Nanyang Technological University
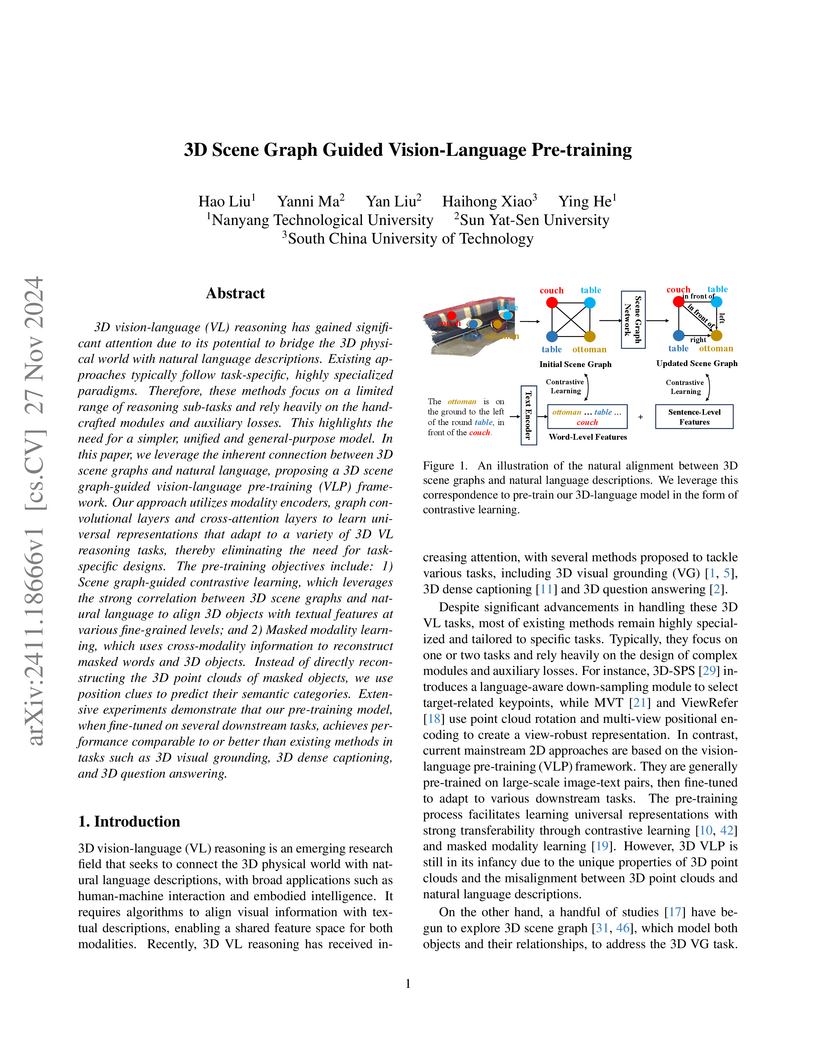
Nanyang Technological UniversityResearchers from Nanyang Technological University, Sun Yat-Sen University, and South China University of Technology developed a general-purpose 3D Vision-Language Pre-training framework that leverages 3D scene graphs to achieve multi-level alignment between 3D scenes and natural language. The framework establishes state-of-the-art or competitive performance across 3D visual grounding, question answering, and dense captioning tasks.
Researchers from Fudan University and Shanghai AI Laboratory introduce "Make-it-Real," a framework that leverages GPT-4V to automatically paint 3D objects with realistic materials from albedo-only inputs. It generates a full suite of SVBRDF maps, achieving up to 77.8% human user preference and 84.8% GPT evaluation preference for refined objects over unrefined ones, significantly enhancing visual authenticity.
CopyrightShield, developed by researchers from Nanyang Technological University and Beihang University, establishes a defense framework to protect diffusion models from copyright infringement attacks by detecting poisoned training samples and mitigating their influence. The approach achieves an F1-score of 0.665 for poisoned sample detection, which is a 25% improvement over prior attribution methods, and reduces the copyright infringement rate by 56.7% while delaying attack initiation by 115.2%, all without compromising generative quality.
