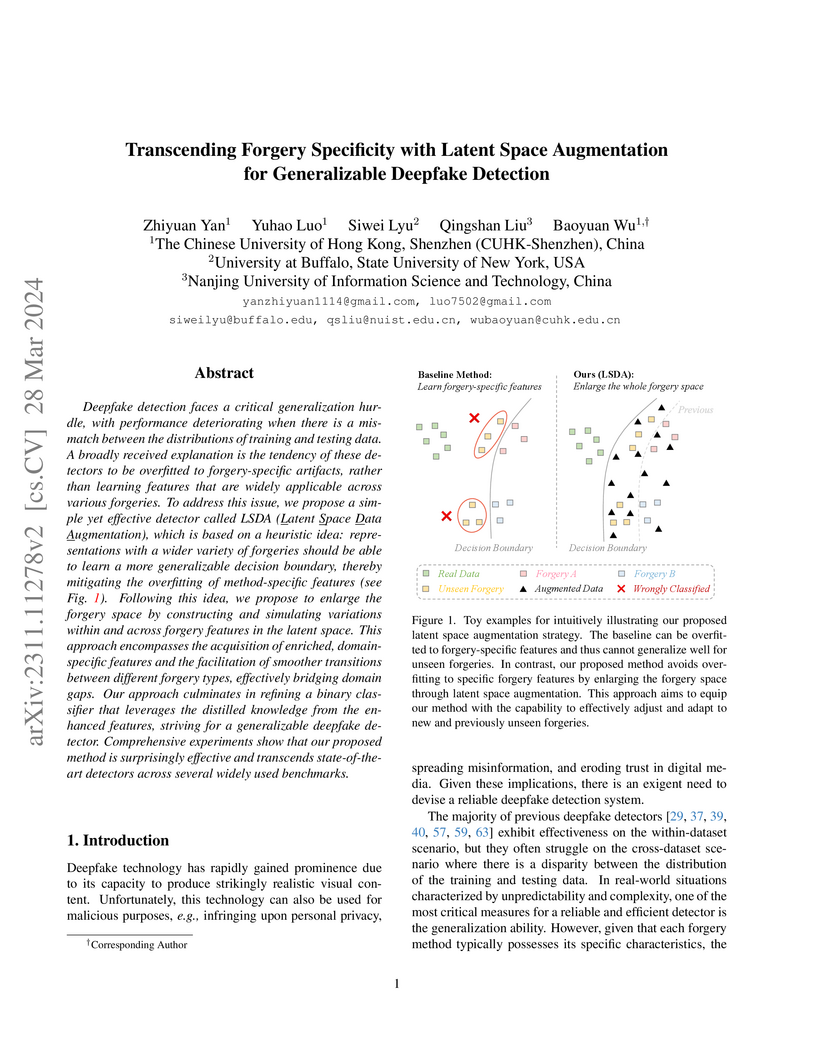
Deepfake detection faces a critical generalization hurdle, with performance deteriorating when there is a mismatch between the distributions of training and testing data. A broadly received explanation is the tendency of these detectors to be overfitted to forgery-specific artifacts, rather than learning features that are widely applicable across various forgeries. To address this issue, we propose a simple yet effective detector called LSDA (\underline{L}atent \underline{S}pace \underline{D}ata \underline{A}ugmentation), which is based on a heuristic idea: representations with a wider variety of forgeries should be able to learn a more generalizable decision boundary, thereby mitigating the overfitting of method-specific features (see Fig.~\ref{fig:toy}). Following this idea, we propose to enlarge the forgery space by constructing and simulating variations within and across forgery features in the latent space. This approach encompasses the acquisition of enriched, domain-specific features and the facilitation of smoother transitions between different forgery types, effectively bridging domain gaps. Our approach culminates in refining a binary classifier that leverages the distilled knowledge from the enhanced features, striving for a generalizable deepfake detector. Comprehensive experiments show that our proposed method is surprisingly effective and transcends state-of-the-art detectors across several widely used benchmarks.
