Khalifa University
14 Jul 2025
A comprehensive systematic review synthesizes Vision Language Action (VLA) models for robotic manipulation, categorizing architectural trends, benchmarking datasets, and evaluating simulation platforms. Researchers from Khalifa University and Universitat Politecnica de Catalunya identify dominant architectural components, reveal critical gaps in multimodal, high-complexity datasets, and outline challenges in simulation for robotic manipulation.
Understanding long-form videos remains a significant challenge for vision--language models (VLMs) due to their extensive temporal length and high information density. Most current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) rely on uniform sampling, which often overlooks critical moments, leading to incorrect responses to queries. In parallel, many keyframe selection approaches impose rigid temporal spacing: once a frame is chosen, an exclusion window suppresses adjacent timestamps to reduce redundancy. While effective at limiting overlap, this strategy frequently misses short, fine-grained cues near important events. Other methods instead emphasize visual diversity but neglect query relevance. We propose AdaRD-Key, a training-free keyframe sampling module for query-driven long-form video understanding. AdaRD-Key maximizes a unified Relevance--Diversity Max-Volume (RD-MV) objective, combining a query-conditioned relevance score with a log-determinant diversity component to yield informative yet non-redundant frames. To handle broad queries with weak alignment to the video, AdaRD-Key employs a lightweight relevance-aware gating mechanism; when the relevance distribution indicates weak alignment, the method seamlessly shifts into a diversity-only mode, enhancing coverage without additional supervision. Our pipeline is training-free, computationally efficient (running in real time on a single GPU), and compatible with existing VLMs in a plug-and-play manner. Extensive experiments on LongVideoBench and Video-MME demonstrate state-of-the-art performance, particularly on long-form videos. Code available at this https URL.
A structured, up-to-date review examines trajectory prediction for autonomous driving, detailing diverse modeling approaches, evaluating performance metrics, and outlining current limitations and emerging research trends. It provides a comprehensive framework to understand progress from physics-based to advanced deep learning methods, emphasizing practical challenges and future directions for robust autonomous navigation systems.
Despite progress in Arabic large language models, such as Jais and AceGPT, their evaluation on commonsense reasoning has largely relied on machine-translated datasets, which lack cultural depth and may introduce Anglocentric biases. Commonsense reasoning is shaped by geographical and cultural contexts, and existing English datasets fail to capture the diversity of the Arab world. To address this, we introduce ArabCulture, a commonsense reasoning dataset in Modern Standard Arabic (MSA), covering cultures of 13 countries across the Gulf, Levant, North Africa, and the Nile Valley. The dataset was built from scratch by engaging native speakers to write and validate culturally relevant questions for their respective countries. ArabCulture spans 12 daily life domains with 54 fine-grained subtopics, reflecting various aspects of social norms, traditions, and everyday experiences. Zero-shot evaluations show that open-weight language models with up to 32B parameters struggle to comprehend diverse Arab cultures, with performance varying across regions. These findings highlight the need for more culturally aware models and datasets tailored to the Arabic-speaking world.
Nanyang Technological University and Khalifa University researchers create WirelessMathBench, a specialized benchmark containing 587 mathematical modeling problems sourced from 40 state-of-the-art wireless communications research papers, revealing that while leading LLMs like OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1 achieve reasonable performance on multiple-choice questions, they struggle significantly with equation completion tasks, attaining only single-digit accuracy rates on fully masked equation reconstructions that require multi-step mathematical derivations and adherence to physical constraints, with performance declining proportionally as equation masking increases.
