Ask or search anything...
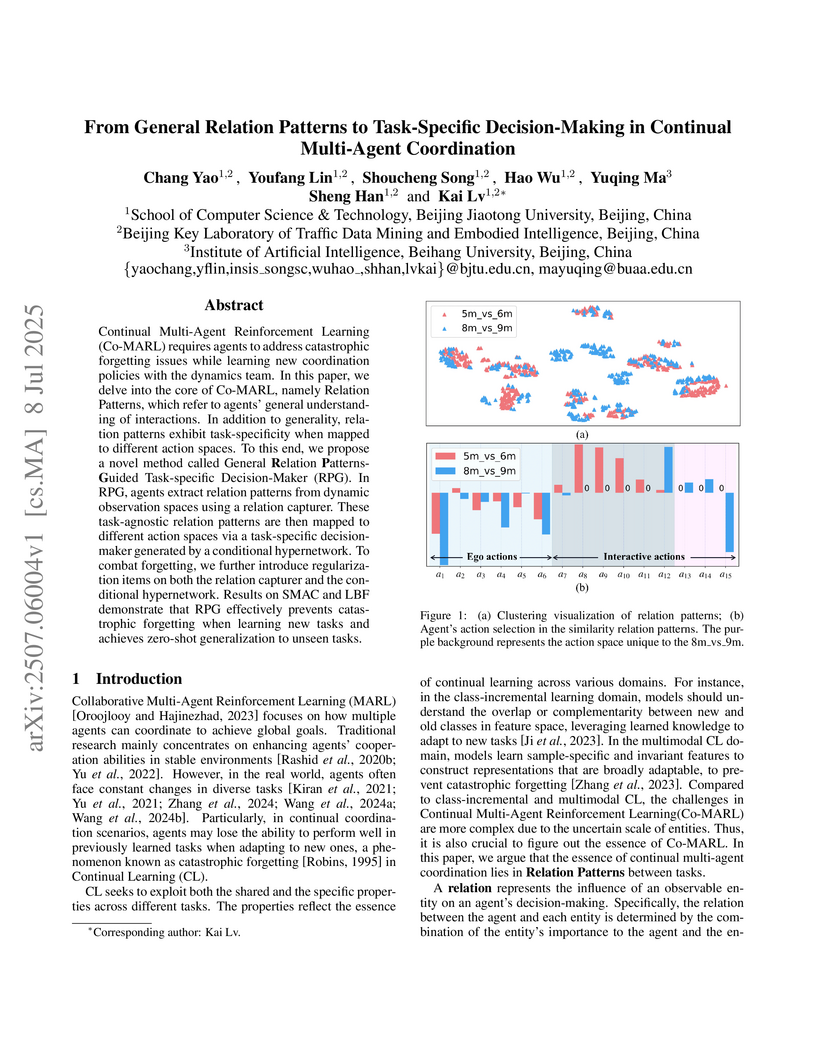
UniModel introduces a visual-only framework that unifies multimodal understanding and generation by representing both text and images as pixel-level data within a single diffusion transformer. This approach enables coherent text-to-image generation and image captioning, demonstrating strong cycle consistency and emergent controllability by operating entirely in a shared visual latent space.
View blogResearchers from TeleAI, China Telecom Corp Ltd, developed an effective solution for Emotional Support Conversation (ESC) by fine-tuning Qwen2.5 Large Language Models with advanced prompt engineering. Their approach, which includes both LoRA and full-parameter fine-tuning, achieved a second-place ranking in the NLPCC 2025 Task 8 evaluation, with their best model yielding a total score of 39.62 and a G-score of 87.20.
View blogDeveloped by TeleAI, TableZoomer is an LLM-powered agent framework designed for large-scale Table Question Answering, efficiently addressing the challenges of massive and heterogeneous tables. It achieved absolute accuracy improvements of 19.34% on DataBench by employing schema-based representation and query-aware zooming, significantly reducing input tokens while maintaining high performance.
View blogResearchers at the University of Science and Technology of China developed VLMPlanner, a hybrid framework integrating visual language models with real-time motion planning for autonomous driving. It processes raw multi-view images and employs a Context-Adaptive Inference Gate for computational efficiency, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the nuPlan benchmark and reducing collision probability.
View blogResearchers from the Institute of Artificial Intelligence (TeleAI), China Telecom Corp Ltd, developed TableReasoner, a framework for Table Question Answering that processes large and complex tables by generating a concise JSON schema. The system effectively mitigates numerical hallucinations through program-assisted reasoning and achieved first place in both subtasks of SemEval-2025 Task 8, demonstrating robust scalability across table sizes.
View blogResearchers from Shanghai Artificial Intelligence Laboratory and Renmin University of China introduce the Depth Information Injection (DI²) framework, which enhances pre-trained RGB-based robotic manipulation policies with 3D perception by integrating predicted depth features. The method achieves an average 63.15% success rate in simulated tasks and 66.67% in real-world scenarios, maintaining robust performance when deployed with RGB-only input.
View blog
 University of Science and Technology of China
University of Science and Technology of China

 National University of Singapore
National University of Singapore Beihang University
Beihang University
 Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University







 Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese Academy of Sciences Renmin University of China
Renmin University of China
 Communication University of China
Communication University of China


 Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University

 Fudan University
Fudan University
 Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University