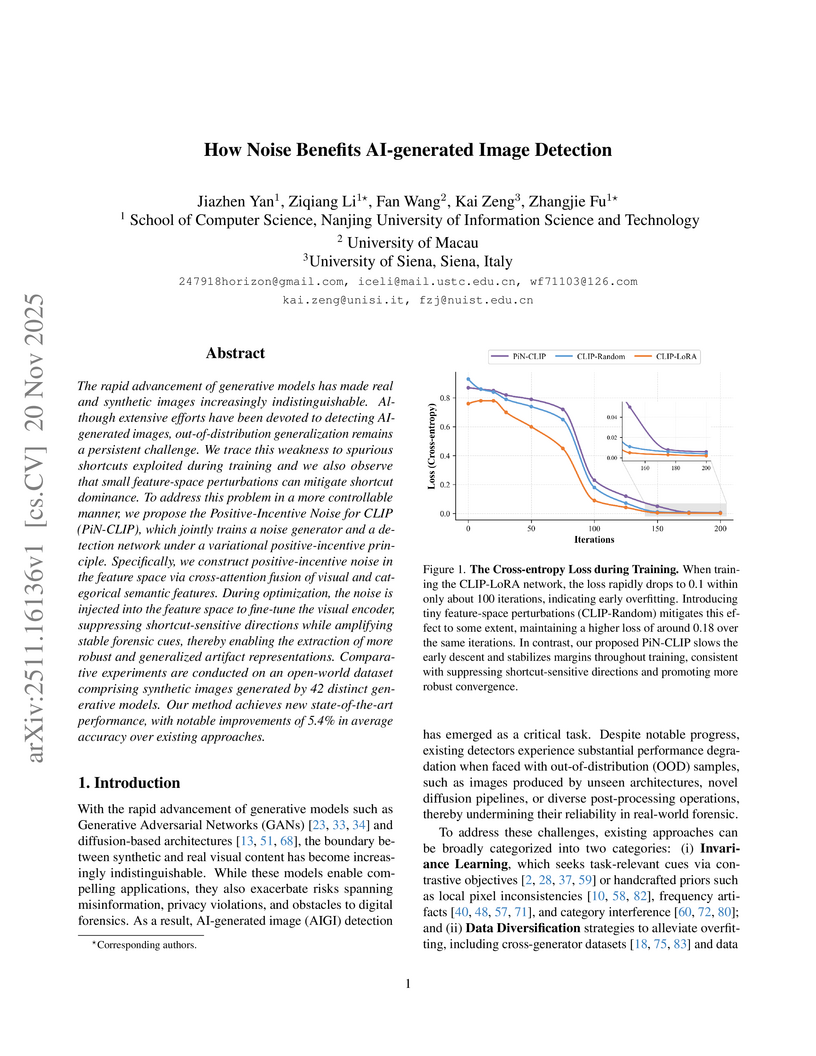
Researchers at Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology developed PiN-CLIP, a framework that uses positive-incentive noise to enhance AI-generated image detection. This method significantly improves out-of-distribution generalization, achieving 95.4% mAcc on GenImage and 85.8% mAcc on AIGIBench, while also increasing robustness to common image perturbations.
The rapid advancement of Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and diffusion models has enabled the creation of highly realistic synthetic images, presenting significant societal risks, such as misinformation and deception. As a result, detecting AI-generated images has emerged as a critical challenge. Existing researches emphasize extracting fine-grained features to enhance detector generalization, yet they often lack consideration for the importance and interdependencies of internal elements within local regions and are limited to a single frequency domain, hindering the capture of general forgery traces. To overcome the aforementioned limitations, we first utilize a sliding window to restrict the attention mechanism to a local window, and reconstruct the features within the window to model the relationships between neighboring internal elements within the local region. Then, we design a dual frequency domain branch framework consisting of four frequency domain subbands of DWT and the phase part of FFT to enrich the extraction of local forgery features from different perspectives. Through feature enrichment of dual frequency domain branches and fine-grained feature extraction of reconstruction sliding window attention, our method achieves superior generalization detection capabilities on both GAN and diffusion model-based generative images. Evaluated on diverse datasets comprising images from 65 distinct generative models, our approach achieves a 2.13\% improvement in detection accuracy over state-of-the-art methods.