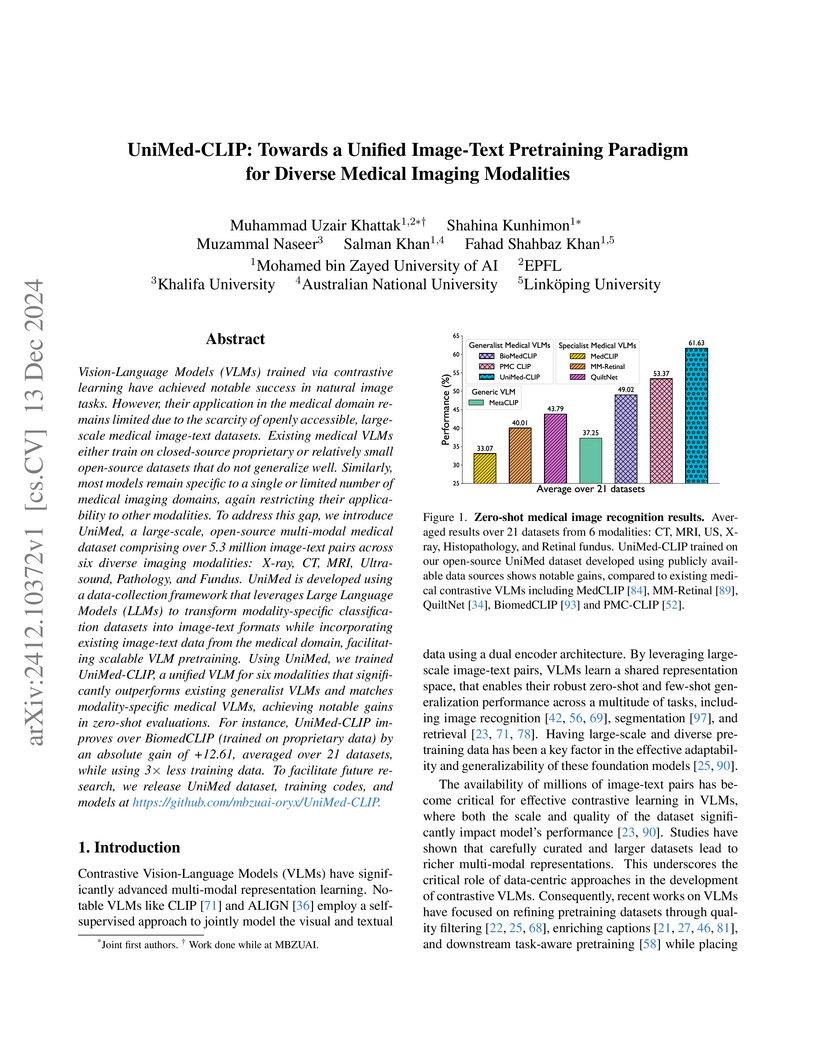
UniMed-CLIP introduces UniMed, an open-source, large-scale, multi-modal medical image-text dataset and a corresponding vision-language model trained on this data. The approach uses large language models to generate diverse captions for image-only datasets, enabling the model to achieve 61.63% average zero-shot performance across 21 medical datasets, a 12.61% improvement over prior generalist medical VLMs.
A comprehensive survey analyzes over 650 transformer-based models across five major AI domains, identifying their applications in Natural Language Processing, Computer Vision, Multi-Modality, Audio/Speech Processing, and Signal Processing, and categorizing them within a novel taxonomy. The work provides a structured overview of the current landscape and suggests future research directions.
Visual Object Tracking (VOT) is a fundamental task with widespread
applications in autonomous navigation, surveillance, and maritime robotics.
Despite significant advances in generic object tracking, maritime environments
continue to present unique challenges, including specular water reflections,
low-contrast targets, dynamically changing backgrounds, and frequent
occlusions. These complexities significantly degrade the performance of
state-of-the-art tracking algorithms, highlighting the need for domain-specific
datasets. To address this gap, we introduce the Maritime Visual Tracking
Dataset (MVTD), a comprehensive and publicly available benchmark specifically
designed for maritime VOT. MVTD comprises 182 high-resolution video sequences,
totaling approximately 150,000 frames, and includes four representative object
classes: boat, ship, sailboat, and unmanned surface vehicle (USV). The dataset
captures a diverse range of operational conditions and maritime scenarios,
reflecting the real-world complexities of maritime environments. We evaluated
14 recent SOTA tracking algorithms on the MVTD benchmark and observed
substantial performance degradation compared to their performance on
general-purpose datasets. However, when fine-tuned on MVTD, these models
demonstrate significant performance gains, underscoring the effectiveness of
domain adaptation and the importance of transfer learning in specialized
tracking contexts. The MVTD dataset fills a critical gap in the visual tracking
community by providing a realistic and challenging benchmark for maritime
scenarios. Dataset and Source Code can be accessed here
"this https URL".