The ContrastPool framework integrates domain-specific knowledge into Graph Neural Networks for classifying fMRI brain networks, achieving superior accuracy across three neurodegenerative diseases while providing interpretable disease-specific insights. It leverages a contrastive dual-attention mechanism and a contrast graph to address fMRI's low signal-to-noise ratio, node alignment, and limited data scale.
Researchers from a collaborative network across Singapore and Taiwan introduced the first application of dataset distillation to speech processing for Speech Emotion Recognition. Their generative model condenses large speech datasets, reducing storage by up to 97% and downstream training time by 95%, while achieving comparable or superior performance, particularly by mitigating data-label imbalance and implicitly enhancing privacy.
Researchers developed and experimentally validated a reinforcement learning-based quantum compiler on a 9-qubit superconducting processor, demonstrating its ability to find shorter, hardware-optimized quantum circuits. This approach achieved superior experimental fidelities on noisy intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) devices compared to conventional compilation methods, notably reducing the 3-qubit Quantum Fourier Transform to just seven CZ gates.
This work introduces Dynamic Fine-Tuning (DFT), a method that mathematically reinterprets Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) as an unstable Reinforcement Learning process with an ill-posed implicit reward. By rectifying this reward structure with a single-line code change, DFT consistently enhances SFT's generalization capabilities across various LLM architectures and tasks, often outperforming complex online and offline RL methods while being more resource-efficient.
28 Oct 2025
GiGPO introduces a two-level advantage estimation structure to improve Large Language Model agent training in complex, multi-turn environments. This reinforcement learning algorithm consistently surpasses prior RL methods and prompting techniques across diverse benchmarks like ALFWorld and WebShop, demonstrating enhanced success rates and tool efficiency with negligible additional computational cost.
27 Mar 2025
A comprehensive survey from an international research consortium led by Peking University examines Large Language Model (LLM) agents through a methodology-centered taxonomy, analyzing their construction, collaboration mechanisms, and evolution while providing a unified architectural framework for understanding agent systems across different application domains.
 KAIST
KAIST University of Washington
University of Washington University of Toronto
University of Toronto Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal New York University
New York University University of Chicago
University of Chicago UC Berkeley
UC Berkeley University of Oxford
University of Oxford Stanford University
Stanford University University of Michigan
University of Michigan Cornell University
Cornell University Nanyang Technological UniversityVector InstituteLG AI Research
Nanyang Technological UniversityVector InstituteLG AI Research MIT
MIT HKUSTUniversity of TübingenHong Kong Baptist University
HKUSTUniversity of TübingenHong Kong Baptist University University of California, Santa CruzCenter for AI SafetyGray Swan AIBeneficial AI ResearchConjectureLawZeroUniversity of Wisconsin
–MadisonMorph LabsInstitute for Applied PsychometricsCSER
University of California, Santa CruzCenter for AI SafetyGray Swan AIBeneficial AI ResearchConjectureLawZeroUniversity of Wisconsin
–MadisonMorph LabsInstitute for Applied PsychometricsCSERThe lack of a concrete definition for Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) obscures the gap between today's specialized AI and human-level cognition. This paper introduces a quantifiable framework to address this, defining AGI as matching the cognitive versatility and proficiency of a well-educated adult. To operationalize this, we ground our methodology in Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory, the most empirically validated model of human cognition. The framework dissects general intelligence into ten core cognitive domains-including reasoning, memory, and perception-and adapts established human psychometric batteries to evaluate AI systems. Application of this framework reveals a highly "jagged" cognitive profile in contemporary models. While proficient in knowledge-intensive domains, current AI systems have critical deficits in foundational cognitive machinery, particularly long-term memory storage. The resulting AGI scores (e.g., GPT-4 at 27%, GPT-5 at 57%) concretely quantify both rapid progress and the substantial gap remaining before AGI.