Researchers from The University of Tokyo and RIKEN AIP introduce SARLANG-1M, the first large-scale benchmark dataset comprising over 1 million SAR image-text pairs to enable Vision-Language Models to understand Synthetic Aperture Radar imagery. Fine-tuning models on this dataset dramatically improves performance, with the QWEN2.5-VL-7B model achieving 73.33% accuracy in SAR VQA, outperforming SAR experts.
Attention mechanisms have become a foundational component in diffusion
models, significantly influencing their capacity across a wide range of
generative and discriminative tasks. This paper presents a comprehensive survey
of attention within diffusion models, systematically analysing its roles,
design patterns, and operations across different modalities and tasks. We
propose a unified taxonomy that categorises attention-related modifications
into parts according to the structural components they affect, offering a clear
lens through which to understand their functional diversity. In addition to
reviewing architectural innovations, we examine how attention mechanisms
contribute to performance improvements in diverse applications. We also
identify current limitations and underexplored areas, and outline potential
directions for future research. Our study provides valuable insights into the
evolving landscape of diffusion models, with a particular focus on the
integrative and ubiquitous role of attention.
01 Oct 2025
Image quality assessment (IQA) is inherently complex, as it reflects both the quantification and interpretation of perceptual quality rooted in the human visual system. Conventional approaches typically rely on fixed models to output scalar scores, limiting their adaptability to diverse distortions, user-specific queries, and interpretability needs. Furthermore, scoring and interpretation are often treated as independent processes, despite their interdependence: interpretation identifies perceptual degradations, while scoring abstracts them into a compact metric. To address these limitations, we propose AgenticIQA, a modular agentic framework that integrates vision-language models (VLMs) with traditional IQA tools in a dynamic, query-aware manner. AgenticIQA decomposes IQA into four subtasks -- distortion detection, distortion analysis, tool selection, and tool execution -- coordinated by a planner, executor, and summarizer. The planner formulates task-specific strategies, the executor collects perceptual evidence via tool invocation, and the summarizer integrates this evidence to produce accurate scores with human-aligned explanations. To support training and evaluation, we introduce AgenticIQA-200K, a large-scale instruction dataset tailored for IQA agents, and AgenticIQA-Eval, the first benchmark for assessing the planning, execution, and summarization capabilities of VLM-based IQA agents. Extensive experiments across diverse IQA datasets demonstrate that AgenticIQA consistently surpasses strong baselines in both scoring accuracy and explanatory alignment.
NS-Net introduces a framework for generalizable AI-generated image detection by decoupling semantic information from CLIP features using NULL-Space projection, preserving fine-grained artifacts with a Patch Selection strategy, and employing contrastive learning. This approach achieves a 7.4% improvement in detection accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methods across 40 diverse generative models.
Omnidirectional depth estimation enables efficient 3D perception over a full 360-degree range. However, in real-world applications such as autonomous driving and robotics, achieving real-time performance and robust cross-scene generalization remains a significant challenge for existing algorithms. In this paper, we propose a real-time omnidirectional depth estimation method for edge computing platforms named Rt-OmniMVS, which introduces the Combined Spherical Sweeping method and implements the lightweight network structure to achieve real-time performance on edge computing platforms. To achieve high accuracy, robustness, and generalization in real-world environments, we introduce a teacher-student learning strategy. We leverage the high-precision stereo matching method as the teacher model to predict pseudo labels for unlabeled real-world data, and utilize data and model augmentation techniques for training to enhance performance of the student model Rt-OmniMVS. We also propose HexaMODE, an omnidirectional depth sensing system based on multi-view fisheye cameras and edge computation device. A large-scale hybrid dataset contains both unlabeled real-world data and synthetic data is collected for model training. Experiments on public datasets demonstrate that proposed method achieves results comparable to state-of-the-art approaches while consuming significantly less resource. The proposed system and algorithm also demonstrate high accuracy in various complex real-world scenarios, both indoors and outdoors, achieving an inference speed of 15 frames per second on edge computing platforms.