17 Sep 2025
Studying wave propagation in nonlinear discrete systems is essential for understanding energy transfer in lattices. While linear systems prohibit wave propagation within the natural band gap, nonlinear systems exhibit {supratransmission}, enabling energy transfer above a critical driving amplitude. This work investigates novel \emph{in-band supratransmissions} for waves with frequencies in a \emph{flat} or \emph{nearly flat} linear band. Flat bands, characterized by zero group velocity and localized modes due to destructive interference, provide an ideal framework for studying wave confinement and energy dynamics. In-band supratransmission originates from a bifurcation of evanescent waves at the flat band frequency. Using nonlinear \emph{diamond} and \emph{stub} lattices as model systems, we explore how lattice topology, nonlinearity, and driving amplitude affect supratransmission. Through bifurcation analysis, stability evaluations, and time-dependent simulations, we examine the transition from energy localization to supratransmission.
Shallow Recurrent Decoder networks are a novel data-driven methodology able to provide accurate state estimation in engineering systems, such as nuclear reactors. This deep learning architecture is a robust technique designed to map the temporal trajectories of a few sparse measures to the full state space, including unobservable fields, which is agnostic to sensor positions and able to handle noisy data through an ensemble strategy, leveraging the short training times and without the need for hyperparameter tuning. Following its application to a novel reactor concept, this work investigates the performance of Shallow Recurrent Decoders when applied to a real system. The underlying model is represented by a fluid dynamics model of the TRIGA Mark II research reactor; the architecture will use both synthetic temperature data coming from the numerical model and leveraging experimental temperature data recorded during a previous campaign. The objective of this work is, therefore, two-fold: 1) assessing if the architecture can reconstruct the full state of the system (temperature, velocity, pressure, turbulence quantities) given sparse data located in specific, low-dynamics channels and 2) assessing the correction capabilities of the architecture (that is, given a discrepancy between model and data, assessing if sparse measurements can provide some correction to the architecture output). As will be shown, the accurate reconstruction of every characteristic field, using both synthetic and experimental data, in real-time makes this approach suitable for interpretable monitoring and control purposes in the framework of a reactor digital twin.
Northwestern Polytechnical University Northeastern University
Northeastern University Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University
Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute
University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra
Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra NVIDIA
NVIDIA Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology
Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design
King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design Aalto University
Aalto University Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University
Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécom
KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécom
 Northeastern University
Northeastern University Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University
Sun Yat-Sen UniversityGhent UniversityKorea University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute
University of MichiganXidian UniversityUniversity of Electronic Science and Technology of ChinaCentral South UniversityUniversity of Hong KongTechnology Innovation Institute Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra
Yale UniversityUniversitat Pompeu Fabra NVIDIA
NVIDIA Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology
Nanyang Technological UniversityUniversity of GranadaChina TelecomUlsan National Institute of Science and Technology King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design
King’s College LondonSingapore University of Technology and Design Aalto University
Aalto University Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University
Virginia TechUniversity of HoustonEast China Normal University KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécom
KTH Royal Institute of TechnologyUniversity of OuluKhalifa UniversityLightOnCentraleSupélecUniversity of LeedsIMECNokia Bell LabsCEA-LetiUniversity of YorkOrangeEricssonBrunel University LondonQualcommChina UnicomBubbleRANITUEMIRATES INTEGRATED TELECOMMUNICATIONS COMPANYFENTECHGSMARIMEDO LABSKATIMCHINA MOBILE COMMUNICATIONS CORPORATIONBeijing Institute of TechnologyEurécomA comprehensive white paper from the GenAINet Initiative introduces Large Telecom Models (LTMs) as a novel framework for integrating AI into telecommunications infrastructure, providing a detailed roadmap for innovation while addressing critical challenges in scalability, hardware requirements, and regulatory compliance through insights from a diverse coalition of academic, industry and regulatory experts.