03 Sep 2025
The paper introduces SimpleTIR, an end-to-end Reinforcement Learning (RL) approach that stabilizes multi-turn Tool-Integrated Reasoning (TIR) in Large Language Models (LLMs) under the Zero RL setting. SimpleTIR resolves training instability and gradient explosions by filtering problematic 'void turns,' achieving state-of-the-art performance on mathematical reasoning benchmarks and fostering diverse, emergent reasoning patterns.
Researchers from S-Lab NTU, SenseTime Research, and Xi’an Jiaotong University introduced NEO, a family of native vision-language models built on a unified primitive and end-to-end training. NEO demonstrates competitive performance against modular VLMs and surpasses other native approaches on various benchmarks, despite using significantly less pre-training and SFT data.
02 Aug 2025
 Google DeepMind
Google DeepMind University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Université de Montréal
Université de Montréal University of Southern California
University of Southern California Stanford University
Stanford University Mila - Quebec AI Institute
Mila - Quebec AI Institute The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Yale University
Yale University University of Georgia
University of Georgia Nanyang Technological University
Nanyang Technological University Microsoft
Microsoft Argonne National Laboratory
Argonne National Laboratory Duke University
Duke University HKUSTKing Abdullah University of Science and Technology
HKUSTKing Abdullah University of Science and Technology University of Sydney
University of Sydney The Ohio State UniversityPenn State UniversityMetaGPT
The Ohio State UniversityPenn State UniversityMetaGPTA comprehensive, brain-inspired framework integrates diverse research areas of LLM-based intelligent agents, encompassing individual architecture, collaborative systems, and safety. The framework formally conceptualizes agent components, maps AI capabilities to human cognition to identify research gaps, and outlines a roadmap for developing autonomous, adaptive, and safe AI.
06 Dec 2025
 Monash UniversityCSIRO
Monash UniversityCSIRO Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University
Chinese Academy of SciencesSichuan University University of Manchester
University of Manchester Beihang University
Beihang University Nanjing University
Nanjing University Zhejiang University
Zhejiang University ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology
ByteDanceShanghai AI LabHarbin Institute of Technology Beijing Jiaotong University
Beijing Jiaotong University Huawei
Huawei Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield
Nanyang Technological UniversityNTUBeijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity of Sheffield TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOM
TencentAlibabaHuawei CloudStepFunTeleAIOPPOHong Kong University of Science and Technology (Guangzhou)KuaiShouM-A-PChinese Academy of Sciences, Institute of AutomationUOMA comprehensive synthesis of Large Language Models for automated software development covers the entire model lifecycle, from data curation to autonomous agents, and offers practical guidance derived from empirical experiments on pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning, alongside a detailed analysis of challenges and future directions.
Puffin, a unified multimodal model, integrates camera-centric understanding and generation by interpreting camera parameters as a "first-class modality" within a linguistic reasoning framework. The model demonstrates superior performance in both estimating camera parameters from images and generating visual content with precise viewpoint control, achieving enhanced spatial intelligence.
01 Feb 2024
Multichannel filtered reference least mean square (McFxLMS) algorithms are
widely utilized in adaptive multichannel active noise control (MCANC)
applications. As a critical and high-computationally efficient adaptive
critical algorithm, it also typically works as a benchmark for comparative
studies of the new algorithms proposed by peers and researchers. However, up to
now, there are few open-source codes for the FxLMS algorithm, especially for
large-count channels. Therefore, this work provides a MATLAB code for the
McFxLMS algorithm, which can be used for the arbitrary number of channels
system. The code is available on GitHub and Mathworks.
Tsinghua University and Nanyang Technological University researchers develop VLA-RL, a reinforcement learning framework that fine-tunes pre-trained vision-language-action models for robotic manipulation, achieving 4.5% performance improvement over supervised fine-tuning baselines on the LIBERO benchmark and matching commercial model performance through trajectory-level RL formulation combined with a robotic process reward model that provides dense rewards for sparse manipulation tasks, while demonstrating test-time scaling benefits where extended training consistently improves robot performance and exhibiting superior action space coverage compared to behavior cloning approaches.