Empathetic response generation necessitates the integration of emotional and
intentional dynamics to foster meaningful interactions. Existing research
either neglects the intricate interplay between emotion and intent, leading to
suboptimal controllability of empathy, or resorts to large language models
(LLMs), which incur significant computational overhead. In this paper, we
introduce ReflectDiffu, a lightweight and comprehensive framework for
empathetic response generation. This framework incorporates emotion contagion
to augment emotional expressiveness and employs an emotion-reasoning mask to
pinpoint critical emotional elements. Additionally, it integrates intent
mimicry within reinforcement learning for refinement during diffusion. By
harnessing an intent twice reflect mechanism of Exploring-Sampling-Correcting,
ReflectDiffu adeptly translates emotional decision-making into precise intent
actions, thereby addressing empathetic response misalignments stemming from
emotional misrecognition. Through reflection, the framework maps emotional
states to intents, markedly enhancing both response empathy and flexibility.
Comprehensive experiments reveal that ReflectDiffu outperforms existing models
regarding relevance, controllability, and informativeness, achieving
state-of-the-art results in both automatic and human evaluations.
01 Sep 2025
This work studies an ultra-reliable and low-latency communications (uRLLC) downlink system using pinching antennas which are realized by activating small dielectric particles along a dielectric waveguide. Our goal is to maximize the data rate by optimizing the positions of the pinching antennas. By proposing a compact and cost-efficient antenna architecture and formulating a finite blocklength-based optimization model, we derive a closed-form solution for the optimal antenna placement under quality-of-service (QoS) and antenna spacing constraints. Meanwhile, a phase-alignment strategy is integrated into the design, enabling coherent signal superposition across the array. Simulation results confirm significant rate improvements over conventional antenna systems while satisfying uRLLC requirements, making the proposed design well-suited for compact and latency-critical future applications.
 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Renmin University of ChinaNanjing University of Information Science and TechnologyHenan UniversityInstitute of Atmospheric PhysicsChina Meteorological AdministrationChinese Academy of Meteorological SciencesInstitute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesShanghai Typhoon InstituteBeijing Key Laboratory of Research on Large Models and Intelligent GovernanceState Key Laboratory of Severe Weather Meteorological Science and Technology
Renmin University of ChinaNanjing University of Information Science and TechnologyHenan UniversityInstitute of Atmospheric PhysicsChina Meteorological AdministrationChinese Academy of Meteorological SciencesInstitute of Atmospheric Physics, Chinese Academy of SciencesShanghai Typhoon InstituteBeijing Key Laboratory of Research on Large Models and Intelligent GovernanceState Key Laboratory of Severe Weather Meteorological Science and TechnologyExtreme precipitation nowcasting demands high spatiotemporal fidelity and extended lead times, yet existing approaches remain limited. Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) and its deep-learning emulations are too slow and coarse for rapidly evolving convection, while extrapolation and purely data-driven models suffer from error accumulation and excessive smoothing. Hybrid 2D radar-based methods discard crucial vertical information, preventing accurate reconstruction of height-dependent dynamics. We introduce a gray-box, fully three-dimensional nowcasting framework that directly processes volumetric radar reflectivity and couples physically constrained neural operators with datadriven learning. The model learns vertically varying 3D advection fields under a conservative advection operator, parameterizes spatially varying diffusion, and introduces a Brownian-motion--inspired stochastic term to represent unresolved motions. A residual branch captures small-scale convective initiation and microphysical variability, while a diffusion-based stochastic module estimates uncertainty. The framework achieves more accurate forecasts up to three-hour lead time across precipitation regimes and ranked first in 57\% of cases in a blind evaluation by 160 meteorologists. By restoring full 3D dynamics with physical consistency, it offers a scalable and robust pathway for skillful and reliable nowcasting of extreme precipitation.
The widespread adoption of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Gemini, and DeepSeek has significantly changed how people approach tasks in education, professional work, and creative domains. This paper investigates how the structure and clarity of user prompts impact the effectiveness and productivity of LLM outputs. Using data from 243 survey respondents across various academic and occupational backgrounds, we analyze AI usage habits, prompting strategies, and user satisfaction. The results show that users who employ clear, structured, and context-aware prompts report higher task efficiency and better outcomes. These findings emphasize the essential role of prompt engineering in maximizing the value of generative AI and provide practical implications for its everyday use.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.