IBM ResearchUniversity of Helsinki Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence
Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence Aalto UniversityKyung Hee UniversityKhalifa UniversityAir UniversityFoundation for Advancement of Science and TechnologyHajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology UniversityUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanPakistan Institute of Engineering Applied Sciences
Aalto UniversityKyung Hee UniversityKhalifa UniversityAir UniversityFoundation for Advancement of Science and TechnologyHajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology UniversityUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanPakistan Institute of Engineering Applied Sciences
 Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence
Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence Aalto UniversityKyung Hee UniversityKhalifa UniversityAir UniversityFoundation for Advancement of Science and TechnologyHajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology UniversityUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanPakistan Institute of Engineering Applied Sciences
Aalto UniversityKyung Hee UniversityKhalifa UniversityAir UniversityFoundation for Advancement of Science and TechnologyHajee Mohammad Danesh Science and Technology UniversityUniversiti Tunku Abdul RahmanPakistan Institute of Engineering Applied SciencesAdvances in deep learning are re-defining how visual data is processed and understand by the machines. Vision Transformers (ViTs) have recently demonstrated prominent performance in computer vision related tasks. However, their performance improves with increasing numbers of labeled data, indicating reliance on labeled data. Humanly annotated data are difficult to acquire and thus shifted the focus from traditional annotations to unsupervised learning strategies that learn structures inside the data. In response to this challenge, self-supervised learning (SSL) has emerged as a promising technique. SSL utilize inherent relationships within the data as a form of supervision. This technique can reduce the dependence on manual annotations and offers a more scalable and resource-effective approach to training models. Taking these strengths into account, it is necessary to assess the combination of SSL methods with ViTs, especially in the cases of limited labeled data. Inspired by this evolving trend, this survey aims to systematically review SSL mechanisms tailored for ViTs. We propose a comprehensive taxonomy to classify SSL techniques based on their representations and pre-training tasks. Furthermore, we highlighted the motivations behind the study of SSL, reviewed prominent pre-training tasks, and highlight advancements and challenges in this field. Furthermore, we conduct a comparative analysis of various SSL methods designed for ViTs, evaluating their strengths, limitations, and applicability to different scenarios.
This comprehensive overview examines how Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) can address the challenges of 6G wireless distributed networks by enabling intelligent, decentralized decision-making among network nodes. It explores the fundamental structures, algorithms, enhancement techniques, and practical applications that will shape the next generation of wireless communication systems.
Khalifa University researchers developed the Temporal Neural Operator (TNO) to model time-dependent Partial Differential Equations, demonstrating accurate long-range temporal extrapolation and generalization to unseen spatial resolutions. The model forecasts European air temperatures on a higher resolution grid, extrapolates global air temperatures five years beyond its training data, and predicts CO2 plume migration for 30 years from limited initial observations.
Real-time animal detection and segmentation in natural environments are vital for wildlife conservation, enabling non-invasive monitoring through remote camera streams. However, these tasks remain challenging due to limited computational resources and the cryptic appearance of many species. We propose a mobile-optimized two-stage deep learning framework that integrates a Threading Detection Model (TDM) to parallelize YOLOv10-based detection and MobileSAM-based segmentation. Unlike prior YOLO+SAM pipelines, our approach improves real-time performance by reducing latency through threading. YOLOv10 handles detection while MobileSAM performs lightweight segmentation, both executed concurrently for efficient resource use. On the cryptic Houbara Bustard, a conservation-priority species, our model achieves mAP50 of 0.9627, mAP75 of 0.7731, mAP95 of 0.7178, and a MobileSAM mIoU of 0.7421. YOLOv10 operates at 43.7 ms per frame, confirming real-time readiness. We introduce a curated Houbara dataset of 40,000 annotated images to support model training and evaluation across diverse conditions. The code and dataset used in this study are publicly available on GitHub at this https URL. For interactive demos and additional resources, visit this https URL.