04 Sep 2025
AgenTracer introduces an automated framework to generate annotated failure trajectories for multi-agent LLM systems and trains a specialized, lightweight model (AgenTracer-8B) for precise failure attribution. This system identifies the root cause of failures, outperforming larger proprietary LLMs and enabling self-correction in existing multi-agent systems with performance gains up to 14.2%.
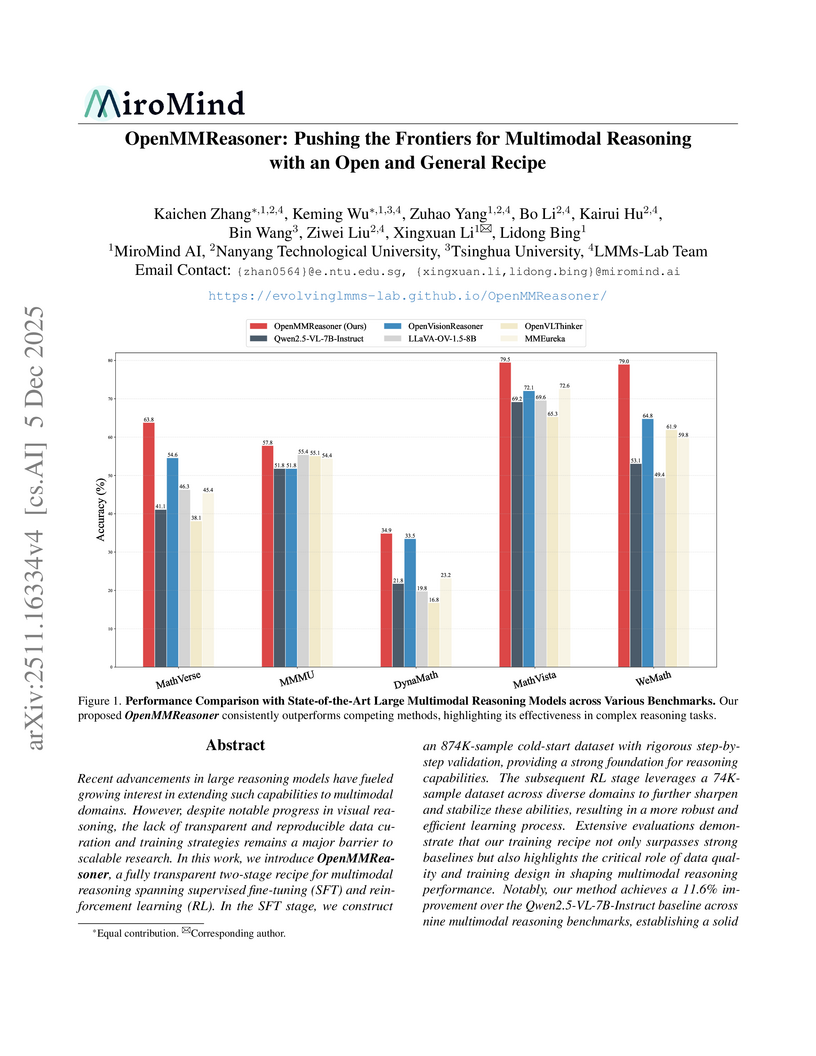
OpenMMReasoner introduces a transparent, two-stage Supervised Fine-tuning and Reinforcement Learning recipe for multimodal reasoning, establishing a new state-of-the-art for open-source models across nine diverse benchmarks. This approach improves token efficiency and boosts cross-domain textual reasoning capabilities, with all components released as open source.
The VChain framework integrates a large multimodal model's reasoning capabilities into video generation through a three-stage, inference-time process, generating videos with enhanced causal and physical coherence. It employs "chain-of-visual-thought" keyframes to guide pre-trained diffusion models, leading to more logically consistent and plausible dynamic sequences.
There are no more papers matching your filters at the moment.