Large multimodal models (LMMs) have shown encouraging performance in the natural image domain using visual instruction tuning. However, these LMMs struggle to describe the content of remote sensing images for tasks such as image or region grounding, classification, etc. Recently, GeoChat make an effort to describe the contents of the RS images. Although, GeoChat achieves promising performance for various RS tasks, it struggles to describe the changes between bi-temporal RS images which is a key RS task. This necessitates the development of an LMM that can describe the changes between the bi-temporal RS images. However, there is insufficiency of datasets that can be utilized to tune LMMs. In order to achieve this, we introduce a change description instruction dataset that can be utilized to finetune an LMM and provide better change descriptions for RS images. Furthermore, we show that the LLaVA-1.5 model, with slight modifications, can be finetuned on the change description instruction dataset and achieve favorably better performance.
Goal-conditioned dynamic manipulation is inherently challenging due to
complex system dynamics and stringent task constraints, particularly in
deformable object scenarios characterized by high degrees of freedom and
underactuation. Prior methods often simplify the problem to low-speed or 2D
settings, limiting their applicability to real-world 3D tasks. In this work, we
explore 3D goal-conditioned rope manipulation as a representative challenge. To
mitigate data scarcity, we introduce a novel simulation framework and benchmark
grounded in reduced-order dynamics, which enables compact state representation
and facilitates efficient policy learning. Building on this, we propose
Dynamics Informed Diffusion Policy (DIDP), a framework that integrates
imitation pretraining with physics-informed test-time adaptation. First, we
design a diffusion policy that learns inverse dynamics within the reduced-order
space, enabling imitation learning to move beyond na\"ive data fitting and
capture the underlying physical structure. Second, we propose a
physics-informed test-time adaptation scheme that imposes kinematic boundary
conditions and structured dynamics priors on the diffusion process, ensuring
consistency and reliability in manipulation execution. Extensive experiments
validate the proposed approach, demonstrating strong performance in terms of
accuracy and robustness in the learned policy.
Researchers from MBZUAI introduce HSAT (Hierarchical Self-Supervised Adversarial Training), a framework that leverages the patient-slide-patch hierarchy in histopathology data to enhance adversarial robustness of vision models, achieving up to 60.70% improvement in robustness against white-box attacks while maintaining higher clean accuracy compared to instance-level adversarial training approaches.
01 Sep 2025
The objective of this study is to address the mobility challenges faced by user equipment (UE) through the implementation of fluid antenna (FA) on the UE side. This approach aims to maintain the time-varying channel in a relatively stable state by strategically relocating the FA to an appropriate port. To the best of our knowledge, this paper introduces, for the first time, the application of large language models (LLMs) in the prediction of FA ports, presenting a novel model termed Port-LLM. Our proposed method for predicting the moving port of the FA is a two-step prediction method. To enhance the learning efficacy of our proposed Port-LLM model, we integrate low-rank adaptation (LoRA) fine-tuning technology. Additionally, to further exploit the natural language processing capabilities of pre-trained LLMs, we propose a framework named Prompt-Port-LLM, which is constructed upon the Port-LLM architecture and incorporates prompt fine-tuning techniques along with a specialized prompt encoder module. The simulation results show that our proposed models all exhibit strong generalization ability and robustness under different numbers of base station antennas and medium-to-high mobility speeds of UE. In comparison to existing methods, the performance of the port predicted by our models demonstrates superior efficacy. Moreover, both of our proposed models achieve millimeter-level inference speed.
Virtual try-on seeks to generate photorealistic images of individuals in desired garments, a task that must simultaneously preserve personal identity and garment fidelity for practical use in fashion retail and personalization. However, existing methods typically handle upper and lower garments separately, rely on heavy preprocessing, and often fail to preserve person-specific cues such as tattoos, accessories, and body shape-resulting in limited realism and flexibility. To this end, we introduce MuGa-VTON, a unified multi-garment diffusion framework that jointly models upper and lower garments together with person identity in a shared latent space. Specifically, we proposed three key modules: the Garment Representation Module (GRM) for capturing both garment semantics, the Person Representation Module (PRM) for encoding identity and pose cues, and the A-DiT fusion module, which integrates garment, person, and text-prompt features through a diffusion transformer. This architecture supports prompt-based customization, allowing fine-grained garment modifications with minimal user input. Extensive experiments on the VITON-HD and DressCode benchmarks demonstrate that MuGa-VTON outperforms existing methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations, producing high-fidelity, identity-preserving results suitable for real-world virtual try-on applications.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.